Oncotarget: Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia
These Oncotarget findings demonstrate that Tomivosertib exhibits potent anti-leukemic properties on AML cells and support the development of clinical translational efforts involving the use of this drug
2021-07-12
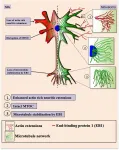
(Press-News.org) Oncotarget published "Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia" which reported that the authors evaluated the therapeutic potential of the highly-selective MNK1/2 inhibitor Tomivosertib on AML cells.
Tomivosertib was highly effective at blocking eIF4E phosphorylation on serine 209 in AML cells.
Moreover, combination of Tomivosertib and Venetoclax resulted in synergistic anti-leukemic responses in AML cell lines.
Mass spectrometry studies identified novel putative MNK1/2 interactors, while in parallel studies we demonstrated that MNK2 - RAPTOR - mTOR complexes are not disrupted by Tomivosertib.
Overall, these Oncotarget findings demonstrate that Tomivosertib exhibits potent anti-leukemic properties on AML cells and support the development of clinical translational efforts involving the use of this drug, alone or in combination with other therapies for the treatment of AML.
These Oncotarget findings demonstrate that Tomivosertib exhibits potent anti-leukemic properties on AML cells and support the development of clinical translational efforts involving the use of this drug
Dr. Leonidas C. Platanias from The Northwestern University as well as The Jesse Brown Veterans Affairs Medical Center said, "Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the second most common form of leukemia in adults, and has a very poor overall survival rate."
Therefore, there continues to be a need for new therapeutic modalities, including approaches targeting negative-feedback signaling pathways that may be activated in response to antileukemic treatments, leading to resistance.
The pro-neoplastic activity of eIF4E is associated with its phosphorylation/activation by MNK1/2 on serine 209 and correlates with enhanced mRNA translation, as well as nuclear export of mRNAs involved in tumorigenesis and cell cycle control.
Several studies have shown that pharmacological targeting of MNK1/2 results in inhibitory activity against AML cells in pre-clinical models.
As a result, the full therapeutic potential of MNK1/2 inhibition for the treatment of AML has not been fully assessed.
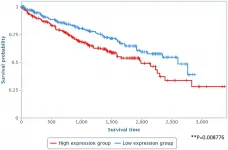
The authors demonstrate that Tomivosertib suppresses eIF4E phosphorylation in AML cells and decreases leukemic cell survival and proliferation.
The Platanias Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Output, "Viewed altogether, these studies indicate that MNK1/2 inhibition would most likely be a successful strategy in only a subset of AML patients. In future studies it will be crucial to ascertain what pathways are responsible for sensitivity to MNK inhibitors. These studies will help to identify potential regulatory programs through which MNK1/2 modulates cell signaling pathways critical for leukemic cell survival and may lead to the development of novel therapeutic interventions for AML."
INFORMATION:
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27952
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27952/text/
Correspondence to - Leonidas C. Platanias - l-platanias@northwestern.edu
Keywords -
MNK,
Tomivosertib,
acute myeloid leukemia,
eIF4E
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a bi-weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
18009220957x105
Copyright © 2021 Impact Journals, LLC
Impact Journals is a registered trademark of Impact Journals, LLC
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "Epigallocatechin-3-gallate modulates Tau Post-translational modifications and cytoskeletal network" which reported that the chemical modulators of Tau PTMs, such as kinase inhibitors and antibody-based therapeutics, have been developed, but natural compounds, as modulators of Tau PTMs are not much explored.
These authors applied biophysical and biochemical techniques like fluorescence kinetics, oligomerization analysis and transmission electron microscopy to investigate the impact of EGCG on Tau glycation in vitro.
EGCG inhibited methyl glyoxal -induced Tau glycation in vitro.
EGCG potently inhibited MG-induced advanced glycation endproducts formation in neuroblastoma cells as well modulated the localization ...
2021-07-12
Oncotarget published "A novel E2F1-regulated lncRNA, LAPAS1, is required for S phase progression and cell proliferation" which reported that long non-coding RNAs are major regulators of many cellular processes, including cell cycle progression and cell proliferation.
Inhibition of LAPAS1 expression increases the percentage of S phase cells, and its silencing in synchronized cells delays their progression through S phase.
In agreement with its suggested role in cell cycle progression, prolonged inhibition of LAPAS1 attenuates proliferation of human cancer cells.
