(Press-News.org) When it was discovered in the 1980s in Argentina, this hadrosaur was diagnosed with a fractured foot. However, a new analysis now shows that this ornithopod commonly known as the duck-billed dinosaur actually had a tumour some 70 million years ago, as well as two painful fractures in the vertebrae of its tail, despite which, it managed to survive for some time.
This dinosaur, called Bonapartesaurus rionegrensis, was discovered in Argentinean Patagonia in the 1980s, and the first analyses of its fossils indicated an ailment of the foot, possibly a fracture, as the Argentinean palaeontologist Jaime Powell pointed out at the time. The study of this animal then came to a standstill until 2016, when Powell invited another team of scientists to resume the research.
"In addition to the ailment of the foot, there were other possible fractures in several neural spines of the vertebrae of the tail," as Penélope Cruzado-Caballero, the lead author of the study, now published in the journal Cretaceous Research, and a scientist at the Research Institute of Palaeobiology and Geology of CONICET and the National University of Río Negro (Argentina), as well as a professor at the University of La Laguna (Tenerife, Spain), has told SINC.
The researchers decided to analyse them all to see this hadrosaur, also known as duck-billed dinosaur, "during its lifetime" and to see how it was able to interact with the environment, with its fellows, and with predators while suffering from these problems.
Scientists were particularly surprised by the condition of the foot. "We were struck by the large overgrowth of bone that gave it a cauliflower-like appearance and covered almost the entire metatarsal," the researcher points out. When studying the histology and CT scans of the fossil, the team did not find a fracture. Instead, the indicators showed a reduction in bone density and several areas where cortical tissue had been destroyed.
"We were probably looking at a cancer or a neoplasm, such as an osteosarcoma," specifies Cruzado-Caballero. The presence of diseases such as tumours confirms that they already existed at a very early age and among a very diverse group of animals.
"Despite the large development of the cancer, it did not significantly affect the muscle insertion zone, so we cannot be sure that the lesion affected its locomotion," says the palaeontologist. The study has allowed us to determine that the tumour did not spread to other bones - since this ornithopod preserved almost half of its skeleton -, "so, although it severely affected the metatarsus, it did not cause its death," she adds.
Tail fractures followed by infections
In addition to the foot tumour, other pathologies were identified in the neural spines of two vertebrae in Bonapartesaurus rionegrensis's tail. According to the scientists, one of the vertebrae had a displaced fracture that had almost healed. "It was probably related to an injury resulting from a strong blow that caused the bone to be displaced and to heal in this manner, giving the spine a curved appearance," Cruzado-Caballero stresses.
The other vertebra had an almost completely healed fracture also produced by a stress event (it is not known if it was due to impact), which did not lead to the displacement of the bone. Although the spine maintains its straight shape, the researchers observed a swelling that formed a callus on the bone as it healed.
"These fractures, especially in the case of the displaced fracture, must have been associated with infections following the rupture of the muscles surrounding the bone," says the researcher, who considers that they must have been painful not only because of the blow, but also because of the infections that could have impeded the mobility of the tail and caused this specimen a great deal of discomfort when it moved.
However, despite the severity of the ailments, the death of Bonapartesaurus rionegrensis did not follow immediately after its injuries, the authors point out. "But we cannot quantify how long it lived afterwards, which means that it could have lived for months or years. Nor can we confirm that these injuries were the final cause of its death," comments the scientist.
This hadrosaur, although badly injured, therefore managed to survive and continued to interact with its fellows, despite the initial pain caused by fractures and infections. These could have been caused by falling, hitting an object or another animal to defend itself from predators, or even by being trampled on the tail by another hadrosaur.
INFORMATION:
Reference:
Penélope Cruzado-Caballero et al. "Osseous paleopathologies of Bonapartesaurus rionegrensis (Ornithopoda, Hadrosauridae) from Allen Formation (Upper Cretaceous) of Patagonia Argentina" Cretaceous Research
The Indian Ocean has been warming much more than other ocean basins over the last 50-60 years. While temperature changes basin-wide can be unequivocally attributed to human-induced climate change, it is difficult to assess whether contemporary heat and freshwater changes in the Indian Ocean since 1980 represent an anthropogenically-forced transformation of the hydrological cycle. What complicates the assessment is factoring in natural variations, regional-scale trends, a short observational record, climate model uncertainties, and the ocean basin's complex circulation.
A ...
