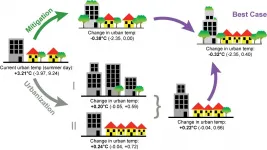
(Press-News.org) Low-income neighborhoods and communities with higher Black, Hispanic and Asian populations experience significantly more urban heat than wealthier and predominantly white neighborhoods within a vast majority of populous U.S. counties, according new research from the University of California San Diego's School of Global Policy and Strategy.
The analysis of remotely-sensed land surface temperature measurements of 1,056 U.S. counties, which have ten or more census districts, was recently published in the journal END
Poor and minority communities suffer more from extreme heat in US cities
Excess urban heat is common within cities, but not all communities burden the consequences equally, according to new UC San Diego research
2021-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
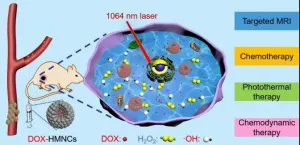
Scientists discover nanoclusters effective for cancer in the second near-infrared synergy therapy
2021-07-13
As a minimally invasive method for cancer therapy at precise locations, NIR-induced photothermal therapy (PTT) has drawn extensively attention. The therapeutic mechanism is the use of photothermal agents (PTAs) in the treatment of tumors,and its therapeutic effect happens only at the tumor site where both light-absorbent and localized laser radiation coexist.
The development of PTAs with NIR-II absorbance, ranging from 1000nm to 1700 nm, can efficiently improve their penetrating ability and therapeutic effects because of their high penetration depth in the body. Howerever, several disadvantages are associated with these NIR-II responsive PTAs for their ...
Lactose-free milk with graphene oxide based nano filtration membranes
2021-07-13
Over the past years, graphene oxide membranes have been mainly studied for water desalination and dye separation. However, membranes have a wide range of applications such as the food industry. A research group led by Aaron Morelos-Gomez of Shinshu University's Global Aqua Innovation Center investigated the application of graphene oxide membranes for milk which typically creates dense foulant layers on polymeric membranes.
Graphene oxide membranes have the advantage to create a porous foulant layer, therefore, their filtration performance can be maintained better than commercial polymeric membranes. The unique chemical and ...
Leading cardiovascular organizations issue joint opinion on improving clinician well-being worldwide
2021-07-13
Clinician well-being is imperative to providing high-quality patient care, yet clinician burnout continues to increase, especially over the last year due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Four leading cardiovascular organizations - the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, the European Society of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation - are calling for global action to improve clinician well-being in a joint opinion paper published today.
"Over the last several decades, there have been significant changes in health care with the expansion of technology, regulatory burden and clerical task loads. These developments have come at a cost to the ...
Study finds disparity in pay for female ophthalmologists in Ontario, Canada
2021-07-13
A new population-based study looking at nearly 30 years of billing data demonstrates that sex-based differences in Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP) payments exists for Canadian ophthalmologists.
A team led by researchers and clinicians from the Donald K. Johnson Eye Institute, part of the Krembil Research Institute at University Health Network (UHN), studied 22,389 Ontario physicians across three decades and found a significant payment gap between female and male ophthalmologists even after accounting for age, and some practice differences. This disparity was more pronounced among ophthalmologists when compared to other surgical, medical procedural and medical non-procedural specialty groups.
"This is real and robust ...
Teens knowing results of their cardiomyopathy genetic tests may improve family function
2021-07-13
DALLAS, July 13, 2021 -- Sharing the results of genetic testing for cardiomyopathy in adolescents ages 13-18 does not appear to cause emotional harm to families or adversely impact family function or dynamics, according to new research published today in Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine, an American Heart Association journal.
Genetic testing for cardiomyopathy in symptomatic children has the potential to confirm a diagnosis, clarify prognosis, determine eligibility for disease-specific cardiomyopathy therapies and even inform risk for other family members. Genetic testing for asymptomatic adults and children also occurs after one of their family members receives positive cardiomyopathy genetic ...
Researchers use prenatal editing in preclinical model to correct lysosomal storage disease
2021-07-13
Philadelphia, July 13, 2021--Adding to the growing body of literature demonstrating the feasibility of correcting lethal genetic diseases before birth, researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have used DNA base editing in a prenatal mouse model to correct a lysosomal storage disease known as Hurler syndrome. Using an adenine base editor delivered in an adeno-associated viral vector, the researchers corrected the single base mutation responsible for the condition, which begins before birth and affects multiple organs, with the potential to cause death in childhood if untreated.
The findings were published ...
More complex than we thought: The body's reaction to contact allergens
2021-07-13
Hair dye, perfume, jewellery. Beautifying to most, but for some they are equivalent to rashes, irritation and reduced quality of life. Together with hay fever and food allergies, allergic contact dermatitis due to exposure to e.g. nickel and perfume ingredients represents the majority of allergic reactions seen among Danes.
Traditionally, researchers have distinguished between immediate and delayed allergic reactions, depending on which parts of the immune system that is responsible for the reaction. E.g., hay fever and food allergies are 'immediate' forms that cause immediate symptoms, whereas it can take days before the skin reacts to things like nickel and perfume. But now a new study ...
Escort services and strip clubs don't increase sex crimes
2021-07-13
A new paper in The Economic Journal, published by by Oxford University Press, indicates that the presence of adult entertainment establishments may decrease sex crimes, significantly.
The role of entertainment establishments (strip clubs, escort services, adult bookstores, and adult movie theaters) in communities is controversial. Citizens often view them as centers of vice. While some have suggested that these clubs and services may improve behavior if people use them instead of committing sex crimes, such establishments may reinforce the view of women as objects, leading to more violence against them.
This paper exploits a unique data set of high frequency precinct level crime information from New York City, due to its controversial stop-and-frisk policing policy. The researchers ...
Resilience, not collapse: What the Easter Island myth gets wrong
2021-07-13
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- New research from Binghamton University, State University of New York suggests that the demographic collapse at the core of the Easter Island myth didn't really happen.
You probably know this story, or a version of it: On Easter Island, the people cut down every tree, perhaps to make fields for agriculture or to erect giant statues to honor their clans. This foolish decision led to a catastrophic collapse, with only a few thousand remaining to witness the first European boats landing on their remote shores in 1722.
But did the demographic collapse at the core of the Easter Island myth really happen? The answer, according to new research by Binghamton ...
A new approach to metastatic melanoma discovered
2021-07-13
Combining chemotherapy and BRAF oncogene inhibitors is a very effective strategy for fighting metastatic melanoma, the leading cause of death from skin cancer in the world. This has been demonstrated in a study by researchers from the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM), Hospital del Mar, and CIBER Cancer (CIBERONC), in collaboration with the Bellvitge Medical Research Institute (ICO-IDIBELL), which has just been published in the journal Oncogene.
The study, which involved the IMIM's Stem Cells and Cancer Research Group and doctors from the Dermatology and Pathology Departments at Hospital del Mar, analysed what effect ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
[Press-News.org] Poor and minority communities suffer more from extreme heat in US citiesExcess urban heat is common within cities, but not all communities burden the consequences equally, according to new UC San Diego research