Cellular uptake of nanoparticles keys for further development of temperature sensing
A paper by Kazan Federal University was published in Journal of Nanoparticle Research
2021-07-16
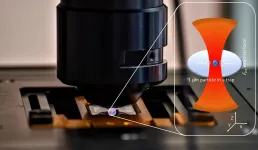
(Press-News.org) The article represents the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and flow cytometry study of A-549 (human lung carcinoma) cellular uptake of Pr3+:LaF3 nanoparticles. The Pr3+:LaF3 nanoparticles are promising platforms for cell nano-sensors.
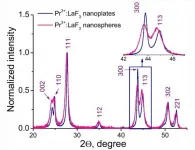
The objective of the work was to study the influence of nanoparticle morphology (nanoplates and nanospheres) on cytotoxicity and the dynamic of cellular uptake.
In the flow cytometry method, the cells go through a small tube (as a flow) and are irradiated by a laser. Cells scatter the laser light, and this scattering efficiency can give new information about some processes inside the cell. TEM method allows visualizing the cells with 0.2 nm (10-9 m) spatial resolution.
Both nanoplates and nanospheres are easily internalized by A-549 cells via macropinocytosis after 2, 10, and 24 hours of nanoparticle exposure. The nanoparticles were not observed in cell nuclei and other organelles. During macropinocytosis, relatively large vesicles (0.2-5 μm) are formed. The flow cytometry experiments revealed that the internalized nanoparticles increase the cells' optical inhomogeneity, which leads to an increase of side scattered light intensity by ~10% without any dynamic during 24 hours (for both morphotypes of nanoparticles). Probably, it can be explained by the fact that macropinocytosis is a dynamic process and some macropinosomes appear and move in the cytoplasm; in turn, other macropinosomes travel back to the cell surface of the membrane and release the content to the extracellular space; consequently, the equilibrium is achieved.
Finally, nanoplates and nanospheres have low tocixity and are easily internalized by cells. These facts pave the way toward creating nano-sensors for cells.
The luminescence of Pr3+:LaF3 nanoparticles (spectral shape) depends on the temperature in the physiological temperature range (20 to 60ºC). This fact, as well as nanosized dimensionality of Pr3+:LaF3 pave the way toward temperature sensing at cell level with spatial resolution less than one micrometer. Such temperature sensors are important in fundamental biology and pharmaceuticals. These sensors allow studying thermodynamic cell responses on external factors (drugs and physical conditions). This information is very important for pre-clinical studies of drugs.
For further development of the research, the authors plan to provide the targeted orientation of the nanoparticles to a specific cell organelle. This property can be achieved by creating a special bio-compatible shell around the Pr3+:LaF3 nanoparticle. This shell should contain special organic molecules which provide attachment to the specific cell organelle. There is also a plan to obtain a temperature map of the whole cell in the microscope.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-16
Measurements of biomechanical properties inside living cells require minimally invasive methods. Optical tweezers are particularly attractive as a tool. It uses the momentum of light to trap and manipulate micro- or nanoscale particles. A team of researchers led by Prof. Dr. Cornelia Denz from the University of Münster (Germany) has now developed a simplified method to perform the necessary calibration of the optical tweezers in the system under investigation. Scientists from the University of Pavia in Italy were also involved. The results of the study have been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The calibration ensures that measurements of different samples and with different devices are comparable. ...
2021-07-16
The ability to predict and interpret modifications of ribonucleic acid (RNA) has been a welcome advance in biochemistry research.
However, existing predictive approaches have a key drawback--they can only predict a single type of RNA modification without supporting multiple types or providing insightful interpretation of their prediction results.
Researchers from Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University, led by Dr Jia Meng, have addressed this issue by developing a model that supports 12 RNA modification types, greatly expanding RNA research prediction and interpretation.
"To the best of our knowledge, ...
2021-07-16
While tropical forests remain threatened and their future is uncertain, the importance of understanding how well individual protected areas avoid deforestation increases. Researchers from the University of Turku and University of Helsinki, Finland, have investigated this question in a newly published study that focuses on the State of Acre in Brazilian Amazonia.
