Early anticoagulant treatment shown to reduce death in moderately ill COVID-19 patients
International RAPID Trial could contribute to clinical practice
2021-07-14
(Press-News.org) COVID-19 is marked by heightened inflammation and abnormal clotting in the blood vessels, particularly in the lungs, and is believed to contribute to progression to severe disease and death. New trial results show that administering a full dose of a standard blood thinner early to moderately ill hospitalized patients with COVID-19 could halt the thrombo-inflammation process and reduce the risk of severe disease and death.
The study, led by investigators at St. Michael's Hospital, a site of Unity Health Toronto, and the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, is available as a preprint on MedRxiv.
Heparin - a blood thinner given regularly at low dose to hospitalized patients - stops clots from forming and reduces inflammation. "This study was designed to detect a difference in the primary outcome that included ICU transfer, mechanical ventilation or death," says Mary Cushman, M.D., M.Sc., study co-principal investigator and a professor of medicine at the University of Vermont's Larner College of Medicine.
The open-label randomized international multi-center RAPID Trial (also known as the RAPID COVID COAG - RAPID Trial) examined the benefits of administering a therapeutic full dose of heparin versus a prophylactic low dose to moderately ill patients admitted to hospital wards with COVID-19.
The primary outcome was a composite of ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death up to 28 days. Safety outcomes included major bleeding. Primary outcome occurred in 37 of 228 patients (16.2%) with therapeutic full dose heparin, and 52 of 237 (21.9%) with low dose heparin (odds ratio [OR], 0.69; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.43-1.10; p=0.12). Four patients (1.8%) with therapeutic heparin died vs. 18 (7.6%) with prophylactic heparin (OR, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.07-0.65).
"While we found that therapeutic heparin didn't statistically significantly lower incidence of the primary composite of death, mechanical ventilation or ICU admission compared with low dose heparin, the odds of all-cause death were significantly reduced by 78 percent with therapeutic heparin," says first author and co-principal investigator Michelle Sholzberg, M.D.C.M., M.Sc., Head of Division of Hematology-Oncology, medical director of the Coagulation Laboratory at St. Michael's Hospital of Unity Health Toronto, and assistant professor at the University of Toronto.
Peter Jüni, M.D., co-principal investigator, director of the Applied Health Research Centre (AHRC)?at St. Michael's, and professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, says that the researchers also presented a meta-analysis of randomized evidence (including data from a large multiplatform trial of ATTACC, ACTIV-4a and REMAP-CAP), which clearly indicated that therapeutic heparin is beneficial in moderately ill hospitalized COVID-19 patients. He adds that an additional meta-analysis presented in the preprint showed that therapeutic heparin is beneficial in moderately ill hospitalized patients but not in severely ill ICU patients.
Another unique aspect of the RAPID Trial was its funding mechanism - a sort of grassroots effort in which support was gathered via Defence Research Development Canada, St. Michael's Hospital Foundation, St. Joseph's Healthcare Foundation, participating institutional grants, and even a GoFundMe campaign, among other sources.
"We called this trial 'The Little Engine that Could,' because of the sheer will of investigators around the world to conduct it," says Cushman.
Sholzberg says, "We believe that the findings of our trial and the multiplatform trial taken together should result in a change in clinical practice for moderately ill ward patients with COVID-19."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-14
A scientific team has shown that the release of neurotransmitters in the brain is impaired in patients with schizophrenia who have a rare, single-gene mutation known to predispose people to a range of neurodevelopmental disorders.
Significantly, the results from the research with human-derived neurons validated previous and new experiments that found the same major decrease in neurotransmitter release and synaptic signaling in genetically engineered human neurons with the same genetic variant - the deletion of neurexin 1 (NRXN1). NRXN1 is a protein-coding gene at the synapse, a cellular junction that ...
2021-07-14
WACO, Texas (July 13, 2021) - Climate change mitigation efforts have led to shifts from fossil-fuel dependence to large-scale renewable energy. However, renewable energy sources require significant land and could come at a cost to ecosystems. A new study led by Ryan McManamay, Ph.D., assistant professor of environmental science at Baylor University, evaluates potential conflicts between alternative energy strategies and biodiversity conservation.
The study, published in Biological Conservation, evaluates potential tradeoffs between climate benefits ...
2021-07-13
Cancer survivors ages 18 to 64 faced fewer financial barriers to health care after the Affordable Care Act was implemented than they did before the landmark law took effect, University of Michigan researchers found.
