INFORMATION:
Researchers shed light on memory effects in multi-step evolution of open quantum system
2021-07-06
(Press-News.org) In a study published in Physical Review Letters, academician GUO Guangcan's team from University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences made progress in the open quantum system research. This team, collaborating with Austrian theoretical physicist Philip Taranto, demonstrated the non-Markovianity in the multi-step evolution of the open quantum system, and proved the measurement-dependent property of quantum memory effects.
In quantum information science, it is crucial to understand and control the memory effects for the development of quantum technology. For the coupling of the system and environment, the evolution of open quantum system presents the non-Markovianity, which paves the way for the study of quantum memory effects.
However, the measurement could cause the collapse of the quantum state of the system, and the detection of the system will affect the subsequent evolution of the system, which confines the previous research on the quantum memory effects to the single-step evolution process. This means that researchers only conduct the measurement at the end of the evolution after the preparation of the initial state without any extra measurement in the evolution process.
To study the multi-step evolution, the researchers first separated the controllable detection from the system evolution by using the process tensor method. They then constructed two kinds of open quantum dynamics with the multi-step evolution through path and polarization degrees of freedom of photon pairs.
By measuring the non-Markovian properties of these two evolution processes with different methods, the researchers demonstrated the measurement-dependent property of quantum memory strength.
This study is the first report of finite quantum Markov order for non-Markovian common-cause processes, which has implications for the approximation of quantum processes with memory.
Memory effects are common in nature. They exist in disease spreading, biochemical processes, and optical fiber transmission. Their duration, strength, and structure are key properties of physical evolution.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Potential of faba beans, rich in protein, has been unlocked
2021-07-06
Faba beans have been an excellent source of food protein since pre-historic times, but about 5% of people, mostly from regions where malaria has been endemic and who carry a certain mutation, can't eat them. Now, an international team of researchers, led by the Universities of Helsinki and Copenhagen as well as Luke Natural Resources Institute Finland, has identified the gene responsible for the production of vicine and convicine, which are harmful to these people. In the work published in Nature Plants, the team reports that the VC1 gene plays a central role in the biosynthesis these compounds.
Faba beans - Pythagoras and his followers avoided them and Roman priests of Jupiter associated them with death. ...
Researchers discover unusual competition between charge density wave and superconductivity
2021-07-06
A research team led by Prof. CHEN Xianhui from University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found an unusual competition between charge density wave (CDW) and superconductivity in CsV3Sb5, a layered kagome metal, which provides key experimental evidence for understanding novel CDW and superconductivity. The result was published on Nature Communications and recommended as featured article.
Traditional superconductivity and CDW are two different electronic states, which both originate from electron phonon coupling and Fermi instability. In the conventional coexistence image of CDW and superconductor, after entering the CDW state, the energy gap is opened due to the nesting of Fermi surface, resulting in the loss of density ...
Gulf Coast ready to develop carbon storage hub
2021-07-06
The stage is set for a new carbon storage economy to emerge along the Gulf Coast, according to a study led by The University of Texas at Austin, with the region offering ample opportunities to capture and store carbon, and recent state and federal incentives giving an added push to get started.
Carbon capture and storage, or CCS, is a technology that keeps CO2 out of the atmosphere by capturing emissions and storing them deep underground. It can help fight climate change by lowering industrial emissions now while renewable energy sources are being developed, said Tip Meckel, a senior research scientist at the Gulf Coast Carbon Center, a research group at the UT Bureau ...
Neanderthal artists? Our ancestors decorated bones over 50,000 years ago
2021-07-06
Since the discovery of the first fossil remains in the 19th century, the image of the Neanderthal has been one of a primitive hominin. People have known for a long time that Neanderthals were able to effectively fashion tools and weapons. But could they also make ornaments, jewellery or even art? A research team led by the University of Göttingen and the Lower Saxony State Office for Heritage has analysed a new find from the Unicorn Cave (Einhornhöhle) in the Harz Mountains. The researchers conclude that, in fact, Neanderthals, genetically the closest relative to modern humans, had remarkable cognitive abilities. The results of the study were published in Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Working with the Unicornu Fossile society, the scientists ...