Importantly, knockdown of SPNS2 rescues the effect of LAPAS1 silencing on cell cycle ...
2021-07-12
Imagine sitting out in the sun, reading a digital screen as thin as paper, but seeing the same image quality as if you were indoors. Thanks to research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, it could soon be a reality. A new type of reflective screen - sometimes described as 'electronic paper' - offers optimal colour display, while using ambient light to keep energy consumption to a minimum.
Traditional digital screens use a backlight to illuminate the text or images displayed upon them. This is fine indoors, but we've all experienced the difficulties of viewing such screens in bright sunshine. Reflective screens, however, attempt to use the ambient light, mimicking the way our eyes ...
2021-07-12
Researchers have identified a specialized protein that appears to help prevent tumor cells from entering the bloodstream and spreading to other parts of the body.
"We have discovered that this protein, TRPM7, senses the pressure of fluid flowing in the circulation and stops the cells from spreading through the vascular system," said Kaustav Bera, a Johns Hopkins University PhD candidate in chemical and biomolecular engineering and a lead author of the study, which was done with colleagues at the University of Alberta and Universitat Pompeu Fabra.
"We found that metastatic tumor cells have markedly reduced levels of this sensor protein, and that is why they ...
2021-07-12
Men over 60 with low-risk prostate cancer could spend ten years with no active treatment, have a better sex life as a result, yet still be very unlikely to die from the disease, new research has found.
The findings come from two new studies looking at 'active surveillance' of prostate cancer - when the disease is closely monitored but not treated - presented at the European Association of Urology congress, EAU21, today.
The first uses data from Sweden's National Prostate Cancer Register, which has information on virtually every man diagnosed with the disease in that country since 1998 - 23,649 of whom went on active surveillance. ...
2021-07-12
Care homes need to be vigilant for outbreaks of COVID-19, even after residents have received two doses of the vaccine, according to new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) held online this year.
Long-term care facilities, such as care homes with elderly residents with multiple underlying conditions, are at high risk of COVID-19 outbreaks and many vaccination campaigns have initially focused on care home residents and the staff looking after them. An outbreak in a French care home, however, raises questions about how effective the vaccine is in the elderly.
Martin Martinot, of ...
2021-07-12
COVID-19 outbreaks in French nursing homes almost certainly started in staff - and none of measures put in place stopped the virus from taking hold, new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), held online this year, shows.
Residents of long-term care facilities represent a small fraction of the general population but account for a disproportionate number of SARS-CoV-2-related deaths in many countries.
In France, 5,203 outbreaks (of 1 case or more) were reported in nursing homes during the first wave of COVID-19. In the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region, there were 651 outbreaks, 3,885 residents had confirmed COVID-19 infection and 1,772 ...
2021-07-12
The flu vaccine may provide vital protection against COVID-19, new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), held online this year, concludes.
An analysis of patient data from around the world strongly suggests that the annual flu shot reduces the risk of stroke, sepsis and DVT in patients with COVID-19. Patients with COVID-19 who had been vaccinated against flu were also less likely to visit the emergency department and be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU).
Immunising the world against COVID-19 is a daunting challenge and, although production and distribution of vaccines increases daily, some countries are not expected to vaccinate large numbers of their population ...
2021-07-12
A vaccine to protect against infection with hepatitis C could be in use within 5 years, says Professor Sir Michael Houghton, who won the Nobel Prize for Medicine and Physiology along with three other scientists for discovering the hepatitis C virus (HCV) in 1989. Sir Michael will discuss the development of a vaccine in a special presentation at this year's European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID), held online this year.
Up to 2 million new HCV infections occur every year around the world, with an estimated 70 million carriers of the virus globally, most of whom are not diagnosed. The virus is estimated to cause some 400,000 deaths annually. Many infected with the virus go on to develop liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
"While the advent of ...
2021-07-12
Water-jet nozzles in electric toilets--commonly used in Japan and other parts of Asia--may be reservoirs for multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP) in hospitals, increasing the risk of dangerous germ transmission among patients, according to new research being presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) held online this year.
"This is the first report of hospital transmissions associated with electric toilets and could have major implications for infection control," says Dr Itaru Nakamura from Tokyo Medical University Hospital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Oncotarget: Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia
These Oncotarget findings demonstrate that Tomivosertib exhibits potent anti-leukemic properties on AML cells and support the development of clinical translational efforts involving the use of this drug