(Press-News.org) A USC analysis of deaths among individuals in U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement custody found that ICE violated its own internal medical care standards in 78% of cases, potentially contributing to deaths in relatively young and healthy men.
The study appears in END
ICE violated internal medical standards, potentially contributing to deaths
Many deaths were preceded by delayed or inappropriate care
2021-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Language isolation affects health of Mexican Americans
2021-07-13
New research from the University of Georgia finds that older Mexican Americans who live in low English-speaking neighborhoods are at greater risk for poor health and even an early death.
Language barriers can be a significant deterrent to health. People who don't speak English well are less likely to seek health care or receive health information. This can lead to delay of care and missed health screenings for chronic disease and cancers. Language isolation is also linked to poor mental health.
These issues only compound as non-English speakers age, said study co-author Kerstin Emerson, a clinical ...
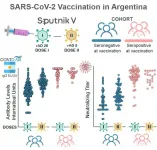
One shot of the Sputnik V vaccine triggers strong antibody responses
2021-07-13
A single dose of the Sputnik V vaccine may elicit significant antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2, finds a study published July 13 in the journal Cell Reports Medicine.
"Due to limited vaccine supply and uneven vaccine distribution in many regions of the world, health authorities urgently need data on the immune response to vaccines to optimize vaccination strategies," says senior author Andrea Gamarnik (@GamarnikLab) of the Fundación Instituto Leloir-CONICET in Buenos Aires, Argentina. "The peer-reviewed data we present provide information for guiding public health decisions in light of the current global health emergency."
Past research has shown that two doses of Sputnik V results in 92% efficacy against ...
This device harvests power from your sweaty fingertips while you sleep
2021-07-13
Feeling extra sweaty from a summer heat wave? Don't worry--not all your perspiration has to go to waste. In a paper publishing July 13 in the journal Joule, researchers have developed a new device that harvests energy from the sweat on--of all places--your fingertips. To date, the device is the most efficient on-body energy harvester ever invented, producing 300 millijoules (mJ) of energy per square centimeter without any mechanical energy input during a 10-hour sleep and an additional 30 mJ of energy with a single press of a finger. The authors say the device represents a significant ...
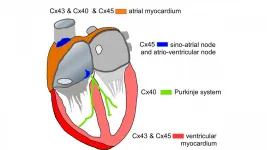
Electric signals between individual cardiac cells regulate heartbeat
2021-07-13
WASHINGTON, July 13, 2021 -- The rhythm in a working heart is regulated by electrical impulses. Disturbances of this bioelectrical process can result in cardiac arrhythmias, or irregularities in heartbeat -- a common ailment that can lead to illness and death.
In Biophysics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Harvard Medical School provide a state-of-the-art update on how electrical impulses in the heart travel from cell to cell.
A functioning heart contracts to pump blood to the body and the lungs. Within the heart, a pacemaker acts as an electrical clock, sending out a signal that tells the heart when to contract. The whole muscle moves together, because ...
Farm robots are the future; let's start preparing now, researcher argues
2021-07-13
No longer science fiction, farm robots are already here--and they have created two possible extremes for the future of agriculture and its impacts on the environment, argues agricultural economist Thomas Daum in a Science & Society article published July 13 in the journal Trends in Ecology & Evolution. One is a utopia, where fleets of small, intelligent robots farm in harmony with nature to produce diverse, organic crops. The other is a dystopia in which large, tractor-like robots subdue the landscape through heavy machinery and artificial chemicals.
He describes the utopian scenario as a mosaic ...
More Americans are receiving addiction treatment, but gaps persist
2021-07-13
PITTSBURGH, July 13, 2021 - Substantially more people in the U.S. with opioid use disorder are receiving evidence-based treatment for the disease, but there are still considerable gaps in care along racial lines, according to the largest analysis to date of opioid use disorder among Medicaid recipients.
The results, published today in JAMA, provide insights that policymakers and medical providers can act on to improve access to quality care for opioid use disorder, one of the leading causes of death in the U.S. The analysis was possible because of a unique network that partnered academic institutes with state Medicaid programs to overcome barriers to data sharing between states.
"Medicaid plays an incredibly important role in our ...
Calling all couch potatoes: This finger wrap can let you power electronics while you sleep
2021-07-13
A new wearable device turns the touch of a finger into a source of power for small electronics and sensors. Engineers at the University of California San Diego developed a thin, flexible strip that can be worn on a fingertip and generate small amounts of electricity when a person's finger sweats or presses on it.
What's special about this sweat-fueled device is that it generates power even while the wearer is asleep or sitting still. This is potentially a big deal for the field of wearables because researchers have now figured out how to harness the energy that can be extracted from human sweat even when a person is not moving.
This type of device is ...
Clinical characterization, prediction of severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection among US adults
2021-07-13
What The Study Did: Researchers used a large data resource of U.S. COVID-19 cases and control patients who tested negative from multiple health systems across the country to evaluate COVID-19 severity and risk factors over time and assess the use of machine learning to predict clinical severity.
Authors: Tellen D. Bennett, M.D., of the University of Colorado School of Medicine in Aurora, and Christopher G. Chute, M.D., of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, are corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.16901)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the ...
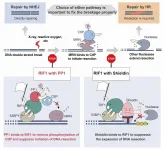
The path(way) less traveled in DNA double-strand break repair
2021-07-13
Osaka, Japan - BRCA1, a protein that is well-known for its role in hereditary breast cancer, is an important part of the cellular system that repairs double-strand DNA breaks. Now, researchers from Japan have discovered a new way in which cells protect these broken DNA ends to make sure that they are repaired correctly.
In a study published in Cell Reports, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) binds to double-strand breaks early on to promote repair by a process known as nonhomologous end joining instead of by homologous ...
CNIO researchers discover a new pathway to tackle follicular lymphoma
2021-07-13
For their own benefit and to grow beyond control, tumours manipulate cell signals to make it appear as if the cells have the nutrients they need. That is the case in follicular lymphoma, a type of tumour that affects the B lymphocytes of the immune system. One in six follicular lymphoma patients has mutations in RagC, a gene involved in the mTOR nutrient signalling pathway.
The team led by Alejo Efeyan, head of the Metabolism and Cell Signalling Group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), has discovered that genetic inhibition of the RagC protein blocks the activation of B lymphocytes and delays the onset of follicular lymphomas without side effects. The study, which was carried out in animal models, was published this ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] ICE violated internal medical standards, potentially contributing to deathsMany deaths were preceded by delayed or inappropriate care