To predict underwater volcano eruptions, scientist looks at images from space
A new study monitored satellite images to obtain sea discoloration data as a novel indicator in detecting if an underwater volcano's eruption is imminent.
2021-07-08
(Press-News.org) A new study suggests sea discoloration data obtained from satellite images as a novel criterion in predicting if eruption looms for an underwater volcano.
There have been frequent eruptions of submarine volcanoes in recent years. The past two years alone recorded the explosions of Anak Krakatau in Indonesia, White Island in New Zealand, and Nishinoshima Island in Japan. Observing signs of volcanic unrest is crucial in providing life-saving information and ensuring that air and maritime travel are safe in the area.
Although predicting when a volcano will erupt can be difficult as each behaves differently, scientists are on the lookout for these telltale signs: heightened seismic activity, expansion of magma pools, increases in volcanic gas release, and temperature rises.
For submarine volcanoes, Yuji Sakuno, remote sensing specialist and associate professor at Hiroshima University's Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering, proposed a new indicator -- sea color.
The relationship between the chemical composition of discolored seawater and volcanic activity has been known for a long time. Still, there have been very few quantitative studies that used remote sensing to explore it. And among these few studies, only the reflectance pattern of discolored seawater has been analyzed.
"This is an extremely challenging research result for predicting volcanic disasters that have frequently occurred in various parts of the world in recent years using a new index called sea color," Sakuno said.
"I was the first in the world to propose the relationship between the sea color information obtained from satellites and the chemical composition around submarine volcanoes."
The findings of the study are published in the April 2021 issue of the journal Water.
Sakuno explained that volcanoes release chemicals depending on their activity, and these can change the color of the surrounding water. A higher proportion of iron can cause a yellow or brown discoloration, while increased aluminum or silicon can stain the water with white splotches.
One problem, however, is that sunlight can also play tricks on sea color. The study looked at how past research that chromatically analyzed hot spring water overcame this hurdle and fixed brightness issues. A relational model between seawater color and chemical composition was developed using the XYZ colorimetric system.
Sakuno examined images of Nishinoshima Island captured last year by Japan's GCOM-C SGLI and Himawari-8 satellites. Himawari-8 was used to observe volcanic activity and GCOM-C SGLI to get sea color data. GCOM-C SGLI's short observation cycle -- it takes pictures of the ocean every 2-3 days -- and high spatial resolution of 250 m makes it an ideal choice for monitoring.
Using the new indicator, Sakuno checked satellite data from January to December 2020 and was able to pick up signs of looming volcanic unrest in Nishinoshima Island approximately a month before it even started.
"In the future, I would like to establish a system that can predict volcanic eruptions with higher accuracy in cooperation with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the Maritime Security Agency, which is monitoring submarine volcanoes, and related research," he said.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-08
A pioneering cultivation strategy that recreates a mangrove environment in the lab has enabled identification of novel bacteria residing in Red Sea mangroves and will help improve understanding of mangrove ecosystem stability, resilience and sustainability.
Mangroves are highly productive, dominant coastal ecosystems that line between 60-70 percent of the world's tropical and subtropical coastlines. They harbor diverse microbial communities thought to make up 80 percent of the ecosystem's biomass. Many of the microbial species, families and taxa are unknown to science.
The cultivation strategy was developed by a team of KAUST researchers, including Fatmah Sefrji and Ramona Marasco.
"Red Sea mangroves are particularly interesting because they represent an extreme and unique ...
2021-07-08
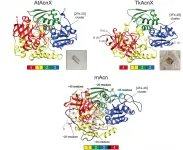
The aconitase superfamily currently contains four functional enzymes including the archetypical aconitase (referred to as "other aconitase enzymes"), and one hypothetical aconitase X (AcnX). The aconitase enzymes catalyze the homologous stereospecific isomerization, and their three-dimensional structures and catalytic mechanisms including the [4Fe-4S] iron-sulfur cluster are very similar each other (Fig. 1a). Therefore, the aconitase superfamily (enzymes) is a typical example that is suitable for the so-called "recruitment hypothesis of enzyme evolution"; the gene duplication of multi-specific enzymes, followed by the narrowing of substrate specificity (ref. 1).
AcnX (subfamily) is further classified into "AcnXType-I" consisting of a single ...
2021-07-08
Researchers at The University of Queensland, working to gain a better understanding of how brain cells work, have discovered the underlying mechanism of a rare genetic mutation that can cause epilepsy.
