(Press-News.org) The future of Samoa's electricity system could go green, a University of Otago study has shown.
Pacific Island nations are particularly susceptible to climate change and face high costs and energy security issues from imported fossil fuels.
For these reasons many Pacific Island nations have developed ambitious 100 per cent renewable energy targets. However, they have not been subject to rigorous peer-reviewed studies to help develop these targets and pathways for achieving them in the same way as more developed countries.
To meet this need, Otago Energy Science and Technology Masters student Tupuivao Vaiaso mapped future scenarios for Samoa's electricity system by carefully balancing renewable supply and electricity demand.
The study, published in Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, shows high proportions (above 90 per cent) of renewable generation coupled with battery or pumped hydro energy storage is technically feasible, and economically viable - it would cost far less than current electricity production.
A special combination of characteristics makes this possible: great solar resources with very little seasonal variation; little variation in demand due to constant seasonal conditions; and high electricity prices from the current use of diesel.
However, the results also show there is a significant trade-off between percentage of renewable supply and affordability. To counter this, Mr Vaiaso says targets should be set just below 100 per cent for it to be economically attractive and/or biomass options (like the recent biomass gasification plant) could potentially be considered for the last few percent.
Co-author Associate Professor Michael Jack, Director of the Energy Management programme in the Department of Physics, says the study shows an affordable pathway to achieve renewable energy targets which is important as cutting emissions must be achieved in a way that does not increase energy hardship.
"These results have important implications for energy policy directions for Samoa and are directly applicable to many other countries in the Pacific," he says.
He believes the study also suggests Pacific Island nations are an important option for the growing trend in international sustainable finance.
"The high price of electricity means that renewable options are much more economically attractive than many other countries. These are essentially low hanging fruit that provide multiple benefits and, I imagine, would be attractive to these funding bodies."
INFORMATION:
*Mr Vaiaso would like to acknowledge financial support for his MSc studies from the New Zealand Aid Programme and the National University of Samoa.
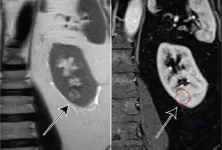
Leesburg, VA, July 22, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), the standardized non-invasive clear cell likelihood score (ccLS)--derived from MRI--correlates with the growth rate of small renal masses (cT1a, END ...
Scientists have completed the largest and most diverse genetic study of type 1 diabetes ever undertaken, identifying new drug targets to treat a condition that affects 1.3 million American adults.
Several potential drugs are already in the pipeline. Drugs targeting 12 genes identified in the diabetes study have been tested or are being tested in clinical trials for autoimmune diseases. That could accelerate the drugs' repurposing for treating or preventing type 1 diabetes, the researchers say.
"This work represents the largest, most ancesty-diverse study of type 1 diabetes ...
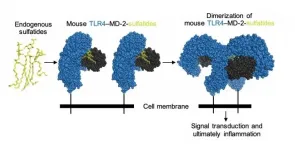
DALLAS - July 20, 2021 - UT Southwestern researchers report the first structural confirmation that endogenous - or self-made - molecules can set off innate immunity in mammals via a pair of immune cell proteins called the TLR4?MD-2 receptor complex. The work has wide-ranging implications for finding ways to treat and possibly prevent autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and antiphospholipid syndrome.
The TLR4?MD-2 receptor complex is well known for its role in the body's response to infection by gram-negative bacteria. Its role in autoimmunity had been long suspected, although direct proof was lacking. The team, led by Nobel Laureate Bruce Beutler, M.D., director of the Center for the Genetics of Host Defense (CGHD), identified lipids called sulfatides ...
In one out of every six local authorities, rates of hunger are more than 150 per cent (one and a half times) the national average. Shockingly, in one in 10 local authorities, the rate is almost double, according to new research by the University of Sheffield.
Researchers at the University of Sheffield Institute for Sustainable Food modelled data from the Food Foundation, who surveyed people across the UK, and for the first time were able to identify food insecurity at a local authority scale. Local authority percentages show the marked variation in levels of food insecurity between local areas and, whereas national ...
Persistence may be the key when quitting smoking using an electronic nicotine delivery system (ENDS), commonly known as vaping, a University of Otago study found.
Researchers found people attempting to switch from cigarettes to ENDS reported highly varied smoking and ENDS use. They recommend people persist in their attempts to transition away from smoking, even if their progress feels slow and uncertain.
Lead author Associate Professor Tamlin Conner, of the Department of Psychology, says, although people may plan to use ENDS exclusively instead of cigarettes, making the switch is not always straightforward.
"We found that dual use of ENDS and cigarettes was very common, suggesting that people ...
A new quantitative study suggests people seeking asylum are more likely to experience mental health deterioration as they spend more time living in refugee camps, backing up qualitative evidence from aid organisations.
The research, co-authored by Dr Francisco Urzua from the Business School (formerly Cass) alongside practitioners from Moria Medical Support (MMS) and academics from Universidad del Desarrollo, Chile and University of Amsterdam, the Netherlands measured incidences of acute mental health crises arising from extended stays in the Moria refugee camp on ...
Researchers from the School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences at King's College London have automated brain MRI image labelling, needed to teach machine learning image recognition models, by deriving important labels from radiology reports and accurately assigning them to the corresponding MRI examinations. Now, more than 100,00 MRI examinations can be labelled in less than half an hour.
Published in European Radiology, this is the first study allowing researchers to label complex MRI image datasets at scale.
The researchers say it would take years to manually perform labelling of more than 100,000 MRI examinations.
Deep learning typically requires tens of thousands of labelled images to ...
Scientists have developed a 'nanobody' - a small fragment of a llama antibody - that is capable of chasing out human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) as it hides away from the immune system. This then enables immune cells to seek out and destroy this potentially deadly virus.
Around four out of five people in the UK are thought to be infected with HCMV, and in developing countries this can be as high as 95%. For the majority of people, the virus remains dormant, hidden away inside white blood cells, where it can remain undisturbed and undetected for decades. ...
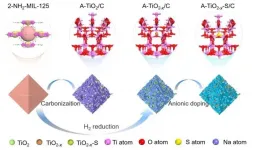
The research team of Prof. Xiaobo Ji and associate Prof. Guoqiang Zou has proposed an ingenious oxygen vacancy (OV)-engineering strategy to realize high content anionic doping in TiO2 and offered valuable insights into devise electrode materials with fast charge transfer kinetics in the bulk phase. The article titled "High content anion (S/Se/P) doping assisted by defect engineering with fast charge transfer kinetics for high-performance sodium ion capacitors" is published in Science Bulletin. Xinglan Deng is listed as first author and Prof. Guoqiang Zou as corresponding author.
The ...
An international research team has come up with an innovative method for metal recovery from industrial waste. The new method allows the simultaneous recovery of multiple metals from waste oxides in a single process. This novel route will lower the burden on waste storage facilities with significant contributions to the economic and environmental sustainability of industrial waste management. The study was published in Journal of Environmental Management. This work is the first in a series of studies aimed at developing cost-effective and environmentally sustainable solutions for industrial waste recycling.
Some of the major industries ...