INFORMATION:
Highly fit teenagers coped better with COVID-19 later in life
2021-07-08
(Press-News.org) Of the Swedish men in their late teens who performed well in the physical fitness tests for military conscription, a relatively high proportion were able to avoid hospital care when they became infected with COVID-19 during the pandemic up to 50 years later. This has been shown by University of Gothenburg researchers in a register study, with results now published in the BMJ Open.
The study is based on the Swedish Conscription Register, which contains particulars of over 1.5 million young Swedish men who began their military service in the years 1969-2005. Almost all of these men then underwent both a bicycle test and a strength test. Some 2,500 of the men included in the Conscription Register were later, in spring 2020, hospitalized with COVID-19.
For their study, the scientists divided the men into three groups based on their results in the fitness and strength tests. The data were merged with three other Swedish registers: the National Inpatient Register (IPR, also known as the Hospital Discharge Register), Intensive Care Register, and Cause of Death Register. The findings show a clear association between fitness and strength in youth and the risk of needing hospital care for COVID-19 infection 15-50 years after conscription.
"At the population level, we can see that both good fitness and good muscle strength in the late teens are protective factors for severe COVID. For those with good fitness at the time of conscription, the risk of dying in spring 2020 was half as high as for the least fit. For those whose strength was good back then, too, we see a similar protective effect," says Agnes af Geijerstam, PhD student at the University of Gothenburg's Sahlgrenska Academy, who is the lead author of the study.
However, since the oldest men in the study had not reached age 70, deaths from COVID-19 were uncommon in the study.
The Conscription Register also contains data on the young men's height and weight.
"Previous studies have shown that obesity is a risk factor for severe COVID. But we see that good fitness and strength are protective factors for everyone, including men with overweight or obesity," says Professor Lauren Lissner, senior coauthor of the study.
Moreover, the study showed a link between the men's height to the risk of COVID-19 infection.
"The taller the men were, the greater their risk of needing advanced care when they had gotten COVID; but per centimeter this increase in risk is very small. Also, unlike fitness and strength, there is no way to influence our height" af Geijerstam says.
There have already been many studies showing the protective effect of good physical fitness in numerous medical conditions, including infections. It has been established that the immune system is strengthened and the propensity to inflammation is reduced by physical activity. Fitness in adolescence is also likely to be associated with active and otherwise healthy lifestyles throughout adult life.
"It's interesting to see that the high fitness and strength levels those men had so many years ago can be linked to protection against severe COVID. Today, young people are becoming ever more sedentary, and that means there's a risk of major problems arising in the long term -- including a reduced resistance to future viral pandemics. Children and adolescents must get ample scope to move around," af Geijerstam says.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
People with ADHD and multiple psychiatric diagnoses stop their ADHD treatment more often
2021-07-08
A research study from the The Lundbeck Foundation Initiative for Integrative Psychiatric Research iPSYCH shows that people with ADHD, who also have another psychiatric diagnosis, are more likely to stop taking their ADHD medicine.
ADHD is one of the most common psychiatric disorders in childhood and is commonly treated with medication. ADHD medicine can be divided into two groups: medicine that has a stimulating effect - also known as stimulants - and non-stimulants, which are often used if a person does not respond well to the other form of medicine.
The medication can be an effective way of reducing symptoms, by ...
New radio receiver opens wider window to radio universe
2021-07-08
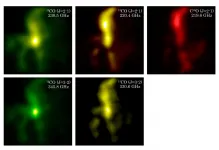
Researchers have used the latest wireless technology to develop a new radio receiver for astronomy. The receiver is capable of capturing radio waves at frequencies over a range several times wider than conventional ones, and can detect radio waves emitted by many types of molecules in space at once. This is expected to enable significant progresses in the study of the evolution of the Universe and the mechanisms of star and planet formation.
Interstellar molecular clouds of gas and dust provide the material for stars and planets. Each type of molecule emits radio waves at characteristic frequencies and astronomers have detected emissions from various molecules ...
Sample preparation in forensic toxicological analysis may have huge impacts
2021-07-08
(Boston)--As analytical instrumentation (gas- and liquid-chromatographs coupled with mass spectrometers) increase in sensitivity and speed, forensic scientists may find themselves still hindered by the process of preparing samples (blood, urine, etc.) for analysis and seeking more efficient approaches.
In an article in WIRES Forensic Science, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine's (BUSM) Biomedical Forensic Sciences program, provide an overview of sample preparation techniques and information on routine sample types that may be encountered in forensic toxicology cases.