Dr Victor Anggono from UQ's Queensland Brain Institute said his team made the ground-breaking findings while researching nerve cell communications, which are an important process in normal brain function.
''We're both excited and astounded to make such an important contribution to the field of cellular and molecular neuroscience,'' Dr Anggono said.
He stressed that the mutation was extremely rare, with only one reported case in the world to date.
Dr Anggono's team studied protein structures, called receptors, that ...
2021-07-08
A study by researchers in the Scene understanding and artificial intelligence (SUNAI) research group, of the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya's (UOC) Faculty of Computer Science, Multimedia and Telecommunications, has developed a method that can learn to identify mosquitoes using a large number of images that volunteers took using mobile phones and uploaded to Mosquito Alert platform.
Citizen science to investigate and control disease-transmitting mosquitoes
As well as being annoying because of their bites, mosquitoes can be the carriers of pathogens. Rising temperatures worldwide are facilitating their spread. This is the case with the tiger ...
2021-07-08
While the UK was in lockdown, certain species of captive amphibians became more visible, a new study suggests.
The COVID-19 pandemic forced the closure of zoos across the UK for several months from March 2020, with gradual re-openings from summer into autumn and winter.
These closures provided a team of researchers, from the University of Exeter and WWT Slimbridge Wetland Centre, a unique opportunity to study the effect of visitor presence on several species of amphibian at Slimbridge.
The project assessed the number of individuals of six species - common toad, common frog, smooth newt, pool frog, golden mantella and golden poison dart frog - visible to observers while their exhibit was closed, when it partially reopened to more staff and when it reopened to visitors.
"Amphibians ...
2021-07-08
Lung cancer has the highest mortality rate of all cancers, and treatment options are extremely limited, especially for patients with oncogenic mutations in the KRAS gene. A great deal of hope was invested in the licensing of immune checkpoint inhibitors, but the reality is that some patients respond very well to this treatment while it is completely ineffective in others. In a paper just published in Science Translational Medicine, a MedUni Vienna research group led by Herwig Moll (Center for Physiology and Pharmacology) identified a potential marker for the success of immunotherapy in lung cancer patients and explained the underlying molecular processes.
K-Ras it is a monomeric G protein that plays a key role in the growth of malignant ...
2021-07-08
When you pour cream into a cup of coffee, the viscous liquid seems to lazily disperse throughout the cup. Take a mixing spoon or straw to the cup, though, and the cream and coffee seem to quickly and seamlessly combine into a lighter color and, at least for some, a more enjoyable beverage.
The science behind this relatively simple anecdote actually speaks to a larger truth about complex fluid dynamics and underpins many of the advancements made in transportation, power generation, and other technologies since the industrial era--the seemingly random chaotic motions known as turbulence play a vital role in chemical and industrial ...
2021-07-08
The ratios between the lengths of the second and fourth fingers, known as the 2D:4D ratio, are different in males and females, which is often explained by levels of androgens and oestrogens. However, an alternative theory states that men have bigger body parts, including fingers, which impacts the 2D:4D ratio. A research team including HSE University scholars refuted this hypothesis by collecting data on finger length from 7,500 people. The results of the study were published in Scientific Reports. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-87394-6
The ...
2021-07-08
A new study conducted before COVID-19 busted open the leaky pipeline for women in leadership underscores the bias that men are naturally presumed to have leadership potential and women are not and highlights the increased efforts needed by organizations to address the incorrect stereotype post-pandemic.
The research published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology highlights the continuing bias in leadership assessments of women, explores the contradictions between the perception and the reality of women's leadership, and shows why the slow rate of career advancement for women will likely continue at a snail's pace.
"The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on women's career progression will likely be felt for years to come as ...
2021-07-08
Faba beans are an excellent source of food protein, but about 4% of the world's population are afflicted by favism, which renders them sensitive to the faba bean anti-nutrients vicine and convicine. Now, an international research team has identified the VC1 gene as responsible for the production of these compounds.
Faba beans have actually been a source of food protein since pre-historic times, but a fraction of the population, mostly from warm southern regions, cannot tolerate them. Pythagoras and his followers avoided them, and Roman priests of Jupiter ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] To predict underwater volcano eruptions, scientist looks at images from space
A new study monitored satellite images to obtain sea discoloration data as a novel indicator in detecting if an underwater volcano's eruption is imminent.