From waste to wealth: Converting CO2 into butanol using phosphorous-rich copper cathodes
2021-07-06
Human activities like the burning of coal and fossil fuels have caused CO2 to accumulate in the atmosphere, which has significantly affected the Earth's climate. As a result, several scientists are looking for ways to convert CO2 into other valuable organic products, such as 1-butanol, which has shown promise as an alternative fuel for vehicles. This could help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
One method of obtaining useful compounds is by the electrochemical reduction reaction (CO2RR). Researchers have developed metal-based catalysts that can fulfill this task. However, there is a caveat: most of these catalysts are expensive and produce a variety of products during the reaction, ...
Study finds genes role in immune response of Florida corals to rapidly spreading disease
2021-07-06
MIAMI--A new study led by scientists at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science is the first to document what coral genes are doing in response to a disease that is rapidly killing corals throughout Florida and the Caribbean. The findings can help to better understand coral immune system as new diseases emerge as the ocean warm.
The collaborative effort between researchers at the UM Rosenstiel School, Mote Marine Laboratory and the Smithsonian Marine Station is the first to document a gene expression response of corals to stony coral tissue loss disease and that the disease causes a shared immune response in at least two coral species -- mountainous star coral (O. faveolata) and great star coral ...
Falling in line: The simple design and control of MOF electric flow
2021-07-06
Metal-organic frameworks (MOF) are crystalline porous organic-inorganic hybrid materials that, by filling its pores with guest molecules, can create functionalities through interactions between the organic-inorganic based frameworks of MOF (host) and its guest molecules. This host-guest chemistry has the potential to bring "designable" electrical properties, allowing for a material to be organized in ways never before possible - paving the way for the next-generation of thin-film smart devices.
"However, most MOFs exhibit poor electrical conductivity", states Professor Masahide Takahashi, ...
Safe nurse staffing standards in hospitals saves lives and lowers costs
2021-07-06
Philadelphia and Santiago -A new study published in The Lancet Global Health showed that establishing safe nurse staffing standards in hospitals in Chile could save lives, prevent readmissions, shorten hospital stays, and reduce costs.
The study, by the Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research (CHOPR) at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, and the Universidad de los Andes - Chile School of Nursing, found very large variations in patient to nurse staffing across 40 hospitals located throughout Chile. Nurse staffing was significantly ...
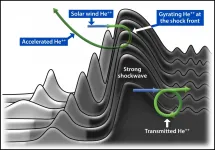
SwRI-led team addresses mystery of heavy elements in galactic cosmic rays
2021-07-06
SAN ANTONIO -- July 6, 2021 -- Scientists have used data from the Southwest Research Institute-led Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission to explain the presence of energetic heavy elements in galactic cosmic rays (GCRs). GCRs are composed of fast-moving energetic particles, mostly hydrogen ions called protons, the lightest and most abundant elements in the universe. Scientists have long debated how trace amounts of heavy ions in GCRs are accelerated.
The supernova explosion of a dying star creates massive shockwaves that propagate through the surrounding space, accelerating ions in their path to very high energies, creating ...
Sentinel-2 constellation of satellites used for the ongoing monitoring of grasslands
2021-07-06
A research group at the University of Cordoba has conducted study focused on evaluating the potential of the Sentinel-2 sensor system's configuration to predict the amount of forage on permanent Mediterranean grasslands.
Pasture quality assessment in permanent grasslands is essential for their conservation and management, as it can facilitate real-time decision-making regarding livestock management. In this regard, the Sentinel-2 satellite constellation, launched in 2015, has proven to be a promising tool for permanent grassland monitoring. This is a sensor system developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) and that provides free and available data worldwide, with a review time of five days, and 13 spectral bands. The spectral configuration of Sentinel-2, ...