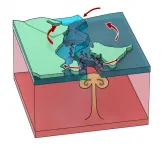
(Press-News.org) Coastal wetlands - such as salt marshes - provide even more flood protection than previously thought, reducing the risk to lives and homes in estuaries, a new study has revealed.
The researchers' simulations showed that wetlands that grow in estuaries, such as salt marshes, can reduce water levels by up to 2 metres and provide protection far inland up estuary channels.
This subsequently saved up to $38 (£27) million in avoided flood damage costs per estuary during a large storm thanks to the wetlands' role in preventing storm floods.
The research is timely as wetlands are facing growing threats from continued urban development. 22 of the largest 32 cities in the world - including London, New York and Tokyo - are built on low-lying land around estuaries, which puts them at increasing risk of flooding in a warming climate.
At the same time climate change is driving increases in the magnitude and frequency of storms, and sea level rise.
The flood prevention role of coastal wetlands, which are common throughout Wales - the focus of this study - as well as the rest of the world, is therefore vital.
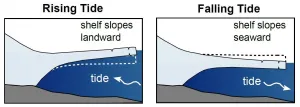
Previous research has focused on wetlands along open coastlines, where the plants absorb wave energy and stop waves pushing inland. However, the new study focuses on estuarine environments, including looking at what happens in upstream estuary areas where waves tend to be much smaller.
Taking this fuller picture into account, the researchers demonstrate that wetlands can have a much bigger storm flood prevention role because they not only absorb wave energy, but simultaneously reduce storm surges as they move up estuary channels.
This happens because the marshes along the estuary edges cause drag or friction, slowing down surges of water caused by storms, and protecting vulnerable upstream areas from flooding.
The research team included experts from Swansea University, with colleagues from the universities of Bangor and Exeter, Plymouth Marine Laboratory and from CSIRO in Tasmania.
The team used hydrodynamic models of eight estuaries of very different size and character in various parts of Wales. They simulated storms of different strengths and modelled the damage they would be likely to cause.
They found that coastal wetlands:
Reduced flooding across all eight estuaries in the study
Lowered storm water levels by as much as 2 metres in upstream areas
Made the biggest difference when faced with the most powerful storms - reducing average flood extents by 35% and damages caused by 37% ($8.4M).
Lead researcher Dr Tom Fairchild of Swansea University said:
'Our study shows that coastal wetlands play a crucial role in reducing storm-driven flooding in estuaries. They are nature's flood defences and we need them now more than ever.
Until now, the role of wetlands for coastal defence has been undervalued because of the focus on open coasts. Traditionally, estuaries -where waves tend to be much smaller - have been assumed to be less important, despite containing extensive wetland areas. Our research challenges that idea, showing that focussing on single processes, or even coastal environments, may risk grossly underestimating the true value of our wetlands'.
Dr John Griffin, co-author of the study and also from Swansea University, added:
'Our work shows that when big storms hit, nature works extra hard for us, preventing or reducing coastal flooding... for free. The upshot is, by protecting and restoring coastal wetlands, we help protect ourselves from the growing threat of flooding. It's a no-brainer.'
INFORMATION:
The research was published in Environmental Research Letters.
NOTES TO EDITORS
Swansea University is a world-class, research-led, dual campus university. The University was established in 1920 and was the first campus university in the UK. It currently offers around 350 undergraduate courses and 350 postgraduate courses to circa 20,000 undergraduate and postgraduate students.
The University's 46-acre Singleton Park Campus is located in beautiful parkland with views across Swansea Bay. The University's 65-acre science and innovation Bay Campus, which opened in September 2015, is located a few miles away on the eastern approach to the city. It has the distinction of having direct access to a beach and its own seafront promenade. Both campuses are close to the Gower Peninsula, the UK's first Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
Swansea was named 'Welsh University of the Year' in The Times and The Sunday Times Good University Guide 2017. The University is in the top 300 best universities in the world, ranked in the 251-300 group in The Times Higher Education World University rankings 2018.
The results of the Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2014 showed the University has achieved its ambition to be a top 30 research University, soaring up the league table to 26th in the UK, with the 'biggest leap among research-intensive institutions' (Times Higher Education, December 2014) in the UK.
The University has ambitious expansion plans as it moves towards its centenary in 2020, as it continues to extend its global reach and realising its domestic and international ambitions.
Swansea University is a registered charity. No.1138342. Visit http://www.swansea.ac.uk
Media contacts:
Kevin Sullivan, Swansea University Public Relations Office
k.g.sullivan@swansea.ac.uk
Populist anti-foreign aid rhetoric works - but only fans of populist politicians are convinced by hostile messages about charity abroad, a new study shows. Those who distrust populist politicians are significantly less susceptible to these messages.
The research shows international aid institutions and non-populist politicians should not be unduly worried about the impact of populism on global development cooperation.