Tropical forests are unique environments that have huge species diversity and also act as important reservoirs of organic carbon, thereby counteracting climate change. However, their area is diminishing due to deforestation, ...
2021-07-16
Tsukuba, Japan - A team of scientists led by Associate Professor Haruka Ozaki of the Center for Artificial Intelligence Research at the University of Tsukuba in collaboration with Dr. Koichi Takahashi from RIKEN used mathematical algorithms to optimize the schedule of automated biology laboratory robots. By analyzing the needs of time-sensitive samples that require investigation using multiple instruments, the researchers were able to maximize the number of experiments that can be performed within time and laboratory resource constraints. This work may help in the design of future automated biology labs and other workspaces.
Biology laboratories have seen increasing automation because many tasks, like pipetting solutions or moving cells from one ...
2021-07-16
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Most of the tests that doctors use to diagnose cancer -- such as mammography, colonoscopy, and CT scans -- are based on imaging. More recently, researchers have also developed molecular diagnostics that can detect specific cancer-associated molecules that circulate in bodily fluids like blood or urine.
MIT engineers have now created a new diagnostic nanoparticle that combines both of these features: It can reveal the presence of cancerous proteins through a urine test, and it functions as an imaging agent, pinpointing the tumor location. In principle, this diagnostic could be used to detect cancer anywhere in the body, including tumors that have metastasized from their original locations.
"This is a really broad sensor intended to respond to both primary tumors and their ...
2021-07-16
Reno, Nev. (July 15, 2021) - Wildfire smoke may greatly increase susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, according to new research from the Center for Genomic Medicine at the Desert Research Institute (DRI), Washoe County Health District (WCHD), and Renown Health (Renown) in Reno, Nev.
In a study published earlier this week in the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology, the DRI-led research team set out to examine whether smoke from 2020 wildfires in the Western U.S. was associated with an increase in SARS-CoV-2 infections in Reno.
To ...
2021-07-16
A new study by Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers of more the 400,000 Medicare patients taking medications for insomnia found that the risk of death is increased when either benzodiazepines or "z-drugs" are taken with opioids.
The study, published July 15 in PLOS Medicine and led by Wayne Ray, PhD, professor of Health Policy at VUMC, compared patients taking these drugs with opioids to comparable patients taking trazodone, another commonly prescribed sleep medication for older patients.
The researchers found that those using benzodiazepines had a 221% increase in the risk of death from ...
2021-07-16
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - July 16, 2021 - An international research group, led by Jamey Marth, Ph.D., a professor at Sanford Burnham Prebys, has shown that the Neuraminidase 3 (Neu3) enzyme is responsible for the onset and progression of colitis--a chronic digestive disease caused by inflammation of the colon. The study, recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, was performed in a model of recurrent human food poisoning previously linked with the condition. The findings represent a scientific advance toward a targeted therapy to help the millions of people worldwide affected by the disorder.
"Our new research demonstrates how increased activity of ...
2021-07-16
Increases in maternal opioid use have led to an almost doubling in the number of babies born with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) in the U.S. in the past 10 years. This statistic led the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and American Academy of Pediatrics to call for stepped-up efforts to reduce opioid use during pregnancy, such as ensuring access to contraception to prevent unintended pregnancies among women who use opioids. More than 75% of women with Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) report having had an unintended pregnancy, but they are less likely to use effective ...
2021-07-16
A team of astronomers has released new observations of nearby galaxies that resemble colourful cosmic fireworks. The images, obtained with the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (ESO's VLT), show different components of the galaxies in distinct colours, allowing astronomers to pinpoint the locations of young stars and the gas they warm up around them. By combining these new observations with data from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), in which ESO is a partner, the team is helping shed new light on what triggers gas to form stars.
Astronomers know that stars are born in clouds of gas, but what sets off star formation, and how galaxies as a whole play into it, remains a mystery. To understand this process, a team of researchers has observed various ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cellular uptake of nanoparticles keys for further development of temperature sensing
A paper by Kazan Federal University was published in Journal of Nanoparticle Research