'Greta Thunberg Effect' belies challenges for autistic community in going green
2021-07-14
(Press-News.org) Autistic people need extra help in going green say researchers behind a new study which argues for a more inclusive environmental agenda.
Climate action movements are gathering extraordinary pace due to international campaigners like Greta Thunberg, whose autism has been well documented. Being autistic has been used to explain and celebrate, but also diminish and denigrate, her activism.
Thunberg, for example, reports that being autistic is a psychological "gift" and "superpower" that underpins her environmental attitudes and behaviours. This has fuelled speculation - in the media and the general public - that autistic personality traits are intrinsically linked to environmentalism. But, until now, there was no investigation to test the autistic aspect of the so-called 'Greta Thunberg Effect'.
Now a new study from the universities of Bath, Cardiff, Essex, and King's College London, in the Journal of Environmental Psychology, suggests that autistic personality traits are unrelated to environmental attitudes. In contrast they can be linked to lower engagement in pro-environmental green behaviours.
Reflecting on their findings based on data from over 2,000 people in the UK and US, they discuss several reasons why people with autistic traits might face challenges going green. This includes sensory challenges that can act as a barrier to using noisy and crowded public transport, as well as issues over changing diet to reduce meat consumption.
The researchers conclude that autism spectrum conditions can present obstacles for pro-environmental action and are calling for greater support for people with autism and mental health conditions as well as more research on the topic.
Practical support might include adapting cognitive behavioural therapy, which is commonly used to facilitate behaviour change in people with mental health conditions, to support pro-environmental behaviours. They suggest it is also important to consider early environmental education for families and teachers supporting children with neurodevelopmental and metal health conditions.
Dr Punit Shah, Associate Professor of Psychology at the University of Bath and the GW4 Neurodevelopmental Neurodiversity Network, explained: "The 'Greta Thunberg Effect' has powerfully emerged in recent years, with many focussing on her autism diagnosis to explain her environmental activism.
"Intuitively, the speculation between autism and environmentalism has resonated with the public, including autistic adults who helped co-produce our new research. We also know from research that interests in animals, nature, and the environment, are widely reported by autistic individuals, which enhances their subjective wellbeing and life satisfaction.
"However, our findings show the link between autism and environmentalism is not clear cut. Given our results, we strongly recommend a move away from 'Thunberg-driven' autism-based narratives, whether positive or negative, of recent advances in climate policy.
Emily Taylor, lead author of the article said: "Our research is some of the first on how neurodevelopmental or mental health conditions may influence environmental attitudes and behaviour, and climate change beliefs. We focussed on autistic traits, but many other psychological differences and difficulties are likely to be associated with barriers to personal action on climate change. For instance, those with anxiety, or high levels of stress more generally, may be unable to move towards pro-environmental behaviours, for example using public transport, and have difficulty sustaining any changes they make.
"We need to think harder about supporting people to manage stress and mental health difficulties, which might then give them the cognitive resources to direct towards engaging in green behaviours. Mental health and environmental science are often thought about separately, but greater coherence - in terms of research and policy - will be crucial for both people's mental wellbeing and the environment."
Dr Shah added: "The United Nations recently called for a 'disability-inclusive' approach to climate action. Although there is some understanding of how 'physical' health impairments are linked to difficulties with engagement in environmental behaviours, there is little understanding of how 'mental' health problems or 'hidden disabilities' may have the same effect.
"Based on our findings, we speculate that the psychological and financial support required for autistic people and people with other mental health conditions to engage in pro-environmental activities is underestimated and must be a focus in the future - for a fairer, more inclusive environmental agenda."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-14
DALLAS, July 14, 2021 -- Heart failure hospitalizations and costs related to methamphetamine use jumped sharply over a decade in California, according to new research published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, an American Heart Association journal.
"Our study results should bring urgent attention to this insidious yet rapidly growing form of severe heart failure - methamphetamine-related heart failure, which is taking the lives of young people, straining health care resources and threatening to spread like wildfire in California, the West and to the rest of the nation," ...
2021-07-14
PHOENIX, Ariz. -- July 14, 2021 -- The results of a study by an international scientific team co-led by the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), an affiliate of City of Hope, suggest that -- like pouring water atop a wellhead before pumping -- the airway cells of patients with chronic lung diseases are "primed" for infection by the COVID-19 virus, resulting in more severe symptoms, poorer outcomes and a greater likelihood of death.
The study -- published today in Nature Communications -- details the genetic changes caused by chronic lung disease in the molecular makeup of a variety of cells, including the epithelial cells that line the lung and airways. The ...
2021-07-14
The extraordinary ability of animals to rapidly evolve in response to predators has been demonstrated via genetic sequencing of a waterflea population across nearly two decades.