Those wanting to convince the public about the importance of foreign aid should focus on communicating their message transparently and clearly, and using local partnerships.
The research, by A. Burcu Bayram from the University of Arkansas and Catarina Thomson from ...
Concerns have been raised about the AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson vaccines regarding very rare but potentially fatal side effects related to low blood platelet counts and blood clots. Recently, reports also emerged that the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine may cause a rare yet serious side effect: heart inflammation. Concerns about side effects may trigger vaccine hesitancy, which the WHO considers one of 'Ten threats to global health'. Securing sufficient acceptance of vaccines is a key challenge in defeating the coronavirus pandemic, both now and in the future.
How ...
What happens when climate change affects the abundance and distribution of fish? Fishers and fishing communities in the Northeast United States have adapted to those changes in three specific ways, according to new research published in Frontiers in Marine Science.
Becca Selden, Wellesley College assistant professor of biological sciences, and a team of colleagues examined how fishing communities have responded to documented shifts in the location of fluke and of red and silver hake. The team found that fishers made three distinct changes to their approaches: following the fish to a new location; fishing for a different kind of fish; and bringing their catch to shore at another port of landing.
Selden began this research as a postdoctoral ...
July 8, 2021 - Until relatively recently, opioids were a mainstay of treatment for pain following total hip or knee replacement. Today, a growing body of evidence supports the use of multimodal analgesia - combinations of different techniques and medications to optimize pain management while reducing the use and risks of opioids, according to a paper in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
"Multimodal analgesia has become the standard of care for total joint arthroplasty as it provides superior analgesia with fewer side effects than opioid-only protocols," write Javad Parvizi, ...
Augmented reality (AR) is poised to revolutionise the way people complete essential everyday tasks, yet older adults - who have much to gain from the technology - will be excluded from using it unless more thought goes into designing software that makes sense to them.
The danger of older adults falling through the gaps has been highlighted by research carried out by scientists at the UK's University of Bath and the Bath-based charity Designability. A Paper describing their work has received an honourable mention at this year's Human Computer Interaction Conference (CHI2021) - the world's largest conference of its kind.
The study concludes that adults aged 50+ are more likely to be successful at completing AR-prompted tasks (such as 'pick up the cube' followed by 'move the cube to the blue ...
Skoltech biologists and their colleagues from Koltzov Institute of Developmental Biology, Russia, and the Chemistry Department of Taras Shevchenko University in Ukraine have discovered fairly unlikely drug candidates for treating liver fibrosis and other pathologies -- among pest control chemicals. In addition, the team looked at modifications of the medication called hymecromone, deeming them promising for anti-fibrotic drugs, too. Published in Glycobiology, the study also sheds light on the possible mechanism of action of the investigated compounds, all of which inhibit the synthesis of hyaluronic acid.
Hyaluronic acid is an important biological compound that is a key component ...
The plates of the Earth's crust perform complicated movements that can be attributed to quite simple mechanisms. That is the short version of the explanation of a rift that began to tear the world apart over a length of several thousand kilometers 105 million years ago. The scientific explanation appears today in the journal Nature Geoscience.
According to the paper, a super volcano split the Earth's crust over a length of 7,500 kilometers, pushing the Indian Plate away from the African Plate. The cause was a "plume" in the Earth's mantle, i.e. a surge of hot material that wells upwards like an atomic mushroom cloud in super slow motion. It has long been known that the ...
WASHINGTON--Tidal stresses may be causing constant icequakes on Saturn's sixth largest moon Enceladus, a world of interest in the search for life beyond Earth, according to a new study. A better understanding of seismic activity could reveal what's under the moon's icy crust and provide clues to the habitability of its ocean.
Enceladus is about 500 kilometers in diameter and almost entirely covered in ice. The moon is nearly 10 times as far away from the Sun as Earth and its bright surface reflects most sunlight, making it very cold, yet researchers have long ...
Newborn infants and babies aged up to three months should be stimulated to manipulate objects and observe adults performing everyday tasks. This incentive helps their social, motor and cognitive development, researchers note in an article published in the May 2021 issue of the journal Infant Behavior & Development.
According to the authors, from the earliest age babies watch adults carrying out activities such as handling utensils and putting them away in drawers or closets. They should themselves have frequent contact with objects to develop the ability to hold things and reach out for them. Through social interaction, ...
Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure in the United States, but identifying type 1 or type 2 diabetes patients at high risk for progressive kidney disease has never had a sure science behind it.
Historically, assessing kidney function meant looking at estimated glomerular filtration rate, a calculation that determines how well blood is filtered by the kidneys, and urine albumin excretion, a urine test to detect the amount of the protein albumin, which is filtered by the kidneys. However, both tests have limited predictive power in early stage diabetes when kidney function is normal.
The therapeutic approach to both type 1 and type 2 diabetic ...