Why does Mercury have a big iron core?
2021-07-06
(Press-News.org) Scientists from Tohoku University and the University of Maryland have pinpointed the strong magnetic field of the early sun as the reason behind the radial variation of rock and metal in rocky planets' cores. This magnetic field, which pulled small iron grains inward, explains Mercury's big iron core and why Mars has so little iron in its core.
The details of their research were published in the journal Progress in Earth and Planetary Science on July 5, 2021.
Planets have iron cores surrounded by a rocky shell, mostly made up of mantle and a thin skin of crust. The four inner planets of our Solar System, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars have their own distinctive size and density. These differences have long since puzzled scientists.
Mercury has a metallic core making up about 3/4 of its mass, with the remaining 1/4 being a rocky silicate shell. The cores of Earth and Venus possess a metallic core of only 1/3 of their mass, with the rest being rock. Mars has a measly core comprising only 1/4 of its mass.
These radical changes in metal content offer clues about what controlled the distribution of raw materials in the early formation of the solar system.
During this period, swirling gas and dust cloud drew matter into the Solar System's center, thus forming the Sun. The rapid delivery to the center caused many collisions and heated the inner region of the Solar System. When the Sun was big enough to have its own internal gravity, it caused its proton-rich core to ignite its nuclear fuel, brightly turning on the Sun. Following this, the Sun's core began convecting, creating a dynamo generating a strong magnetic field.
The high temperatures of the inner Solar System turned elements into a vapor state. As the element cloud cooled down it rained out mineral compounds. Evidence from primitive meteorites reveals the compounds precipitated were either silicates or metals. The sun's magnetic field pulled the metal particles inwards.
The composition of inner rocky planets is remarkably similar to primitive meteorites. Also known as chondrites, these meteorites are jumbled mixtures of rock and metal in different proportions. Unlike rocky planets, they do not have cores.
The raw materials making up the rocky planets are just four unevenly distributed elements: oxygen, iron, magnesium, and silicon. This represents about 93% of a rocky planet's mass. Around 70% of that is equal measure oxygen and iron, whilst the rest consists of equal measure magnesium and silicon.
"Planetary cores are a big deal," proclaims coauthor of the study Bill McDonough. "They control where elements end up in the planet." McDonough points to the Earth's abundance of the nutrient phosphorus concentrated in its core as an example. "Planetary habitability also depends upon the size and compositions of its core in addition to the lifetime of its dynamo."
The core's dynamo generates a magnetic shield that protects us from cancer-causing cosmic rays. Once Mars lost its core dynamo, its surface water disappeared quickly thereafter.
Early on in Solar System formation, a cloudy disc of gas and dust surrounded the Sun and planets, serving as a conduit for the Sun's magnetic field. The strength of the magnetic field weakened as it got further away from the Sun. Mercury formed in the prime location - close to where the Sun's magnetic field was strongest, thus explaining its large iron core.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-06
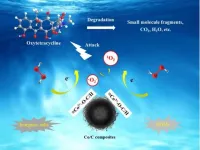
Recently, a research team led by Prof. KONG Lingtao at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has prepared a type of hollow amorphous Co/C composites to activate hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to generate singlet oxygen, achieving selective elimination of oxytetracycline (OTC) in complicated water matrices. The relevant results was published in Chemical Engineering Journal.
OTC is the most common tetracycline antibiotic in the field of animal husbandry. It can be detected in water, soil and other areas which features ...
2021-07-06
The study is the first on epidemiology and causes of traumatic brain injury in over 20 years. The research team reports in the journal BMJ Open of 4 June 2021.
Falling and cycling without a helmet are common causes
From a minor fall on a bicycle to a serious road traffic accident: The causes of a traumatic brain injury are manifold. About 90 percent of the approximately 270,000 cases per year are classified as mild, ten percent as moderate or severe. Current findings show that traumatic brain injury is increasing in the age group of over-65s. The research team at BG Kliniken in Bochum, Hamburg, Berlin, Halle, Frankfurt, Ludwigshafen and Murnau found that there has been a shift in the age group most frequently affected and ...
2021-07-06
[Background]
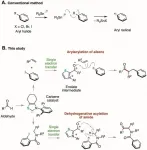
Aryl halides*1) with a benzene ring directly bonded to a halogen atom are readily available and chemically stable, so they are used as a source of benzene rings in organic synthesis. For example, a chemical reaction that generates a highly reactive aryl radical*2) from an aryl halide using a toxic tin compound has long been known as a method for supplying a benzene ring (Figure 1A). In recent years, chemical reactions have been developed, in which an aryl halide is reduced using a metal catalyst or a photocatalyst*3) followed by cleavage of the bond between the benzene ring and the halogen atom to generate ...
