INFORMATION:
Modelling COVID-19 cases in Africa
2021-07-06
(Press-News.org) An international team including Lancaster University researchers has created a strategy for understanding the evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic throughout the African continent.
Their COVID-19 surveillance strategy will improve the ability of African countries to interpret the complex data available to them during the pandemic.
Professor Peter Diggle, Dr Chris Jewell and Dr Claudio Fronterre from the Centre for Health Informatics, Computing and Statistics (CHICAS) at Lancaster Medical School worked with colleagues in the USA, Uganda and Switzerland to create a data-driven disease surveillance framework to track and predict country-level case incidence.
The first COVID-19 case on the continent was reported in Egypt on February 14, 2020. By August 13, 2020, over 1 million new cases and over 20,000 deaths had been reported in all African Union (AU) Member States according to the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. Over 44 million cases and 190,000 deaths in Africa are projected within the first year of the pandemic.
Although Africa has a younger population, a lack of adequate healthcare in combination with comorbidities such as HIV is predicted to lead to increased risk of severe COVID-19 in those infected.
The researchers observed the effect of the human development index, containment policies, testing capacity, specific humidity, temperature and landlocked status of countries on the local within-country and external between-country transmission.
They found that a country's testing capacity, social policy, landlocked status, temperature and humidity are important contributing factors explaining the within and between-country transmission of cases.
"Because high quality mobility data is challenging to obtain across Africa, the approach provides the ability to distinguish cases arising from within a country or from its neighbours.
"In settings with fragile health systems, coupled with the vulnerability of lower Human Development Index economies, the capacity to effectively track the pandemic is especially challenging. Such challenges point to the potential advantages in regional efforts to coordinate resources to test and report cases. Seeking equitable behavioral and social interventions, balanced with coordinated country-specific strategies in infection suppression, should be a continental priority to control the COVID-19 pandemic in Africa."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Comprehensive genetic study of cleft lip and palate
2021-07-06
Cleft lip and palate is one of the most common congenital malformations. Its causes are mainly genetic. However, it is still largely unknown exactly which genes are affected. A new international study led by the University of Bonn now provides new insights. The results are published in the journal Human Genetics and Genomics Advances, but are already available online.
The researchers from the Institute of Human Genetics at the University Hospital Bonn combined various data sources in their work. In the course of their research, they discovered five new regions in the human genome in which variations in the DNA sequence are associated with an ...
New report aims to improve VR use in healthcare education
2021-07-06
A new report that could help improve how immersive technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are used in healthcare education and training has been published with significant input from the University of Huddersfield.
Professor David Peebles, Director of the University's Centre for Cognition and Neuroscience, and Huddersfield PhD graduate Matthew Pears contributed to the report - 'Immersive technologies in healthcare training and education: Three principles for progress' - recently published by the University of Leeds with input from range of academics, technologists and health professionals.
The principles have also been expanded upon in a letter to the prestigious journal BMJ ...
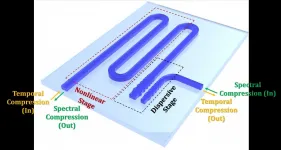
Ultra-strong squeezing of light demonstrated for ultrafast optical signal processing
2021-07-06
A train carrying cargo has finite space. The amount of cargo that can be carried onboard is limited by the size of the cargo and the capacity of the train. Analogously, the amount of time taken up by an optical signal limits the amount of data that can be carried. Temporally shorter signals allow more data to be squeezed into a given time duration, in a method called optical time division multiplexing. Photonics researchers have recently succeeded in squeezing light in time by 11 times. The developed temporal compression system allows an equivalent increase in the number of bits transmitted by light ...
Study shows laboratory developed protein spikes consistent with COVID-19 virus
2021-07-06
A new international study has found that the key properties of the spikes of SARS-CoV-2 virus which causes COVID-19 are consistent with those of several laboratory-developed protein spikes, designed to mimic the infectious virus.
