Scientists adopt deep learning for multi-object tracking
Their novel framework achieves state-of-the-art performance without sacrificing efficiency in public surveillance tasks
2021-07-19
(Press-News.org) Computer vision has progressed much over the past decade and made its way into all sorts of relevant applications, both in academia and in our daily lives. There are, however, some tasks in this field that are still extremely difficult for computers to perform with acceptable accuracy and speed. One example is object tracking, which involves recognizing persistent objects in video footage and tracking their movements. While computers can simultaneously track more objects than humans, they usually fail to discriminate the appearance of different objects. This, in turn, can lead to the algorithm to mix up objects in a scene and ultimately produce incorrect tracking results.
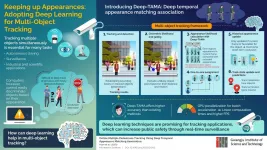
At the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology in Korea, a team of researchers led by Professor Moongu Jeon seeks to solve these issues by incorporating deep learning techniques into a multi-object tracking framework. In a recent study published in Information Sciences, they present a new tracking model based on a technique they call 'deep temporal appearance matching association (Deep-TAMA)' which promises innovative solutions to some of the most prevalent problems in multi-object tracking. This paper was made available online in October 2020 and was published in volume 561 of the journal in June 2021.
Conventional tracking approaches determine object trajectories by associating a bounding box to each detected object and establishing geometric constraints. The inherent difficulty in this approach is in accurately matching previously tracked objects with objects detected in the current frame. Differentiating detected objects based on hand-crafted features like color usually fails because of changes in lighting conditions and occlusions. Thus, the researchers focused on enabling the tracking model with the ability to accurately extract the known features of detected objects and compare them not only with those of other objects in the frame but also with a recorded history of known features. To this end, they combined joint-inference neural networks (JI-Nets) with long-short-term-memory networks (LSTMs).
LSTMs help to associate stored appearances with those in the current frame whereas JI-Nets allow for comparing the appearances of two detected objects simultaneously from scratch--one of the most unique aspects of this new approach. Using historical appearances in this way allowed the algorithm to overcome short-term occlusions of the tracked objects. "Compared to conventional methods that pre-extract features from each object independently, the proposed joint-inference method exhibited better accuracy in public surveillance tasks, namely pedestrian tracking," highlights Dr. Jeon. Moreover, the researchers also offset a main drawback of deep learning--low speed--by adopting indexing-based GPU parallelization to reduce computing times. Tests on public surveillance datasets confirmed that the proposed tracking framework offers state-of-the-art accuracy and is therefore ready for deployment.
Multi-object tracking unlocks a plethora of applications ranging from autonomous driving to public surveillance, which can help combat crime and reduce the frequency of accidents. "We believe our methods can inspire other researchers to develop novel deep-learning-based approaches to ultimately improve public safety," concludes Dr. Jeon. For everyone's sake, let us hope their vision soon becomes a reality!
INFORMATION:
Reference
Authors: Young-Chul Yoon (1), Du Yong Kim (2), Young-Min Song (4), Kwangjin Yoon (3), and Moongu Jeon (4)
Title of original paper: Online multiple pedestrians tracking using deep temporal appearance matching association
Journal: Information Sciences
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.10.002
Affiliations:
(1) Robotics Lab, Hyundai Motor Company
(2) School of Engineering, RMIT University
(3) SI-Analytics Company, Ltd.
(4) School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, GIST
About the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST)
The Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) is a research-oriented university situated in Gwangju, South Korea. As one of the most prestigious schools in South Korea, it was founded in 1993 and aims to create a strong research environment to spur advancements in science and technology and to promote collaboration between foreign and domestic research programs. With the motto, "A Proud Creator of Future Science and Technology," GIST has consistently received one of the highest university rankings in Korea.
Website: http://www.gist.ac.kr/
About the authors
The first author, Young-Chul Yoon, is a researcher at the Robotics Lab of Hyundai Motors. This research was performed while he was pursuing a master's degree on multi-object tracking at GIST EECS under the supervision of Dr. Moongu Jeon. His research won 3rd prize from the CVPR2019 multi-object tracking challenge among 36 competitors.
The corresponding author, Dr. Moongu Jeon, is a full professor at GIST. His main research interests are in artificial intelligence, machine learning, visual surveillance, and autonomous driving. He has published over 200 technical papers in these research areas.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-19
A new Tel Aviv University study found that, like humans, bats living in Tel Aviv enjoy the wide variety and abundance of food that the city has to offer, in contrast to rural bats living in Beit Guvrin, who are content eating only one type of food. The study was led by research student Katya Egert-Berg, under the guidance of Prof. Yossi Yovel, head of Tel Aviv University's Sagol School of Neuroscience and a faculty member of the School of Zoology in the George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences and the Steinhardt Museum of Natural History, as well as a recipient of the 2021 Kadar Family Award for Outstanding ...