In fact, they believe the ACA helped the financial burden (problems related to the cost of medical care) for younger cancer survivors fall to its lowest estimated levels in 20 years.
"There has been a lot of talk about the ACA affecting people who don't have the Medicare safety net," said Christopher Su, M.D., a clinical fellow in the division of hematology and oncology at Michigan Medicine and the first author of the paper. "We were able to drill down to that and show that it did make a difference to younger cancer ...
2021-07-13
The COVID-19 pandemic and the situations of stress and sadness associated with it have not significantly increased the prevalence of depression and anxiety among participants in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brazil) who live in the city of São Paulo.
ELSA-Brazil has been monitoring the overall health of 15,000 civil servants at six public universities and research centers in Brazil since 2008. The survey on mental health during the pandemic was conducted in São Paulo and involved 2,117 members of the staff of the University of São Paulo (USP) - in active service or retired - who are participants in the nationwide study and aged 50-80.
The survey is supported by São Paulo Research Foundation ...
2021-07-13
In early March 2020, the University of Washington became the first four-year U.S. university to transition to online-only classes due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Many researchers predicted severe consequences of these physical distancing measures. To understand how this change affected college students' mental health, UW researchers surveyed 147 UW students over the 2020 spring quarter, which began shortly after the university transitioned to online-only classes. The team compared the students' responses to a previous survey of 253 students in spring quarter 2019.
The researchers didn't see much change in average levels of students' depressive symptoms, anxiety, stress or loneliness between 2019 and 2020 or between the beginning and the end of spring quarter ...
2021-07-13
Magnetars are bizarre objects -- massive, spinning neutron stars with magnetic fields among the most powerful known, capable of shooting off brief bursts of radio waves so bright they're visible across the universe.
A team of astrophysicists has now found another peculiarity of magnetars: They can emit bursts of low energy gamma rays in a pattern never before seen in any other astronomical object.
It's unclear why this should be, but magnetars themselves are poorly understood, with dozens of theories about how they produce radio and gamma ray bursts. The recognition of this unusual pattern of gamma ray activity ...
2021-07-13
Bacterial vaginosis is the most common and recurrent gynecological condition affecting nearly 30% of women between the ages of 15 and 44, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A University of Arizona Health Sciences-led study recently identified a specific bacteria family and uncovered how it contributes to bacterial vaginosis, paving the way for new insights into disease prevention and treatment.
Led by Melissa Herbst-Kralovetz, PhD, a member of the BIO5 Institute and associate professor of basic medical sciences at the College of Medicine - Phoenix, researchers found that members of the Veillonellaceae bacteria family contribute to an increase in inflammation and cell death, and alter the acidity of the cervical microenvironment. These changes support bacterial ...
2021-07-13
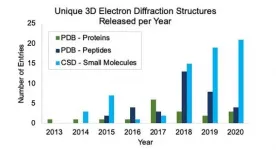
CAMBRIDGE July 13, 2021 - To date, solving structures of potential therapeutics using X-ray diffraction (XRD) has been an assumed, pivotal step in the drug development process. But a recent paper by a team of researchers led by NanoImaging Services shows how microcrystal electron diffraction (MicroED) is growing to obtain the structures of potential pharmaceuticals.
Three-dimensional crystal structures that show the relative positions of atoms, bonds and intramolecular interactions are needed to understand stability, reactivity, solubility and, ultimately, suitability ...
2021-07-13
New Rochelle, NY, July 13, 2021--Males with COVID-19 had significantly higher rates of hospitalization and of transfer to the intensive care unit (ICU) according to a new study. A higher percentage of males died of COVID-19 compared to females, as reported in the study published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women's Health. Click here to read the article now.
Joanne Michelle Gomez, MD, Rush University Medical Center, and coauthors, studied the first 8,108 positive COVID-19 patients that presented to the Rush University System from March 1-June 21, 2020. Nineteen percent of males required hospitalization, compared to 13% of females. ...
2021-07-13
In a new study of adults from the general population who were infected with COVID-19 in 2020, more than a quarter report not having fully recovered after six to eight months. Those findings are described this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Milo Puhan and colleagues at the University of Zurich, Switzerland.
While initial public health responses to the SARS-CoV-2 virus focused on reducing the acute burden of COVID-19, a growing body of evidence indicates that the infection can also result in longer-term physical and mental health consequences. These long-term consequences, currently referred to as "post-COVID-19 syndrome" or "Long Covid" are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Early anticoagulant treatment shown to reduce death in moderately ill COVID-19 patients
International RAPID Trial could contribute to clinical practice