A central component in designing serological tests and vaccines to protect against COVID-19 is the manufacture of protein "spikes". These recombinant spikes closely mimic those sticking out of surface of the infectious virus and trigger the body's immune system into action.
Laboratory manufactured spikes are also used for serological testing (also referred to as antibody testing) and as research reagents. The findings show how that viral spike manufactured through different methods in laboratories across the globe ...
Remdesivir in COVID-19: Indication of considerable added benefit for a part of the patients
2021-07-06
Since July 2020, remdesivir has been conditionally approved in Europe for the treatment of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older with pneumonia who require supplemental oxygen but no invasive ventilation. In an early benefit assessment, the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has now investigated whether the drug, which was originally developed for the treatment of Ebola virus disease, offers these patients an added benefit compared to the appropriate comparator therapy (here: therapy according to physician's choice).
This investigation yielded an indication of a considerable added benefit of remdesivir compared to the appropriate comparator therapy for adults with pneumonia ...
Researchers shed light on memory effects in multi-step evolution of open quantum system
2021-07-06
In a study published in Physical Review Letters, academician GUO Guangcan's team from University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences made progress in the open quantum system research. This team, collaborating with Austrian theoretical physicist Philip Taranto, demonstrated the non-Markovianity in the multi-step evolution of the open quantum system, and proved the measurement-dependent property of quantum memory effects.
In quantum information science, it is crucial to understand and control the memory effects for the development of quantum technology. For the coupling of the system and environment, the evolution of open quantum system presents the non-Markovianity, ...
Potential of faba beans, rich in protein, has been unlocked
2021-07-06
Faba beans have been an excellent source of food protein since pre-historic times, but about 5% of people, mostly from regions where malaria has been endemic and who carry a certain mutation, can't eat them. Now, an international team of researchers, led by the Universities of Helsinki and Copenhagen as well as Luke Natural Resources Institute Finland, has identified the gene responsible for the production of vicine and convicine, which are harmful to these people. In the work published in Nature Plants, the team reports that the VC1 gene plays a central role in the biosynthesis these compounds.
Faba beans - Pythagoras and his followers avoided them and Roman priests of Jupiter associated them with death. ...
Researchers discover unusual competition between charge density wave and superconductivity
2021-07-06
A research team led by Prof. CHEN Xianhui from University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found an unusual competition between charge density wave (CDW) and superconductivity in CsV3Sb5, a layered kagome metal, which provides key experimental evidence for understanding novel CDW and superconductivity. The result was published on Nature Communications and recommended as featured article.
Traditional superconductivity and CDW are two different electronic states, which both originate from electron phonon coupling and Fermi instability. In the conventional coexistence image of CDW and superconductor, after entering the CDW state, the energy gap is opened due to the nesting of Fermi surface, resulting in the loss of density ...
Gulf Coast ready to develop carbon storage hub
2021-07-06
The stage is set for a new carbon storage economy to emerge along the Gulf Coast, according to a study led by The University of Texas at Austin, with the region offering ample opportunities to capture and store carbon, and recent state and federal incentives giving an added push to get started.
Carbon capture and storage, or CCS, is a technology that keeps CO2 out of the atmosphere by capturing emissions and storing them deep underground. It can help fight climate change by lowering industrial emissions now while renewable energy sources are being developed, said Tip Meckel, a senior research scientist at the Gulf Coast Carbon Center, a research group at the UT Bureau ...
Neanderthal artists? Our ancestors decorated bones over 50,000 years ago
2021-07-06
Since the discovery of the first fossil remains in the 19th century, the image of the Neanderthal has been one of a primitive hominin. People have known for a long time that Neanderthals were able to effectively fashion tools and weapons. But could they also make ornaments, jewellery or even art? A research team led by the University of Göttingen and the Lower Saxony State Office for Heritage has analysed a new find from the Unicorn Cave (Einhornhöhle) in the Harz Mountains. The researchers conclude that, in fact, Neanderthals, genetically the closest relative to modern humans, had remarkable cognitive abilities. The results of the study were published in Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Working with the Unicornu Fossile society, the scientists ...