2021-07-06
Together with their multifaceted action mechanisms, activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and so-called APOBEC proteins are important factors in the body's immune response and offer fast and effective protection against a large number of DNA and RNA viruses. The task of AID is to strengthen the human immune response, while APOBECs are able to block the virus. A MedUni Vienna research team comprising Anastasia Meshcheryakova, Diana Mechtcheriakova and Peter Pietschmann from the Institute of Pathophysiology and Allergy Research has now addressed the potential interrelations between AID/APOBECs and the SARS-CoV-2 virus, ...
2021-07-06
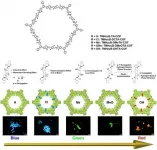
Ishikawa, Japan - Many researchers in the field of materials science constantly seek novel and versatile platforms that can be used to tailor materials to match their intended use. One example of this are covalent organic frameworks (COFs), an emerging class of crystalline porous polymers with a favorable set of fundamental properties, namely crystallinity, stability, and porosity. This combination makes them, in theory, adjustable to many modern applications. Unfortunately, owing to the way COFs are usually obtained, these properties are not very pronounced, resulting in unstable, low-crystallinity solids with limited porosity.
At the Japan Advanced Institute of ...
2021-07-06
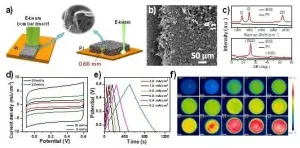
Recently, Prof. WANG Zhenyang's research group from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has prepared macroscopic thick three-dimensional (3D) porous graphene films.
Using high-energy electron beam as the energy source and taking advantages of high kinetic energy and low reflection characteristics of e-beam, the researchers directly induced polyimide precursor into a 3D porous graphene crystal film with a thickness of up to 0.66 mm. Related research results were published in the journal Carbon.
Graphene has been proved ...
2021-07-06
A new nanotechnology development by an international research team led by Tel Aviv University researchers will make it possible to generate electric currents and voltage within the human body through the activation of various organs (mechanical force). The researchers explain that the development involves a new and very strong biological material, similar to collagen, which is non-toxic and causes no harm to the body's tissues. The researchers believe that this new nanotechnology has many potential applications in medicine, including harvesting clean energy to operate devices implanted ...
2021-07-06
Recently, with the help of a steady-state strong magnetic field experimental device, scientists constructed nano-scale borate bioactive glass (Nano-HCA@BG), which can effectively reduce the biological toxicity of borate bioglass, improve the biocompatibility of the glass, and promote the effect of borate bioglass on skin repair.
Prof. WANG Junfeng from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with Prof. ZHANG Teng from Fuzhou University in this study, said, "it is expected to become the next generation of skin wound repair dressings." Related research was published in Chemical Engineering Journal.
Borate bioglass is a glass with boron element (B) as the glass network matrix. With good dopability and degradability, it ...
2021-07-06
Sleep deprivation - from lifestyle choices, pandemic stress, or late-night computer study - can quickly lead to loss of energy and function during the day and even feelings of anger and depression, an Australian sleep institute study has shown.
The study, led by Flinders University, asked 34 health teenagers (20 males) aged between 15 and 17 to spent 10 days and nine nights in a specially designed sleep centre.
They were allocated to one of three sleep 'doses' for five consecutive nights- from five hours, 7.5 hours, or 10 hours in bed per night - with two baseline and two 'recovery' nights of up to 10 hours' time in bed.
Their mood was measured every three hours after waking up to assess responses to feelings such as 'depressed', 'afraid', 'angry', 'confused', ...
2021-07-06
Wetland, forest, and ocean are the three largest ecosystems in the world. Although the area of wetland ecosystem accounts for only 4-6% of the total land area, the carbon reserves of wetland ecosystem accounts for 12-24% of the global land carbon reserves. Under the background of global climate change, the research on carbon sequestration of wetland has become an important subject of global carbon cycle research.
The area of marshes in China ranks third in the world, and herbaceous marsh is the most widely distributed among all the types of marshes. As an important quality parameter of marsh ecosystem, aboveground biomass of vegetation is a crucial index estimating the carbon storage of marsh vegetation, and the basis for studying ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Why does Mercury have a big iron core?