(Press-News.org) Ishikawa, Japan - Many researchers in the field of materials science constantly seek novel and versatile platforms that can be used to tailor materials to match their intended use. One example of this are covalent organic frameworks (COFs), an emerging class of crystalline porous polymers with a favorable set of fundamental properties, namely crystallinity, stability, and porosity. This combination makes them, in theory, adjustable to many modern applications. Unfortunately, owing to the way COFs are usually obtained, these properties are not very pronounced, resulting in unstable, low-crystallinity solids with limited porosity.
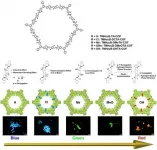
At the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Dr. Zhongping Li, Associate Professor Yuki Nagao, and colleagues are trying to put an end to this issue and showcase the true potential of COFs. In their latest study, which was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition as Very Important Paper, Dr. Nagao, Professor Donglin Jiang at the National University of Singapore, and his team devised a novel strategy for easily tuning the light-emitting properties of hydrazone-linked COFs to produce red, green, or blue (RGB) light by using a single material. This work was the result of a lot of efforts by many researchers including first-author Zhongping Li, Keyu Geng, Ting He, Ke Tian Tan, Ning Huang, Qiuhong Jiang, and Donglin Jiang at the National University of Singapore.
The researchers had been exploring a new concept that involves introducing atoms or small molecular groups into the pore walls of COFs. Though the changes in composition are relatively minor, the orderly introduction of these groups in surface sites causes drastic effects in the electronic structure of the entire molecule, altering some of its physicochemical properties. Without really expecting it, the researchers found that the small perturbations introduced in single surface sites greatly modified the light-emission characteristics of hydrazone-linked COFs.
More specifically, by introducing hydrogen, chlorine, methoxy, methyl, or hydroxy surface sites on the pore walls of COFs (see Figure 1), the team produced compounds that could be fine-tuned to emit light at various distinct frequencies within the RGB spectrum. Surprisingly, these COFs are among the few known material frameworks that can be easily tailored to emit any one of the three primary colors, and even colors in-between (see Figure 2). This is in stark contrast to most available RGB technologies, which require different materials to produce the three primary colors. "Thanks to the exciting features we observed, COF-based materials offer a solution to the low tunability problems found in organic/polymeric light-emitting materials," remarks Dr. Li, "By introducing perturbations with multiple wall surface sites, our frameworks can be used to edit the light-emission of materials to achieve any given color in a pre-designable and digital way."
Importantly, aside from these useful color tunability properties, the synthesized COFs were also up there in terms of luminescence, stability, and sensitivity to guest molecules. This combination of features makes the proposed framework especially attractive for light-emitting and sensing implementations using organic and polymeric materials, as well as for other types of applications, as Dr. Li explains: "Our perturbation strategy of introducing single atoms or small groups to induce electronic effects is compatible with further functionalization and should be widely applicable to other types of COFs."
It's possible that the strategy devices in this study will shape a new regime in light-emitting organic materials, which shall be useful for highly sophisticated applications and daily-life devices alike. Further refinement of similar methods will let us truly harness the power that even small, yet rational changes can have in the macroscopic behavior of certain materials.
INFORMATION:
Reference
Title of original paper: "Editing Light Emission with Stable Crystalline Covalent Organic Frameworks via Wall Surface Perturbation"
Journal: Angewandte Chemie International Edition
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202107179
Funding information:
This work is supported by an MOE tier 1 grant (R-143-000-A71-114) and a NUS start-up grant (R-143-000-A28-133).
About Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Japan
Founded in 1990 in Ishikawa prefecture, the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) was the first independent national graduate school in Japan. Now, after 30 years of steady progress, JAIST has become one of Japan's top-ranking universities. JAIST counts with multiple satellite campuses and strives to foster capable leaders with a state-of-the-art education system where diversity is key; about 40% of its alumni are international students. The university has a unique style of graduate education based on a carefully designed coursework-oriented curriculum to ensure that its students have a solid foundation on which to carry out cutting-edge research. JAIST also works closely both with local and overseas communities by promoting industry-academia collaborative research.
About Associate Professor Yuki Nagao from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Japan
Dr. Yuki Nagao is an Associate Professor at the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Japan since 2012. He obtained his B.S. and M.S. from University of Tsukuba, Japan in 2001 and 2003, respectively and his Ph.D. from Kyushu University, Japan in 2006. He specializes in designing polymer materials conducive to interface proton transport with a focus on developing proton batteries and fuel cells. He has published over 100 papers with over 1400 citations to his credit. For more information about his research, visit: https://www.jaist.ac.jp/english/areas/mc/laboratory/nagao.html
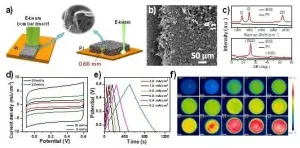
Recently, Prof. WANG Zhenyang's research group from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has prepared macroscopic thick three-dimensional (3D) porous graphene films.
