(Press-News.org) Ultra-processed food linked to higher risk of IBD
Further studies needed to identify contributory factors in processed foods that might account for these associations
A higher intake of ultra-processed food is associated with higher risk of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), finds a study published by The BMJ today.
Ultra-processed foods include packaged baked goods and snacks, fizzy drinks, sugary cereals, ready meals containing food additives, and reconstituted meat and fish products - often containing high levels of added sugar, fat and salt, but lacking in vitamins and fibre.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is more common in industrialised nations and it is thought that dietary factors might play a role, but data linking ultra-processed food intake with IBD are limited.
To explore this further, an international team of researchers drew on detailed dietary information from 116,087 adults aged 35-70 years living in 21 low, middle, and high income countries who were taking part in the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study.
PURE is examining the impact of societal influences on chronic diseases in different countries around the world.
Participants were enrolled in the study between 2003 and 2016 and were assessed at least every three years. Over an average follow-up of 9.7 years, new diagnoses of IBD, including Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, were recorded.
During this time, 467 participants developed IBD (90 with Crohn's disease and 377 with ulcerative colitis).
After taking account of other potentially influential factors, the researchers found that higher intake of ultra-processed food was associated with a higher risk of IBD.
For example, compared with less than one serving of ultra-processed food per day, they found an 82% increased risk of IBD among those who consumed five or more servings per day, and a 67% increased risk for 1-4 servings per day.
Different subgroups of ultra-processed food, including soft drinks, refined sweetened foods, salty snacks, and processed meat, each were associated with higher risks of IBD.
In contrast, intakes of white meat, red meat, dairy, starch, and fruit, vegetables, and legumes (such as peas, beans and lentils) were not associated with IBD.
Results were consistent for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, and were similar after further analysis to test the risk of developing IBD based on age and region, suggesting that the findings are robust.
This is an observational study so can't establish causality. What's more, results relied on self-reported diagnoses and did not account for dietary changes over time. And the researchers cannot rule out the possibility that other unmeasured (confounding) factors may have affected their results.
Nevertheless, they say their findings "support the hypothesis that intake of ultra-processed foods could be an environmental factor that increases the risk of IBD."
As white meat, unprocessed red meat, dairy, starch, and fruit, vegetables, and legumes were not found to be associated with development of IBD, this study suggests that it might not be the food itself that confers this risk but rather the way the food is processed or ultra-processed, they explain.
"Further studies are needed to identify specific potential contributory factors among processed foods that might be responsible for the observed associations in our study," they conclude.
INFORMATION:
Externally peer reviewed? Yes
Evidence type: Observational
Subjects: People
Highlights
The physician-scientist workforce doing kidney research in the United States is increasingly made up of women and international medical graduates.
However, this workforce is older, declining in relative number, and is less overwhelmingly focused on basic rather than clinical science.
Washington, DC (July 14, 2021) -- U.S. physician-scientists make enormous contributions to biomedical research. New research published in CJASN demonstrates increasing representation of women and international graduates within the physician-scientist workforce doing kidney research; however, this workforce is declining in relative number, is getting older, and is less overwhelmingly focused ...
Researchers at UC San Francisco have successfully developed a "speech neuroprosthesis" that has enabled a man with severe paralysis to communicate in sentences, translating signals from his brain to the vocal tract directly into words that appear as text on a screen.
The achievement, which was developed in collaboration with the first participant of a clinical research trial, builds on more than a decade of effort by UCSF neurosurgeon Edward Chang, MD, to develop a technology that allows people with paralysis to communicate even if they are unable to speak on their own. The study appears July 15 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"To our knowledge, this is the first successful demonstration of direct decoding of full words from the brain activity of someone who is ...
MINNEAPOLIS - Keeping your brain active in old age has always been a smart idea, but a new study suggests that reading, writing letters and playing card games or puzzles in later life may delay the onset of Alzheimer's dementia by up to five years. The research is published in the July 14, 2021, online issue of Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"The good news is that it's never too late to start doing the kinds of inexpensive, accessible activities we looked at in our study," said study author Robert S. Wilson, PhD, of Rush University Medical Center in Chicago. "Our findings suggest it may be beneficial to start doing these ...