In a new study, published in Nature Communications, scientists at the Universities of Birmingham in the UK, the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven in Belgium, and the Leibniz Institute for Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB), Berlin, were able to identify more than 300 genes that vary in the genome of the waterflea.
These genes, which account for about about 3 per cent of all sequenced waterflea genes, ...
2021-07-14
Cancer cell death is triggered within three days when X-rays are shone onto tumor tissue containing iodine-carrying nanoparticles. The iodine releases electrons that break the tumor's DNA, leading to cell death. The findings, by scientists at Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) and colleagues in Japan and the US, were published in the journal Scientific Reports.
"Exposing a metal to light leads to the release of electrons, a phenomenon called the photoelectric effect. An explanation of this phenomenon by Albert Einstein in 1905 heralded the birth of quantum physics," says iCeMS molecular biologist Fuyuhiko Tamanoi, who led the study. "Our research provides ...
2021-07-14
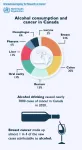
July 14, 2021 (Toronto) A new study from the World Health Organization's (WHO) International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), published in the journal Lancet Oncology, has found an association between alcohol and a substantially higher risk of several forms of cancer, including breast, colon, and oral cancers. Increased risk was evident even among light to moderate drinkers (up to two drinks a day), who represented 1 in 7 of all new cancers in 2020 and more than 100,000 cases worldwide.
In Canada, alcohol use was linked to 7,000 new cases of cancer in 2020, including 24 per cent of breast cancer cases, 20 per cent of colon cancers, 15 per cent of rectal cancers, and 13 per cent of oral and liver cancers.
"All ...
2021-07-14
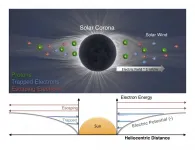
As the Parker Solar Probe ventures closer to the sun, we are learning new things about our home star.
In a new study, physicists led by the University of Iowa report the first definitive measurements of the sun's electric field, and how the electric field interacts with the solar wind, the fast-flowing current of charged particles that can affect activities on Earth, from satellites to telecommunications.
The physicists calculated the distribution of electrons within the sun's electric field, a feat made possible by the fact that the Parker Solar Probe jetted within 0.1 astronomical units (AU), or a mere 9 million miles, from the sun--closer than any spacecraft has approached. From the electrons' distribution, the physicists ...
2021-07-14
For the first time, scientists have seen stony coral cells engulf dinoflagellates - single-celled, photosynthetic algae that are crucial for keeping coral alive
The researchers used a cell line called IVB5, which contains endoderm-like cells cultured from the stony coral, Acropora tenuis
Around 40% of coral cells incorporated the algae in around 30 minutes and remained healthy for one month
The research is a step towards understanding the partnership between coral and dinoflagellates and could shed light on how coral bleaching occurs
In a world-first, scientists in Japan have observed individual stony coral cells engulfing single-celled, photosynthetic algae.
The microscopic algae, known as dinoflagellates, were ...
2021-07-14
A new paper in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that disruptions in health care due to the COVID 19 pandemic may increase breast cancer deaths.
In March 2020 public health measures prohibited most elective procedures, including mammography, due to hospital capacity and limited personal protective equipment. This reduced mammograms up to 80%. Breast cancer patients also experienced treatment delays and reductions in planned or expected chemotherapy treatments.
Researchers here used three independently-developed breast cancer simulation models from the National Cancer Institute's Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network to ...
2021-07-14
Washington/Philadelphia, July 14, 2021--New research finds that high school students who attended school remotely during the COVID-19 pandemic suffered socially, emotionally, and academically compared with those who attended in person.
The study was published today in Educational Researcher (ER) by researchers Angela L. Duckworth, Tim Kautz, Amy Defnet, Emma Satlof-Bedrick, Sean Talamas, Benjamin Lira, and Laurence Steinberg. ER is a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
"Many news stories have reported on individual stories of teenagers who have suffered from anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges during the pandemic," said lead author Duckworth, ...
2021-07-14
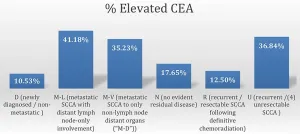
Oncotarget published "CEA as a blood-based biomarker in anal cancer" which reported that the mean Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) among subgroups by clinical status at the time of presentation to our institution was highest among those patients with metastatic Squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal (SCCA) to visceral organs, however this finding was not statistically significant by ANOVA .
By clinical subgroup, the percentage of patients with an abnormally elevated CEA was highest in those patients with metastatic disease to lymph nodes followed by recurrent/unresectable SCCA , and metastatic SCCA ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Greta Thunberg Effect' belies challenges for autistic community in going green