Using high-energy electron beam as the energy source and taking advantages of high kinetic energy and low reflection characteristics of e-beam, the researchers directly induced polyimide precursor into a 3D porous graphene crystal film with a thickness of up to 0.66 mm. Related research results were published in the journal Carbon.
Graphene has been proved ...
A new nanotechnology development by an international research team led by Tel Aviv University researchers will make it possible to generate electric currents and voltage within the human body through the activation of various organs (mechanical force). The researchers explain that the development involves a new and very strong biological material, similar to collagen, which is non-toxic and causes no harm to the body's tissues. The researchers believe that this new nanotechnology has many potential applications in medicine, including harvesting clean energy to operate devices implanted ...
Recently, with the help of a steady-state strong magnetic field experimental device, scientists constructed nano-scale borate bioactive glass (Nano-HCA@BG), which can effectively reduce the biological toxicity of borate bioglass, improve the biocompatibility of the glass, and promote the effect of borate bioglass on skin repair.
Prof. WANG Junfeng from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with Prof. ZHANG Teng from Fuzhou University in this study, said, "it is expected to become the next generation of skin wound repair dressings." Related research was published in Chemical Engineering Journal.
Borate bioglass is a glass with boron element (B) as the glass network matrix. With good dopability and degradability, it ...
Sleep deprivation - from lifestyle choices, pandemic stress, or late-night computer study - can quickly lead to loss of energy and function during the day and even feelings of anger and depression, an Australian sleep institute study has shown.
The study, led by Flinders University, asked 34 health teenagers (20 males) aged between 15 and 17 to spent 10 days and nine nights in a specially designed sleep centre.
They were allocated to one of three sleep 'doses' for five consecutive nights- from five hours, 7.5 hours, or 10 hours in bed per night - with two baseline and two 'recovery' nights of up to 10 hours' time in bed.
Their mood was measured every three hours after waking up to assess responses to feelings such as 'depressed', 'afraid', 'angry', 'confused', ...
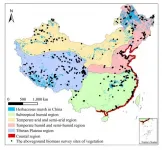
Wetland, forest, and ocean are the three largest ecosystems in the world. Although the area of wetland ecosystem accounts for only 4-6% of the total land area, the carbon reserves of wetland ecosystem accounts for 12-24% of the global land carbon reserves. Under the background of global climate change, the research on carbon sequestration of wetland has become an important subject of global carbon cycle research.
The area of marshes in China ranks third in the world, and herbaceous marsh is the most widely distributed among all the types of marshes. As an important quality parameter of marsh ecosystem, aboveground biomass of vegetation is a crucial index estimating the carbon storage of marsh vegetation, and the basis for studying ...
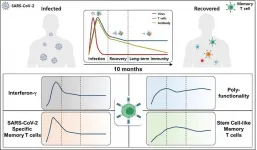
A KAIST immunology research team found that most convalescent patients of COVID-19 develop and maintain T cell memory for over 10 months regardless of the severity of their symptoms. In addition, memory T cells proliferate rapidly after encountering their cognate antigen and accomplish their multifunctional roles. This study provides new insights for effective vaccine strategies against COVID-19, considering the self-renewal capacity and multipotency of memory T cells.
COVID-19 is a disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. When patients recover from COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2-specific adaptive immune memory is developed. The adaptive immune system consists ...
While this isn't the fountain of youth, scientists may have improved healing in our joints - even in areas that become weaker as we grow older. The meniscus is a durable, yet flexible tissue found in joints like our wrist and knees that helps them absorb shock during movement. Occasionally tears can occur in the meniscus due an awkward movement or structural weakness from old age. When we are young, there is plenty of blood flowing to this area allowing for quick healing, but as we get older, the meniscus receives less and less blood - with the inner most area becoming ...
An international team including Lancaster University researchers has created a strategy for understanding the evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic throughout the African continent.
Their COVID-19 surveillance strategy will improve the ability of African countries to interpret the complex data available to them during the pandemic.
Professor Peter Diggle, Dr Chris Jewell and Dr Claudio Fronterre from the Centre for Health Informatics, Computing and Statistics (CHICAS) at Lancaster Medical School worked with colleagues in the USA, Uganda and Switzerland to create a data-driven disease surveillance framework to track and predict ...
Cleft lip and palate is one of the most common congenital malformations. Its causes are mainly genetic. However, it is still largely unknown exactly which genes are affected. A new international study led by the University of Bonn now provides new insights. The results are published in the journal Human Genetics and Genomics Advances, but are already available online.
The researchers from the Institute of Human Genetics at the University Hospital Bonn combined various data sources in their work. In the course of their research, they discovered five new regions in the human genome in which variations in the DNA sequence are associated with an ...
A new report that could help improve how immersive technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are used in healthcare education and training has been published with significant input from the University of Huddersfield.
Professor David Peebles, Director of the University's Centre for Cognition and Neuroscience, and Huddersfield PhD graduate Matthew Pears contributed to the report - 'Immersive technologies in healthcare training and education: Three principles for progress' - recently published by the University of Leeds with input from range of academics, technologists and health professionals.
The principles have also been expanded upon in a letter to the prestigious journal BMJ ...