(Press-News.org) Alexandria, Va., USA - Parach Sirivichayakul, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, presented the poster "Preventing Approximal Caries in Primary Teeth With Topical Fluorides" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
There is limited evidence regarding the use of silver diamine fluoride (SDF) for caries prevention in primary teeth. This randomized clinical trial evaluated the effectiveness of 38% SDF, 5% sodium fluoride (NaF) varnish and placebo control in preventing approximal caries in primary teeth.
Children aged 4-6 years who had at least one sound approximal surface at the distal surface of canines or the mesial or distal surface of the first and second molars assessed from bitewing radiographs were recruited. The participants were randomly allocated into three intervention groups as follows: Group 1 = control (water) , Group 2 = 5% NaF varnish (Duraphat) and Group 3 = 38% SDF (Topamine). All agents were applied semi-annually and the new caries development was assessed by the bitewing radiographic examinations at 6-, 12-, and 18-month follow-ups by two blind calibrated investigators.
The new approximal caries development rates of Group 1, 2, and 3 at the 18-month examination were 22.5%, 13.6%, and 24.3%, respectively (p END
Preventing approximal caries in primary teeth with topical fluorides
2021-07-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover a 'layer hall effect' in a 2D topological Axion antiferromagnet
2021-07-21
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (7/21/2021) - Researchers have discovered a "layer" Hall effect in a solid state chip constructed of antiferromagnetic manganese bismuth telluride, a finding that signals a much sought-after topological Axion insulating state, the team reports in the current edition of the journal Nature.
Researchers have been trying to find evidence of a topological Axion insulating (TAI) state and developed some candidate materials based on theoretical calculations. The layered Hall effect represents the first clear experimental evidence of the state, a feature bound by the laws of quantum physics, according to Boston College Assistant Professor ...
City-funded housing repairs in low-income neighborhoods associated with drop in crime
2021-07-21
PHILADELPHIA--Investing in structural home repairs in historically segregated, low-income, Black and Latino neighborhoods has been associated with reduced crime rates. In Philadelphia, when a home received repairs through a city-funded program, total crime dropped by 21.9% on that block, and as the number of repaired houses on a block increased, instances of crime fell even further, according to research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania published today in JAMA Network Open.
In an effort to address an old housing stock and high levels of historical disinvestment in Philadelphia, the city implemented the Basic Systems Repair ...
Glass sponges have properties for the design of ships, planes and skyscrapers
2021-07-21
Rome (Italy), July 21st, 2021 - The remarkable structural properties of the basket sponge (E. aspergillum) might seem fathoms removed from human-engineered structures. However, insights into how the organism's latticework of holes and ridges influences the hydrodynamics of seawater in its vicinity could lead to advanced designs for buildings, bridges, marine vehicles and aircraft, and anything that must respond safely to forces imposed by the flow of air or water.
While past research has investigated the structure of the sponge, there have been few studies of the hydrodynamic fields ...
The need for nuance in carbohydrate recommendations
2021-07-21
Carbohydrates have traditionally been the largest source of energy intake for much of the world's population1. However, without a standard definition for carbohydrate quality, some foods that contain carbohydrates are often stigmatized based on isolated and reductionist assessment methods that fail to consider their contributions to nutrient intakes and balanced, healthy diets. A new perspective piece, published in Advances in Nutrition, brings to light the pressing need to define carbohydrate quality, to better assess the value of nutrient-dense carbohydrate-containing foods in healthy lifestyles. Ultimately, the authors call for a more holistic approach to carbohydrate guidance to address the complex ...
Traditional Japanese food may hold building blocks of COVID-19 treatments
2021-07-21
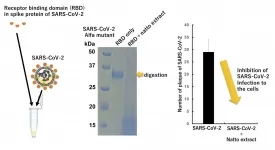
Natto, a fermented soybean dish often served for breakfast in Japan, originated at the turn of the last millennium but may hold an answer to a modern problem: COVID-19, according to a new study based on cell cultures.
Long thought to contribute to longer, healthier lives across Japan -- the country with the longest life expectancy on Earth and home to more than a quarter of the world's population aged 65 years or older -- natto was previously found to be a diet staple in those who were least likely to die from stroke or cardiac disease. Now, researchers have found that extract made from the sticky, strong smelling natto may inhibit the ability of the virus that causes COVID-19 to infect cells.
The team published its results on July 13th in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. ...
Researchers discover nucleotide sequence responsible for effectively fighting pathologies
2021-07-21
Researchers from HSE University have discovered nucleotide sequences characteristic of microRNA isoforms (microRNAs with errors). The discovery will help predict errors in microRNA behaviour and create drugs that can detect targets (such as viruses) more effectively. The results of the study have been published in the RNA Biology journal.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are very small molecules that regulate all the processes in a cell, including the transformation of inherited information in RNA or proteins (gene expression). Each microRNA has its own unique set of targets--genes whose activity it can suppress. Recent studies show that even slight changes in microRNA nucleotide sequences (so-called microRNA isoforms or isomiRs) can completely rebuild numerous targets. This can drastically ...
A novel method for the rapid repair of peripheral nerve injuries
2021-07-21
Each year, hundreds of thousands of people worldwide suffer from peripheral nerve injuries, which often leave them with long-term disabilities. The peripheral nervous system is analogous to the circulatory system; a network of vessels that reaches all parts of the body, but instead of blood flowing through vessels, electrical signals propagate information through thin fibers called axons, which are engulfed within nerve trunks. These nerve trunks are the communication network relaying information from all parts of the body to the brain, coordinating activity, and generating motor and sensory function. If one of the nerve trunks is damaged or torn - a common condition in limb injuries ...
A global comparison of life-cycle GHG emissions from passenger cars
2021-07-21
A far-reaching new study of the life-cycle greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from passenger cars, including SUVs, draws sharp and meticulous distinctions between the climate impacts of battery and fuel cell electric vehicles on one hand and combustion vehicles on the other.
The detailed findings can be summarized straightforwardly. Only battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) powered by renewable electricity can achieve the kind of deep reductions in GHG emissions from transportation that comport with the Paris Agreement's goal of ...
Toxic facility relocation depends on community pressure
2021-07-21
URBANA, Ill. - No one wants to live near a toxic plant. Toxic-releasing facilities such as paper, pulp, and other manufacturing plants negatively affect human health, environmental quality, and property values. And communities with lower income and educational attainment are more likely to house such facilities.
Since mandatory reporting about toxic facilities became publicly available in 1990, affected communities have increasingly expressed concern through the media, and engaged in targeted collective action and "toxic torts" lawsuits for health and environmental damages.
New ...
Wearable brain-machine interface turns intentions into actions
2021-07-21
A new wearable brain-machine interface (BMI) system could improve the quality of life for people with motor dysfunction or paralysis, even those struggling with locked-in syndrome - when a person is fully conscious but unable to move or communicate.
A multi-institutional, international team of researchers led by the lab of Woon-Hong Yeo at the Georgia Institute of Technology combined wireless soft scalp electronics and virtual reality in a BMI system that allows the user to imagine an action and wirelessly control a wheelchair or robotic arm.
The team, which included researchers from the University of Kent (United Kingdom) and Yonsei University (Republic of Korea), describes the new motor imagery-based BMI system this month ...