Glenview, Illinois - The American College of Chest Physicians® (CHEST) recently released a new clinical guideline, Screening for Lung Cancer: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. The guideline contains 16 evidence-based recommendations and an update of the evidence base for the benefits, harms, and implementation of low-dose chest computed tomography (CT) screening.
Lung cancer is by far the leading cause of cancer death among both men and women, making up almost 25% of all cancer deaths. Evidence suggests that low-dose CT screening for lung cancer can reduce cancer-related deaths in the group that is screened. The new guidelines ...
Professors in Syracuse University's College of Arts and Sciences explored whether or not the scientific community will ever be able to settle on a 'total number' of species of living vertebrates, which could help with species preservation. By knowing what's out there, researchers argue that they can prioritize places and groups on which to concentrate conservation efforts.
Research professor Bruce Wilkinson and professor Linda Ivany, both from the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, recently co-authored a paper in the Biological Journal of the Linnean Society where they determined that forecasting the total number of species may never be possible.
When asking the question, 'how many species?,' it is important to note that only a fraction of ...
PITTSBURGH, July 14, 2021 - More doesn't necessarily mean better--including in cancer treatment.
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and University of Wisconsin-Madison scientists report today in Science Translational Medicine that combining targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy with immunotherapy significantly boosts eradication of metastatic cancer in mice, even when the radiation is given in doses too low to destroy the cancer outright.
"We're excited--with such low doses of radiation, we didn't expect the response to be so positive," said lead author Ravi Patel, M.D., assistant professor at Pitt and radiation oncologist at UPMC Hillman Cancer Center. "In clinical trials, we tend to go with the maximum tolerable dose, ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Facebook posts by members of the U.S. Congress reveal the depth of the partisan divide over the COVID-19 pandemic, new research shows.
A study of all 12,031 Facebook posts concerning the pandemic by members of Congress between March and October 2020 showed that Democrats generally took a more negative or neutral tone on the issue, while Republicans were more likely to have a positive tone in their posts.
Public crises, like the pandemic, highlight how central social media is to messaging and how important it is to understand how rhetoric impacts engagement and sharing of messages said Laura Moses, co-author of the study and a doctoral student in political science at The Ohio State University.
"When ...
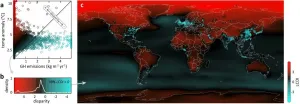
New research, led by the Monterey Bay Aquarium, illustrates the disparity between the narrow origins and far-reaching impacts of greenhouse emissions responsible for disrupting the global climate system. Published in Science Advances today, the study was built upon the most comprehensive accounting of global emissions from the burning of fossil fuels. It reveals that the regions generating the most emissions are different from those expected to suffer the most severe warming. The result of this comparison shows the fundamental disparities - quite literally putting them on the map - associated with where, and who, will experience the greatest impacts of climate change.
"One of the dirty tricks of climate change is that local pollution has far-reaching consequences," ...
An analysis of the tone used in pandemic-related social media posts from U.S. Congress members over an 8-month period in 2020 finds clear partisan differences, with Democrats using a slightly negative tone compared with Republicans, who appeared to use more strongly positive language in their COVID-19 messaging. Democrats were also far more likely than Republicans to use neutral language. The study also indicates that tone plays a critical role in elite communications, finding that the public engages more with content that has a negative tone. The study authors note that messaging from political elites during a crisis such ...
A new study on the effects of Airbnb listings on Boston neighborhoods suggests that the prevalence of listings may hamper local social dynamics that prevent crime. However, tourists themselves do not appear to generate or attract higher levels of crime. Babak Heydari, Daniel T. O'Brien, and Laiyang Ke of Northeastern University in Boston, MA, USA present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 14, 2021.
Widespread sentiment holds that Airbnb listings cause increased crime in residential neighborhoods. However, there has been limited research to explore and clarify this link.
To better understand the relationship ...