(Press-News.org) A new study conducted before COVID-19 busted open the leaky pipeline for women in leadership underscores the bias that men are naturally presumed to have leadership potential and women are not and highlights the increased efforts needed by organizations to address the incorrect stereotype post-pandemic.
The research published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology highlights the continuing bias in leadership assessments of women, explores the contradictions between the perception and the reality of women's leadership, and shows why the slow rate of career advancement for women will likely continue at a snail's pace.
"The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on women's career progression will likely be felt for years to come as many women stepped away from the workforce," said Dr. Margaret Hopkins, professor of management in The University of Toledo's John B. and Lillian E. Neff College of Business and Innovation and lead author of the study. "This can only exacerbate the slow progress of women moving more fully into senior leadership roles -- something that organizations and society must be fully attentive to correcting."
The contemporary view of effective leadership places a strong emphasis on social skills, flexibility and engaging others, behaviors typically associated with women.
But when women exhibit gender role behaviors such as teamwork and empathy, they also pay a price in their leadership performance assessments.
Based on data collected from a sample of 91 senior leaders in one U.S. financial services organization over three years, women were penalized in performance evaluations when they displayed those leadership characteristics.
On the other hand, women also were viewed negatively when exhibiting stereotypical masculine behaviors such as a competitive drive to achieve, task orientation and directing others. Men were positively evaluated for their leadership potential when exhibiting those same behaviors.
"Entrenched archetypes that define leadership as a masculine enterprise remain in spite of data that relates more stereotypical feminine behaviors to effective leadership," said Hopkins, an expert on women in leadership, executive coaching and emotional intelligence. "Our study found no evidence of acknowledging this more contemporary view of leadership when organizations actually assess women's performance and potential for leadership."
The researchers discovered that whether women demonstrated people-oriented, relational skills or whether they exhibited achievement-oriented behaviors, there was a negative effect on their leadership performance assessments and leadership potential appraisals. However, this was not the case for the male leaders in the study.
In order to change the dynamic, Hopkins said there are best-practice strategies that both women and organizations can take.
"My co-authors and I do not support the notion that the onus is on the women to change," Hopkins said. "Rather, organizational structures and systems must change to provide leadership opportunities for both women and men in equal measure."
She said organizational decision-makers can investigate organizational policies and practices to determine how they might be contributing to impediments for women in leadership roles.
Not only should leadership assessment instruments be examined for possible bias, but also the methods by which individuals conduct assessments of women leaders should be reviewed for inherent bias.
"Hiring procedures, training and development opportunities, benefits packages, leave policies, and performance, salary and promotional evaluations can all play a part in contributing to gender stereotypes," Hopkins said. "Organizational systems that rely on a limited framework for essential leadership behaviors will restrict their ability to recruit and develop outstanding leaders."
To help mitigate these inaccurate perceptions and biases of their leadership performance and potential, Hopkins suggests that women find both female and male allies and sponsors, create strategic networks, seek high-profile assignments to highlight their skills and abilities, and develop and communicate their individual definitions of career success.
The financial services organization at the focus of this study is one of the Top 100 U.S. Best Banks named by Forbes magazine. The sample of senior leaders included 26 women and 65 men, representative of the gender composition of the senior leadership team.
The researchers said a comparison of males and females in one organization ensured that any observed gender differences were not due to factors such as differences in industries or management hierarchies across organizations.
Researchers from UToledo, Bowling Green State University, Case Western Reserve University and San Diego Gas and Electric collaborated on the study.
INFORMATION:
Faba beans are an excellent source of food protein, but about 4% of the world's population are afflicted by favism, which renders them sensitive to the faba bean anti-nutrients vicine and convicine. Now, an international research team has identified the VC1 gene as responsible for the production of these compounds.
Faba beans have actually been a source of food protein since pre-historic times, but a fraction of the population, mostly from warm southern regions, cannot tolerate them. Pythagoras and his followers avoided them, and Roman priests of Jupiter ...
You have probably often said to yourself: "This time, I will only buy what I need!" But then you still ended up coming home with things that were not on your shopping list.
How can you prevent such impulse buying? A team from the Chair of Psychology II at Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany, looked at this question. The answer is not that simple, says psychologist Dr Anand Krishna. It depends on what type of person you are: a pleasure-seeker or a person who focuses on security.
Anand Krishna and his JMU colleagues Sophia Ried and Marie Meixner have published ...