Forensic toxicology encompasses a large variety of scenarios including drug-facilitated crimes, understanding ...
When bosses are abusive, how employees interpret their motives makes a difference: study
2021-07-08
A new UBC Sauder School of Business study shows that depending on how employees understand their boss' motivation, employees can feel anger or guilt, and consequently, react differently to abusive supervision.
Former Apple CEO Steve Jobs was a famously harsh corporate leader, one who pushed his employees to extremes to achieve the company's lofty aims.
But while many aspiring leaders still believe that the "tough love" approach is effective, a new study from UBC Sauder shows that, even when abusive leadership is meant to push employees to new heights, it can land them in deep lows in the long term.
Abusive supervision -- which includes behaviours like yelling at employees, giving them the silent treatment, or putting them down in front of their ...
Depression, suicidal thoughts plague ailing coal miners, study finds
2021-07-08
More than a third of coal miners and former coal miners suffering from black lung disease struggle with depression, and more than one in 10 has recently considered suicide, a new study finds.
The study is believed to be the first to examine mental-health issues in a large population of coal miners in the United States. Based on the troubling results, the researchers are calling for more mental health resources and treatment for current and former miners. They also are urging further study of potential contributors to the problem, including social determinants of health, ...
Ancient ostrich eggshell reveals new evidence of extreme climate change thousands of years ago
2021-07-08
Evidence from an ancient eggshell has revealed important new information about the extreme climate change faced by human early ancestors.
The research shows parts of the interior of South Africa that today are dry and sparsely populated, were once wetland and grassland 250,000 to 350,000 years ago, at a key time in human evolution.
Philip Kiberd and Dr Alex Pryor, from the University of Exeter, studied isotopes and the amino acid from ostrich eggshell fragments excavated at the early middle Stone Age site of Bundu Farm, in the upper Karoo region ...
Total-body PET imaging exceeds industry standards
2021-07-08
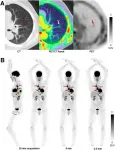
Reston, VA--A performance evaluation of the uEXPLORER total-body PET/CT scanner showed that it exhibits ultra-high sensitivity that supports excellent spatial resolution and image quality. Given the long axial field of view (AFOV) of the uEXPLORER, study authors have proposed new, extended measurements for phantoms to characterize total-body PET imaging more appropriately. This research was published in the June issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
uEXPLORER is the world's first commercially available total-body PET scanner. The scanner has an AFOV of 194 cm, which allows PET data collection from the ...
Tiny but mighty precipitates toughen a structural alloy
2021-07-08
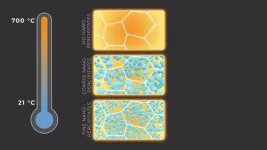
Scientists at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, have found a way to simultaneously increase the strength and ductility of an alloy by introducing tiny precipitates into its matrix and tuning their size and spacing. The precipitates are solids that separate from the metal mixture as the alloy cools. The results, published in the journal Nature, will open new avenues for advancing structural materials.
Ductility is a measure of a material's ability to undergo permanent deformation without breaking. It determines, among other ...
Collective battery storage beneficial for decarbonized world
2021-07-08
Batteries are potentially a game-changing technology as we decarbonize our economy, and their benefits are even greater when shared across communities, a University of Otago-led study has found.
Co-author Associate Professor Michael Jack, Director of the Energy Programme in the Department of Physics, says reducing costs are seeing rapid deployment of batteries for household use, mainly for storing solar and wind power for later use, but they could have a variety of uses in a future electricity grid.
"For example, they could be used to feed energy back into the grid when there is a shortfall in renewable supply. ...
US saw surge in firearm purchases and violence during first months of COVID-19 pandemic
2021-07-08
Firearm purchases and firearm violence surged dramatically during the first five months of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study from the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research Program (VPRP), published in Injury Epidemiology.
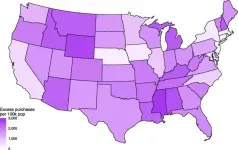
From March through July 2020, an estimated 4.3 million more background checks for firearm purchases occurred nationwide than would have ordinarily -- an 85 percent increase. The total number of firearm purchases during this period was 9.3 million.
From April through July 2020, there was a 27% increase in interpersonal firearm injuries, which includes firearm homicides or nonfatal firearm assault injuries. This is approximately 4,075 more injuries ...