Reduced vs. standard CT dose for lung nodules in children, young adults with cancer
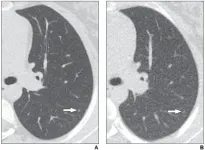
Reduced-dose CT depicts greater than 90% of lung nodules in children and young adults with cancer, identifying the presence of nodules with moderate sensitivity and high specificity
2021-07-09
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, July 9, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), reduced-dose CT depicts greater than 90% of lung nodules in children and young adults with cancer, identifying the presence of nodules with moderate sensitivity and high specificity.
"CT performed at 0.3 mSv mean effective dose has acceptable diagnostic performance for lung nodule detection in children and young adults and has the potential to reduce patient dose or expand CT utilization (e.g., to replace radiography in screening or monitoring protocols)," wrote corresponding author Andrew T. Trout of Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center in Ohio.
Trout and colleagues' prospective study enrolled patients 4-21 years old with known or suspected malignancy who were undergoing clinically indicated chest CT. Study participants underwent an additional investigational reduced-dose chest CT in the same imaging encounter. Three independent radiologists blind-reviewed the separated and deidentified CT examinations, with one radiologist performing a subsequent review to match nodules between the standard- and reduced-dose examinations.
Among the 78 patients (44 male, 34 female; mean age, 15.2 years) with cancer who underwent standard-dose chest CT and reduced-dose chest CT (mean effective dose 0.3 ± 0.1 mSv, representing 83% dose reduction) in the same imaging encounter, the reduced-dose protocol detected greater than 90% of lung nodules identified on the standard-dose examination.
Noting that no prior study has directly compared clinical to reduced-dose CT for detection of lung nodules in children, "reduced-dose CT may be a feasible option for detection of pulmonary metastatic disease in situations in which radiation dose is a primary consideration or as an option to reduce dose in patients undergoing serial chest CT to monitor known disease," the authors of this AJR article concluded.
INFORMATION:
Founded in 1900, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is the first and oldest radiological society in North America, dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of radiology and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in medical imaging since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with an annual scientific meeting, monthly publication of the peer-reviewed American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), quarterly issues of InPractice magazine, AJR Live Webinars and Podcasts, topical symposia, print and online educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-09
Every pandemic affects life and actions of people, which in turn controls the course of the pandemic. Until now the factors that determine our social, political and psychological sphere could not be described by mathematical models, making it difficult to venture forecasts for the Corona pandemic. The new study will improve the situation. Researcher Prof. Kai Wirtz of the Hereon Institution for Coastal Systems - Analysis and Modeling quantitatively describes the social phenomena hinted at above. "As a scientist, social modeling has been driving me for a while. It has also reached coastal research in the meantime. The greatest challenge in this development was the integration ...
2021-07-09
In spite of many clinical options, people with mental health problems including eating disorders often do not access professional help within the crucial first 12 months - in part because of lack of information in the community about accessing targeted services.
Anxiety and depression are normal reactions to situations such as pandemic lockdowns but arming yourself with some useful strategies can alleviate this, says Flinders University Distinguished Professor of Psychology Tracey
Wade.
For example, a randomised trial of 'unguided' low intensity cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) was found to decrease signs of anxiety and depression in the comparative study led by Curtin University and international experts, including Matthew Flinders Professor Wade.
The results of the study ...
2021-07-09
Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, convert sustenance into energy, fueling the cell's activities. In addition to power, mitochondria also produce reactive oxygen species, byproduct molecules primed to help facilitate communication among the other units in the cells. But when produced too abundantly, they damage DNA and render some cellular components dysfunctional. Now, an international research team has revealed how mitochondria keep their reactive oxygen species production in check.
They published their results on June 30 in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
"Excessive generation of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria damages ...
2021-07-09
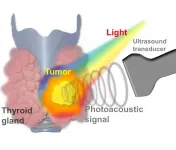
A lump in the thyroid gland is called a thyroid nodule, and 5-10% of all thyroid nodules are diagnosed as thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer has a good prognosis, a high survival rate, and a low recurrence rate, so early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. Recently, a joint research team in Korea has proposed a new non-invasive method to distinguish thyroid nodules from cancer by combining photoacoustic (PA) and ultrasound image technology with artificial intelligence.