2021-07-19
The July issues of two of the American Psychiatric Association journals, The American Journal of Psychiatry and Psychiatric Services are available online.
The American Journal of Psychiatry is the most widely read psychiatric journal in the world. Its July issue offers a collection of articles discussing the impacts of structural racism, socioeconomic deprivation and stigmatization on mental health. This includes the article From Womb to Neighborhood: A Racial Analysis of Social Determinants of Psychosis in the United States, which was featured at the APA Annual Meeting in May. Among other highlights:
Dismantling Structural Racism in Psychiatry: A Path to Mental Health Equity
Modification of Heritability for Educational Attainment and Fluid Intelligence by Socioeconomic ...
2021-07-19
When it comes to making eggs, female flies and female humans are surprisingly similar. And that could be a boon for women seeking better birth control methods, a UConn researcher reports in the July 5 issue of PNAS.
There are about 61 million women of reproductive age in the US, and about 43 million of them are sexually active but don't want a pregnancy right now, according to the Guttmacher Institute. And while there are a dozen or so different methods of birth control available, most have undesirable side effects for some of the women who try them. Despite the need, ...
2021-07-19
Using advanced remote sensing techniques can help the early detection of oak tree decline and control many other forest diseases worldwide, says new research from Swansea University.
The research published in Remote Sensing of Environment examined holm oak decline, which in its early stages causes changes to the tree's physiological condition that is not readily visible. It is only later, when the tree is more advanced in its decline, that outward changes to its leaf pigment and canopy structure become apparent.
The researchers used an integrated approach of hyperspectral and thermal imaging, a 3-D radiative transfer ...
2021-07-19
Philadelphia, July 19, 2021--Researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have developed a novel method for producing new antibiotics to combat resistant bacteria. Through an approach that would target bacteria with an antibiotic that is masked by a prodrug, which the bacteria would themselves remove, the researchers identified a method that would allow for development of new, effective antibiotics that could overcome issues of resistance. The findings were published today in eLife.
"We've created a sort of 'Trojan Horse' that would allow antibiotics to reach desired tissues undisturbed, ...
2021-07-19
(Edmonton, AB) Firefighters at the centre of the battle against the massive Fort McMurray wildfire in 2016 have persistent lung damage, according to new findings published by a University of Alberta occupational health research team.
"Those who were dealing with burning organic matter were exposed to a barrage of small particles in the smoke, and the ones with the highest exposure have long-term consequences," said principal investigator Nicola Cherry, an occupational epidemiologist, professor of medicine and Tripartite Chair of Occupational Health in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry.
The firefighters had more ...
2021-07-19
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - An experimental drug reported in Nature Communications suggests that a "path is clearly achievable" to treat currently untreatable cases of cystic fibrosis disease caused by nonsense mutations. This includes about 11 percent of cystic fibrosis patients, as well as patients with other genetic diseases, including Duchenne muscular dystrophy, β-thalassemia and numerous types of cancers, that are also caused by nonsense mutations.
The drug is a small molecule with a novel mechanism of action, say David Bedwell, Ph.D., and Steven Rowe, M.D., MSPH, co-senior authors. Bedwell is professor and chair of the University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Biochemistry and Molecular ...
2021-07-19
Scientists from the University of Graz, Kanzelhöhe Observatory, Skoltech, and the World Data Center SILSO at the Royal Observatory of Belgium, have presented the Catalogue of Hemispheric Sunspot Numbers. It will enable more accurate predictions of the solar cycle and space weather, which can affect human-made infrastructure both on Earth and in orbit. The study came out in the Astronomy & Astrophysics journal, and the catalogue is available from SILSO -- the World Data Center for the production, preservation, and dissemination of the international sunspot number.
Our Sun is a big boiling ball of gas, most of which is so hot that electrons are ripped off from atoms, creating a circulating mix of charged particles, called plasma. These moving charges ...
2021-07-19
A potentially life-saving treatment for heart attack victims has been discovered from a very unlikely source - the venom of one of the world's deadliest spiders.
A drug candidate developed from a molecule found in the venom of the Fraser Island (K'gari) funnel web spider can prevent damage caused by a heart attack and extend the life of donor hearts used for organ transplants.
The discovery was made by a team led by END ...
2021-07-19
The research team led by Prof. WEI Haiming and Prof. TIAN Zhigang from Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with the research group led by Prof. SUN Zimin from the First Affiliated Hospital of USTC revealed the pathological mechanism of severe pre-engraftment syndrome (PES) after umbilical cord blood transplantation, not only providing a treatment strategy for patients with PES, but significantly guiding for further improvement in the curative effect of unrelated cord blood transplantation (UCBT). This study was published in Nature Communications.
UCBT is an important means to cure hematological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists adopt deep learning for multi-object tracking
Their novel framework achieves state-of-the-art performance without sacrificing efficiency in public surveillance tasks