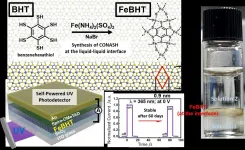
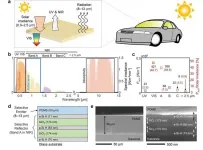
(Press-News.org) Converting light to electricity effectively has been one of the persistent goals of scientists in the field of optoelectronics. While improving the conversion efficiency is a challenge, several other requirements also need to be met. For instance, the material must conduct electricity well, have a short response time to changes in input (light intensity), and, most importantly, be stable under long-term exposure.
Lately, scientists have been fascinated with "coordination nanosheets" (CONASHs), that are organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials in which organic molecules are bonded to metal atoms in a 2D network. The interest in CONASHs stems mainly from their ability to absorb light at multiple wavelength ranges and convert them into electrons with greater efficiency than other types of nanosheets. This feat was observed in a CONASH comprising a zinc atom bonded with a porphyrin-dipyrrin molecule. Unfortunately, the CONASH quickly became corroded due to the low stability of organic molecules in liquid electrolytes (a medium commonly used for current conduction).
"The durability issue needs to be solved to realize the practical applications of CONASH-based photoelectric conversion systems," says Prof. Hiroshi Nishihara from Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, who conducts research on CONASH and has been trying to solve the CONASH stability problem.
Now, in a recent END
Unlocking efficient light-energy conversion with stable coordination nanosheets
Scientists design a high-performance, self-powered, UV photodetector using 2D nanosheets that show record photocurrent stability under air exposure
2021-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Life-saving snake venom
2021-07-15
Indiana Jones hates snakes. And he's certainly not alone. The fear of snakes is so common it even has its own name: ophidiophobia.
Kibret Mequanint doesn't particularly like the slithery reptiles either (he actually hates them too) but the Western University bioengineer and his international collaborators have found a novel use for snake venom: a body tissue 'super glue' that can stop life-threatening bleeding in seconds.
Over the past 20 years, Mequanint has developed a number of biomaterials-based medical devices and therapeutic technologies - some of which are either licensed to medical companies or are in the advanced stage of preclinical testing.
His latest collaborative research discovery ...
Engineers find imaging technique could become treatment for deep vein thrombosis
2021-07-15
Penn State College of Engineering researchers set out to develop technology capable of localizing and imaging blood clots in deep veins. Turns out their work may not only identify blood clots, but it may also be able to treat them.
The team, led by Scott Medina, assistant professor of biomedical engineering, published its results in Advance Healthcare Materials.
"Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of blood clots in deep veins, typically in a person's legs," said Medina. "It's a life-threatening blood clotting condition that, if left unaddressed, can cause deadly pulmonary embolisms -- when the clot travels to the lungs and blocks an artery. To manage DVT, and prevent these life-threating complications, it's critical to be able to rapidly detect, monitor and treat it."
The ...
New research at ESMT Berlin shows potential variance in academic research
2021-07-15
The research seeks to understand what drives decisions in data analyses and the process through which academics test a hypothesis by comparing the analyses of different researchers who tested the same hypotheses on the same dataset. Analysts reported radically different analyses and dispersed empirical outcomes, including, in some cases, significant effects in opposite directions from each other. Decisions about variable operationalizations explained the lack of consistency in results beyond statistical choices (i.e., which analysis or covariates to use).
"Our findings illustrate the importance of analytical choices and how different statistical methods can lead to different conclusions," says Martin Schweinsberg. ...
New guidance on how to diagnosis and manage osteoporosis in chronic kidney disease
2021-07-15
Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) typically suffer from impaired bone quality and quantity, with a non-vertebral fracture risk which is 4-to 6-fold higher than the fracture risk of matched controls. However, despite their high risk of fragility fractures, the vast majority of patients with chronic CKD stages 4 to 5D, are not receiving osteoporosis therapy.
