Silicon with a two-dimensional structure
Heidelberg chemists succeed in producing synthesis and complete characterisation for the first time
2021-07-22
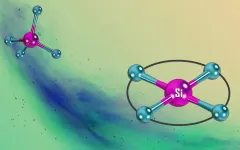
(Press-News.org) Silicon, a semi-metal, bonds in its natural form with four other elements and its three-dimensional structure takes the form of a tetrahedron. For a long time, it seemed impossible to achieve the synthesis and characterisation of a two-dimensional equivalent - geometrically speaking, a square. Now scientists from the field of Inorganic Chemistry at Heidelberg University have succeeded in producing a crystalline complex with such a configuration. PD Dr Lutz Greb from the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry underlines that it has surprising physical and chemical properties and, in the field of molecular chemistry, will open up new approaches to using the second most abundant element in the Earth's crust for catalysis and materials research.
As a classical semi-metal, silicon possesses properties of both metals and non-metals, and belongs to the carbon group on the periodic table. Like carbon, silicon bonds with four elements. Its three-dimensional structure then corresponds to a tetrahedron, a body with four sides. Due to the high stability of a tetrahedron, other structures are not known in natural silicon with four bonds - silicon(IV) for short. Considered purely geometrically, the two-dimensional equivalent to a tetrahedron is a square. These configurations are already known for carbon but, according to Dr Greb, a square-planar structure has not yet been produced in the field of silicon(IV) chemistry, even after over 40 years of intensive effort.
Dr Greb's working group has succeeded for the first time in synthesising and completely characterising a square-planar silicon(IV) species. It was possible to show this with the aid of X-ray crystallography. The scientists grew a monocrystal which they irradiated with a finely focused beam of X-rays. The diffraction of the X-rays when encountering the atoms of the monocrystal led to an unmistakable pattern from which it is possible to calculate the position of the atom nuclei. This measurement enabled the researchers to show that they were dealing with molecules with square-planar silicon(IV). Further studies with spectroscopic methods supported this configuration. It displays physical and chemical properties that the researchers did not expect, e.g. colour in a naturally colourless class of substances.
"Synthesising this configuration from the components we chose is comparatively simple once you have understood the key conditions," explains Dr Fabian Ebner, who is meanwhile a postdoctoral researcher at the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry. It surprised the scientists, however, that the square-planar silicon(IV) molecule constitutes a stable, isolable compound at all. "Due to the high reactivity, there are many conceivable ways of decomposition. Still, we have always believed that it is possible to isolate this compound," Dr Greb emphasises.
Lutz Greb received a Starting Grant from the European Research Council (ERC) for his research in the area of structurally constrained main-group elements. The Foundation of German Business supported Fabian Ebner's work. The research results were published in the journal Chem.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-22
The touchscreen technology used in billions of smartphones and tablets could also be used as a powerful sensor, without the need for any modifications.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge have demonstrated how a typical touchscreen could be used to identify common ionic contaminants in soil or drinking water by dropping liquid samples on the screen, the first time this has been achieved. The sensitivity of the touchscreen sensor is comparable to typical lab-based equipment, which would make it useful in low-resource settings.
The researchers say their proof of concept could one day be expanded for a wide range of sensing applications, including for biosensing or medical diagnostics, right from the phone in your pocket. The results are reported ...
2021-07-22
Many applications, from fiber-optic telecommunications to biomedical imaging processes require substances that emit light in the near-infrared range (NIR). A research team in Switzerland has now developed the first chromium complex that emits light in the coveted, longer wavelength NIR-II range. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, the team has introduced the underlying concept: a drastic change in the electronic structure of the chromium caused by the specially tailored ligands that envelop it.
Many materials that emit NIR light are based on expensive or rare metal complexes. Cheaper alternatives that emit in the NIR-I range between 700 and 950 nm have been developed but NIR-II-emitting complexes of non-precious metals remain extremely rare. Luminescence in the NIR-II range (1000 to 1700 ...