PHILADELPHIA--Alzheimer's disease and related diseases can still only be confirmed in deceased patients' brains via autopsy. Even so, the development of biomarkers can give patients and their families answers during life: Alzheimer's disease can be accurately detected via peptides and proteins in a patient's cerebrospinal fluids (CSF), which can be collected through a lumbar puncture and tested while the patient is alive. In 2018, a new framework suggested combining three Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in CSF - pathologic amyloid plaques (A), tangles (T), and neurodegeneration (N), collectively called ATN. According to recent research from the Perelman School ...
An international team of researchers led by Kumamoto and Tokyo Universities (Japan) have shown that the L452R mutation of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which is common to two mutant strains (Epsilon and Delta), is involved in cellular immunity evasion via the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) A24, and enhances viral infectivity. HLA-A24 is one of the most prominent HLA-class I alleles, especially in East/Southeast Asian populations, which might make them particularly vulnerable to coronavirus variants with this mutation.
The ongoing novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19) pandemic has, as of June 2021, infected over 150 million and killed over 3.5 million people worldwide. Vaccination drives ...
A Korean research team has identified the origin of bifurcated current sheets, considered one of the most unsolved mysteries in the Earth's magnetosphere and in magnetized plasma physics.
A POSTECH joint research team led by Professor Gunsu S. Yun of the Department of Physics and Division of Advanced Nuclear Engineering and Dr. Young Dae Yoon from the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory has theoretically established the process of collisionless equilibration of disequilibrated plasma current sheets. In addition, by comparing this with particle simulations and satellite data from NASA, the origin of the bifurcated ...
Overview:
Professor Hiromi Nakano of Toyohashi University of Technology used a material with a unique periodical structure (smart material: Li-M-Ti-O [M = Nb or Ta]) as a host material to synthesize new Mn4+-activated phosphors that exhibit red light emissions at 685 nm when excited at 493 nm. Because the valence of the Mn ions in the material changes from Mn4+ to Mn3+ according to the sintering temperature, composition, and crystal structure, there is a difference in the photoluminescence intensity of the phosphors. XRD, TEM, and XANES were used to clarify the relationship between the photoluminescence intensity and the sintering temperature, ...
Chinese researchers along with international colleagues recently reported a 6,700-year-long, precisely dated and well-calibrated tree-ring stable isotope chronology from the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. It reveals full-frequency precipitation variability in the Asian Summer Monsoon (ASM) from interannual to multimillennial timescales with a long-term decreasing trend and several abrupt climate change events.
The international research team comprised 20 scientists from research groups based in China, Norway, Germany, United Kingdom, USA, Sweden, Canada, and Switzerland ...
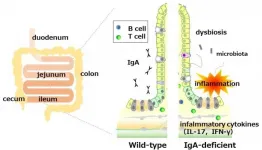
Tokyo, Japan - While researchers have known for years that immunoglobulin A (IgA) is important for gut health, it has remained unclear exactly what role it plays in preventing infection and disease. But now, researchers from Japan have found that eliminating IgA disrupts the balance of the intestinal ecosystem, making it susceptible to disease.
In a study published online in May in Gut, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed that IgA deficiency results in substantial inflammation of the ileum, a specific part of the small intestine.
IgA is present in large quantities in the small intestine, where it helps protect the body against microorganisms that could potentially cross the lining of the gut to cause ...
A new study by a team of researchers has found that the consolidation of traditional smallholder farms in China has a devastating effect on the biodiversity of wild pollinators in the area.
Pollinators play an essential role when it comes to supporting global food production.
However, wild pollinators are on the decline for several reasons, including the loss of floral resources and nesting sites. This loss of biodiversity could have far-reaching consequences for global food production in future.
"Biodiversity is essential for all life, with pollinators being one of the most important groups," says Dr Yi Zou from Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - A 17-year study in Oregon, Washington and California found that removal of invasive barred owls arrested the population decline of the northern spotted owl, a native species threatened by invading barred owls and the loss of old-forest habitats.
The conservation and management of northern spotted owls became one of the largest and most visible wildlife conservation issues in United States history after the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service listed the spotted owl as threatened under the Endangered Species Act in 1990 because of rapid declines in the owl's old-forest habitats. Four years later, the Northwest Forest Plan was adopted and reduced the rate of logging of old-growth forests on federal lands.
Despite more ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Scientists from the department of Anatomy and Embryology at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Tsukuba created a computer model to simulate the development of complex structures based on the Delta-Notch signaling pathway. This work may lead to a more comprehensive picture of the process that results in the formation of organs and other physiological systems.
The development of a tiny embryo consisting of undifferentiated cells into a healthy fetus with spatially defined organs depends on the complex interplay between genetic instructions and signaling molecules. For example, "Notch" genes are ...