A newly published review by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) CKD-MBD working group now provides concise recommendations, with a clear management algorithm, to support clinicians' knowledge and confidence in managing ...
Antihypertension drug may help patients with noncancerous brain tumors affecting hearing
2021-07-15
BOSTON - New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Massachusetts Eye and Ear indicates that the blood pressure drug losartan may benefit patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), a hereditary condition associated with vestibular schwannomas, or noncancerous tumors along the nerves in the brain that are involved with hearing and balance. The findings, which are published in Science Translational Medicine, are especially important because vestibular schwannomas are currently treated with surgery and radiation therapy (which carry risks of nerve damage), and no drug is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat these tumors or their associated hearing ...
Autophagy may be the key to finding treatments for early Huntington's disease
2021-07-15
Amsterdam, July 15, 2021 - Huntington's Disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition characterized by motor, cognitive, and psychiatric symptoms, and motor symptoms are often preceded by cognitive changes. Recent evidence indicates that autophagy plays a central role in synaptic maintenance, and the disruption in autophagy may be at the root of these early cognitive changes. Understanding this mechanism better may help researchers develop treatments for patients with HD early in their disease progression, report scientists in a review article published in the Journal of Huntington's Disease.
In this review, experts describe how autophagy, the cellular process responsible ...
What does the sleeping brain think about?
2021-07-15
We sleep on average one third of our time. But what does the brain do during these long hours? Using an artificial intelligence approach capable of decoding brain activity during sleep, scientists at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, were able to glimpse what we think about when we are asleep. By combining functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG), the Geneva team provides unprecedented evidence that the work of sorting out the thousands of pieces of information processed during the day takes place during ...
Wolf pups born on Isle Royale, moose poised for decline
2021-07-15
The COVID-19 pandemic halted the in-person wintertime survey of wolves and moose on the island for the first time in 63 years. Consequently, there are no estimates of wolf or moose abundance for 2021, and the next estimates are scheduled in February 2022. But though the Isle Royale Winter Study didn't happen quite as planned, researchers were still able to visit the remote national park in the spring.
Now, fieldwork has resumed and Michigan Technological University researchers have already uncovered new information about these two iconic wildlife populations. In particular, wolves produced at least two litters of pups, and moose appear poised for decline.
In the Isle Royale Winter Study, Michigan ...
A genome of photosynthetic animals decoded
2021-07-15
Plants, algae and some bacteria are able to perform photosynthesis, which is the process of transforming sunlight energy into sugar. Animals are generally unable to use this process to acquire energy, but there are a few known exceptions to this. Some sea slugs take up chloroplasts from the algae that they consume into their cells. These chloroplasts retain their ability to perform photosynthetic activity within the animal cells for several months, and thus provide them with photosynthesis-derived nutrition. This process is called "kleptoplasty", and it has attracted much attention due to its amazing uniqueness in making animals photosynthetic for over 50 years.
A pressing question is how these sequestered chloroplasts retains their photosynthetic capability without algal nuclei. ...
Visibly transparent radiative cooler under direct sunlight
2021-07-15
Since the Paris Climate Agreement that took effect in 2016, 121 countries have pledged to become carbon neutral by 2050 as the world tries to reduce its fuel consumption. The Korean government also unveiled its 2050 Carbon Neutral Strategy on December 7, 2020 and declared Carbon Zero, making transition to new and renewable energy a topic of conversation. Recently, a joint research team from POSTECH and Korea University has developed a radiative cooling material that can reduce energy consumption by selectively reflecting or transmitting sunlight.
A research team led by Professor Junsuk Rho, Ph.D. candidate Minkyung Kim, and Dr. Dasol Lee of POSTECH's departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering, and a team led by Professor Heon Lee and Soomin of the Department of Materials ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Unlocking efficient light-energy conversion with stable coordination nanosheetsScientists design a high-performance, self-powered, UV photodetector using 2D nanosheets that show record photocurrent stability under air exposure