2021-07-22
A research team led by Wim Annaert (VIB-KU Leuven) uncovered the early assembly of gamma-secretase, a protein complex linked to numerous cellular processes including the development of Alzheimer's disease. In a first step, two dimeric subcomplexes are formed, which independently exit the ER and only afterwards assemble into a four-subunit complex. This 'buckle up' mechanism is thought to prevent premature assembly and activity. The new insights are very relevant, as gamma-secretase is an important potential therapeutic target for Alzheimer's and other ...
2021-07-22
A research team led by Dr Aixin YAN, Associate Professor from the Research Division for Molecular & Cell Biology, Faculty of Science, in collaboration with Honorary Clinical Professor Patrick CY WOO from the Department of Microbiology, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKU), reported the development of a transferrable and integrative type I CRISPR-based platform that can efficiently edit the diverse clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a superbug capable of infecting various tissues and organs and a major source of nosocomial infections. The ...
2021-07-22
As cities worldwide expand their networks of cycling paths and more cyclists take to the streets, the chances of cycling accidents and potential collisions increase as well, underscoring the need for proper cycling safety in dense urban areas.
According to a World Health Organisation report in 2020, more than 60 per cent of the reported bicycle-related deaths and long-term disabilities are a result of accidents with head injuries.
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), in collaboration with French specialty materials leader Arkema, have developed a tougher, safer bicycle helmet using a combination of materials. The new helmet prototype has higher energy absorption, reducing the amount of energy ...
2021-07-22
With the application of a novel three-dimensional imaging technology, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have discovered that one portion of the autonomic nervous system in the liver undergoes severe degeneration in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The study, which is conducted in mice and human liver tissue, shows that the degeneration of nerves is correlated with the severity of liver pathology. The results are being published in the journal Science Advances.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common hepatic disorder, with prevalence around 25 percent globally. Approximately ...
2021-07-22
The building sector in the U.S. accounts for 39 percent of energy use, with commercial buildings responsible for about half of that. As cities grapple with climate change, making commercial buildings more efficient is a key part of the solution.
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering and the Mascaro Center for Sustainable Innovation used the City of Pittsburgh to create a model built upon the design, materials and purpose of commercial buildings to estimate their energy usage and emissions. While other models may ...
2021-07-22
FRANKFURT/HANNOVER. The international team of geoscientists led by Prof. Silke Voigt from the Goethe University Frankfurt, Prof. Ireneusz Walaszczyk from the University of Warsaw and Dr André Bornemann from LBEG have thoroughly investigated 40 metres of the geological strata sequence in the former limestone quarry at Hasselberg. The researchers determined that this is only sequence in the transition between Turonian and Coniacian without gaps and it therefore represents a perfect rock sequence to serve geoscientists from all over the world as a reference for their research - a "Global Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP)" or, in the jargon of geosciences, a "golden nail".
Certain group of bivalve mollusks of the family Inoceramidae, first appeared in the Coniacian, and ...
2021-07-22
ORLANDO, July 22, 2021 - Disagreement seems to spread online posts faster and further than agreement, according to a new study from the University of Central Florida.
The finding comes from an examination of posts labeled controversial on social news aggregation site Reddit. To perform the study, the researchers analyzed more than 47,000 posts about cybersecurity in a Reddit dataset that was collected by the Computational Simulation of Online Social Behavior (SocialSim) program of the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
Researchers found that these posts were seen by nearly twice the number of people and traveled nearly twice as fast when compared ...
2021-07-22
In a new study, published recently in the journal Circulation Research, scientists discover how the production of protective molecules known as specialised pro-resolving mediators (SPM) is altered in patients with COVID-19.
The results suggest that treatments which increase SPM production, such as dexamethasone or SPM based drugs, could play a key role in limiting inflammation in these patients.
Currently there is little understanding around the mechanisms that lead to uncontrolled inflammation in patients with COVID-19.
The study found a link between decreased SPM blood levels and disrupted white blood cell responses in patients with a higher disease burden. The findings also revealed that dexamethasone, the first drug ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Silicon with a two-dimensional structure
Heidelberg chemists succeed in producing synthesis and complete characterisation for the first time