INFORMATION:
MCDB is available at http://www.combio-lezhang.online/MCDB/index_html/.
Article reference: Le Zhang, Lei Zhang, Yue Guo, Ming Xiao, Lu Feng, Chengcan Yang, Guan Wang, Liang Ouyang, MCDB: A comprehensive curated mitotic catastrophe database for retrieval, protein sequence alignment, and target prediction, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021, ISSN 2211-3835, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.032
Keywords: Mitotic catastrophe; Database; Protein sequence analysis; Target prediction; Data mining
The Journal of the Institute of Materia Medica, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association.
For more information please visit https://www.journals.elsevier.com/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/
Editorial Board: https://www.journals.elsevier.com/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/editorial-board
APSB is available on ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b).
Submissions to APSB may be made using Editorial Manager® (https://www.editorialmanager.com/apsb/default.aspx).
CiteScore: 12.5
Impact Factor: 11.413
ISSN 2211-3835
MCDB: A comprehensive curated mitotic catastrophe database
2021-07-14
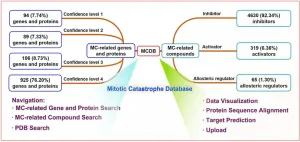
(Press-News.org) Mitotic Catastrophe Database (MCDB) is a proprietary, standard, and comprehensive database for Mitotic catastrophe (MC) related data facilitating the exploration of MC for all researchers in the fields of medicinal chemistry, molecular biology, bioinformatics and oncology.
MC is a form of programmed cell death induced by mitotic process disorders, which is important in tumor prevention, development, and drug resistance. As availability of MC data underpins tumor-related biomedical and clinical studies, the development of a professional and comprehensive database to curate MC-related data is a matter of increasing priority.
MCDB consists of 1214 genes/proteins and 5014 compounds collected and organized from more than 8000 research articles. MCDB defines the confidence level, classification criteria, and uniform naming rules for MC-related data, which greatly improves data reliability and retrievability. MCDB also develops protein sequence alignment and target prediction functions. The former can be used to predict new potential MC-related genes and proteins, and the latter can facilitate the identification of potential target proteins of unknown MC-related compounds.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UNF study indicates black teen girls seek inclusive body types in anti-obesity advertising
2021-07-14
Jacksonville, Fla. - A recent qualitative research study conducted by the University of North Florida, in partnership with Indianan University-Purdue Indianapolis and UF Health Jacksonville, shows that black teenage girls want inclusive body types to be featured in advertising to combat teen obesity rates. Insights provided in the study are ideal for pediatricians and healthcare educators developing advertising and patient care plans to combat obesity among African American teens.
The study investigated social and cultural consequences of food consumption among African American teenage girls between the ages of 14-18 in Jacksonville, Fla., and explored best practices ...
Scientists find way to navigate a heavy uphill climb
2021-07-14
A team of scientists has uncovered how heavy, motorized objects climb steep slopes--a newly discovered mechanism that also mimics how rock climbers navigate inclines.
The findings, which appear in the journal Soft Matter, stem from a series of experiments in which motorized objects were placed in liquid and then moved up tilted surfaces.
"These 'micro-swimmers' are about 20 times heavier than the fluid they swim in, but they were able to climb steep slopes that are almost vertical," explains Jun Zhang, one of the paper's authors and a professor of physics and mathematics at New York University's Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and NYU Shanghai.
The work enhances our understanding of "gravitaxis"--directional ...
When corals meet algae: First stages of symbiosis seen for the first time
2021-07-14
The physical interactions between coral and algal cells as they combine to form a symbiotic relationship have been observed for the first time. Within minutes of being introduced, coral cells had started to engulf the algae, where they were either digested or moved to a protective 'bubble' within the cell. This new study, published in Frontiers in Marine Science, will form the basis of further research to understand what drives their symbiosis at a cellular and molecular level, including the eviction of algae, which is the cause of coral bleaching.
"We watched coral cells develop pseudopodia ...
Medication or exercise? What works best for seniors with mild to moderate depression?