The two major challenges in industrial enzymatic catalysis are the limited number of chemical reaction types that are catalyzed by enzymes and the instability of enzymes under harsh conditions in industrial catalysis. Expanding enzyme catalysis to a larger substrate scope and greater variety of chemical reactions and tuning the microenvironment surrounding enzyme molecules to achieve high enzyme performance are urgently needed.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Jun Ge from Tsinghua University, China reviewed their efforts using the de novo approach to synthesize hybrid enzyme catalysts that can address these two challenges and the structure-function relationship is discussed to reveal ...
A research team at the University of Córdoba has developed and evaluated models for the prediction of solar radiation in nine locations in southern Spain and North Carolina (USA).
Measuring solar radiation is costly, as are all the tasks related to the maintenance and calibration of the most commonly used sensors: pyranometers and radiometers. The result is a paucity of reliable data. Hence, a research group from the University of Córdoba has developed and evaluated several Machine Learning models to predict solar radiation in nine locations (southern Spain and North Carolina, USA) spanning a range of different geo-climatic conditions ...
Washington, DC, July 8, 2021 - A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP), published by Elsevier, reports that the type of one-on-one treatment plans delivered to toddlers, aged 12-30 months, diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) did not lead to any significantly different outcomes. Neither the type of evidence-based intervention provided, nor the number of hours of therapy were shown to have an impact.
The treatments, or intervention methods, delivered by specialized staff to the very young, during the study were either the Early ...
Of the Swedish men in their late teens who performed well in the physical fitness tests for military conscription, a relatively high proportion were able to avoid hospital care when they became infected with COVID-19 during the pandemic up to 50 years later. This has been shown by University of Gothenburg researchers in a register study, with results now published in the BMJ Open.
The study is based on the Swedish Conscription Register, which contains particulars of over 1.5 million young Swedish men who began their military service in the years 1969-2005. Almost all of these men then underwent both a bicycle test and a strength test. Some 2,500 of the men included in the Conscription Register were later, in spring 2020, hospitalized with COVID-19.
For their study, the scientists ...
A research study from the The Lundbeck Foundation Initiative for Integrative Psychiatric Research iPSYCH shows that people with ADHD, who also have another psychiatric diagnosis, are more likely to stop taking their ADHD medicine.
ADHD is one of the most common psychiatric disorders in childhood and is commonly treated with medication. ADHD medicine can be divided into two groups: medicine that has a stimulating effect - also known as stimulants - and non-stimulants, which are often used if a person does not respond well to the other form of medicine.
The medication can be an effective way of reducing symptoms, by ...
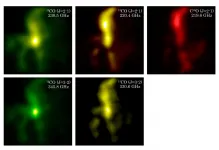
Researchers have used the latest wireless technology to develop a new radio receiver for astronomy. The receiver is capable of capturing radio waves at frequencies over a range several times wider than conventional ones, and can detect radio waves emitted by many types of molecules in space at once. This is expected to enable significant progresses in the study of the evolution of the Universe and the mechanisms of star and planet formation.
Interstellar molecular clouds of gas and dust provide the material for stars and planets. Each type of molecule emits radio waves at characteristic frequencies and astronomers have detected emissions from various molecules ...
(Boston)--As analytical instrumentation (gas- and liquid-chromatographs coupled with mass spectrometers) increase in sensitivity and speed, forensic scientists may find themselves still hindered by the process of preparing samples (blood, urine, etc.) for analysis and seeking more efficient approaches.
In an article in WIRES Forensic Science, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine's (BUSM) Biomedical Forensic Sciences program, provide an overview of sample preparation techniques and information on routine sample types that may be encountered in forensic toxicology cases.
Forensic toxicology encompasses a large variety of scenarios including drug-facilitated crimes, understanding ...
A new UBC Sauder School of Business study shows that depending on how employees understand their boss' motivation, employees can feel anger or guilt, and consequently, react differently to abusive supervision.
Former Apple CEO Steve Jobs was a famously harsh corporate leader, one who pushed his employees to extremes to achieve the company's lofty aims.
But while many aspiring leaders still believe that the "tough love" approach is effective, a new study from UBC Sauder shows that, even when abusive leadership is meant to push employees to new heights, it can land them in deep lows in the long term.
Abusive supervision -- which includes behaviours like yelling at employees, giving them the silent treatment, or putting them down in front of their ...