The joint research team - composed of Professor Chulhong Kim and Dr. Byullee Park of POSTECH's Department of Electrical Engineering, Department of Convergence IT Engineering and Department of Mechanical ...
2021-07-09
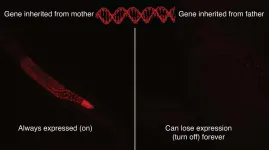
Evidence suggests that what happens in one generation--diet, toxin exposure, trauma, fear--can have lasting effects on future generations. Scientists believe these effects result from epigenetic changes that occur in response to the environment and turn genes on or off without altering the genome or DNA sequence.
But how these changes are passed down through generations has not been understood, in part, because scientists have not had a simple way to study the phenomenon. A new study by researchers at the University of Maryland provides a potential tool for unraveling the mystery of how experiences can cause inheritable changes to an animal's biology. By mating nematode worms, they produced permanent epigenetic changes that lasted for more than 300 generations. The research ...
2021-07-09
Eyewitnesses can identify perpetrators more accurately when they are able to manipulate 3D images of suspects, according to a new study.
A team of researchers in the University of Birmingham's School of Psychology developed and tested new interactive lineup software which enables witnesses to rotate and view lineup faces from different angles.
When the eyewitnesses were able to rotate the image to match the alignment of the face in their memory, they were more likely to accurately pick out the criminal from the lineup.
Lineups are used around the globe to help police identify criminals. Typically these involve ...
2021-07-09
Most countries have not introduced nationwide prostate-cancer screening, as current methods result in overdiagnoses and excessive and unnecessary biopsies. A new study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, which is published in The New England Journal of Medicine, indicates that screening by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and targeted biopsies could potentially cut overdiagnoses by half. The results are presented today at the European Association of Urology Congress.
"Our results from a large, randomised study show that modern methods for prostate cancer screening maintain the benefits of screening, while decreasing the harms substantially. This addresses the greatest barrier to the introduction of nationwide screening," ...
2021-07-09
Players of the popular game Red Dead Redemption 2 learn how to identify real American wildlife, new research shows.
The game, set in the American West in 1899, features simulations of about 200 real species of animals.
The new study, by the University of Exeter and Truro and Penwith College, challenged gamers to identify photographs of real animals.
On average, RDR2 players were able to identify 10 of 15 American animals in a multiple-choice quiz - three more than people who had not played the game.
The best performers were players who had completed the game's main storyline (meaning they had played for at least 40-50 hours) ...
2021-07-09
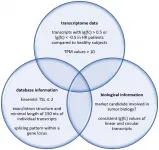
Oncotarget published "Transcriptome analyses of urine RNA reveal tumor markers for human bladder cancer: validated amplicons for RT-qPCR-based detection" which reported that in case of bladder cancer, urine RNA represents an early potentially useful diagnostic marker.
Here the authors describe a systematic deep transcriptome analysis of representative pools of urine RNA collected from healthy donors versus bladder cancer patients according to established SOPs.
This analysis revealed RNA marker candidates reflecting coding sequences, non-coding sequences, and circular RNAs.
Next, they designed and validated PCR amplicons for a set of novel marker candidates and tested them in human bladder cancer cell lines.
This ...
2021-07-09
INDIANAPOLIS - A new study from U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute, IUPUI and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai researchers reports that primary care physicians recognize the need for better coordination and welcome health information exchange (HIE) event notifications as a means of improving the flow of information to enable provision of better patient care.
Individuals often receive medical care from more than one healthcare system. Care coordination among providers, for example after discharge from an emergency department or hospital in one system, with the patient's primary care physician in another, is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Reduced vs. standard CT dose for lung nodules in children, young adults with cancer
Reduced-dose CT depicts greater than 90% of lung nodules in children and young adults with cancer, identifying the presence of nodules with moderate sensitivity and high specificity