2021-07-14
Depression is the most frequently diagnosed psychiatric disorder among older adults, with 8% to 16% of older patients presenting with clinically significant depressive symptoms. Researchers in Spain conducted a randomized clinical trial of 347 older adults with mild to moderate depression, comparing the effectiveness of physical exercise and antidepressants as treatment methods. Study participants were assigned to either a group engaged in supervised physical exercise or a group that received antidepressant treatment by their general practitioners. Depressive symptoms were not significantly different after one month between the two groups. However, after three and six months, the number of people who showed improvement was significantly higher in the ...
Antidepressants may improve outcomes in people with diabetes and depression
2021-07-14
WASHINGTON--People with diabetes and depression who take antidepressants may have a lower risk of death and of serious diabetes complications, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
People with diabetes face a higher risk of depression, which makes them more likely to die or develop diabetes complications including heart and kidney disease, stroke, eye, and foot problems. Depression makes diabetes complications worse due to stress, body weight changes, and lack of exercise.
"People with depression and diabetes have poorer health outcomes than those with diabetes alone, and regular antidepressant treatment could lower their risk of complications," said study author Shi-Heng Wang, Ph.D., of the China Medical ...
Brain organoid study highlights potential role of genetic and environmental interaction in autism spectrum disorder
2021-07-14
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health have shown in a brain organoid study that exposure to a common pesticide synergizes with a frequent autism-linked gene mutation.
The results represent one of the clearest pieces of evidence yet that genetic and environmental factors may be able to combine to disturb neurodevelopment. Researchers suspect that genetic and environmental factors might contribute to the increased prevalence of autism spectrum disorder, a developmental disorder characterized by cognitive function, social, and communication impairments.
The study's use of brain organoids also points the way towards quicker, less expensive, and more human-relevant ...
How climate change and fires are shaping the forests of the future
2021-07-14
Forest fires are already a global threat. "But considering how climate change is progressing, we are probably only at the beginning of a future that will see more and bigger forest fires," explains Rupert Seidl, Professor of Ecosystem Dynamics and Forest Management in Mountain Landscapes at TUM.
In many places, fire is part of the natural environment, and many tree species have become naturally adapted to recurrent fires. These adaptations range from particularly thick bark, which protects the sensitive cambium in the trunk from the fire, to the cones of certain types of pine, which open only due to the heat of fire, allowing a quick regeneration and recovery of affected woodland .
AI is accelerating ecosystem models
"The interaction ...
Putting a strain on semiconductors for next-gen chips
2021-07-14
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from the U.S. and Singapore have created a neural network that can help tweak semiconductor crystals in a controlled fashion to achieve superior properties for electronics. This enables a new direction of development of next-generation chips and solar cells by exploiting a controllable deformation that may change the properties of a material on the fly. The paper was published in the journal npj Computational Materials.
Materials at the nanoscale can withstand major deformation. In what's called the strained state, they can exhibit remarkable optical, thermal, electronic, and other properties due to a change in interatomic distances. The intrinsic properties of a strained ...
Primary care provides clinical guidance, answers about COVID-19 testing, vaccine
2021-07-14
Researchers examined the role of primary care physicians and other clinicians in delivering vaccinations in the United States. They used two main datasets to create an in-depth analysis of services delivered to Medicare patients, followed by analysis of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality's 2017 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) to determine where patients are getting vaccinated and by whom. In the 2017 Medicare Part B Fee-For-Service, primary care physicians provided the largest share of services for vaccinations (46%), followed by mass immunizers (45%), then nurse practitioners/physician assistants (5%). The MEPS showed that primary care physicians provided a majority of clinical visits ...
July/August 2021 Annals of Family Medicine tip sheet
2021-07-14
Primary Care Poised to Provide Clinical Guidance, Answers About COVID-19 Testing, Vaccine Administration
Researchers examined the role of primary care physicians and other clinicians in delivering vaccinations in the United States. They used two main datasets to create an in-depth analysis of services delivered to Medicare patients, followed by analysis of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality's 2017 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) to determine where patients are getting vaccinated and by whom. In the 2017 Medicare Part B Fee-For-Service, primary care physicians provided the largest share of services for vaccinations (46%), followed by mass immunizers (45%), then nurse practitioners/physician ...