INFORMATION:
The University of Exeter has launched a 'Green Futures' campaign and website to drive action on the environment and climate emergency. To find out more please visit https://greenfutures.exeter.ac.uk.
Scientists identify five new plant species in Bolivia
2021-07-23
(Press-News.org) Scientists have identified five new plant species in the Bolivian Andes.
The species are all part of the genus Jacquemontia, which are twining or trailing plants with pretty blue flowers.
With rapid biodiversity loss taking place across South America and worldwide, identifying plant species is a vital step towards protecting them.
The new study, which classifies and describes the 28 Jacquemontia species now known to live in Bolivia and Peru, was carried out by the universities of Exeter and Oxford, and the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
"Many plant species have not been identified and classified, especially in the tropics," said Rosie Clegg, of the University of Exeter and Kew.
"If you don't know what a species is, you can't conserve it.
"Working with local collaborators in Bolivia, we have identified five new Jacquemontia species - and our work so far suggests most of them are relatively rare."
Jacquemontia plants often grow in open, bushy or grassy habitats, however, even widespread species are often scattered in their distribution and some species are highly specialised, growing even on bare rock with very little soil or water, while some require fire to stimulate seed germination.
The researchers now want to discover more about these species, and where each can be found as - at present - some are only known to exist in a single location.
Plants limited to a small area are highly vulnerable to threats such as the arrival of invasive species and habitat destruction for agriculture, mining and road and reservoir construction.
Clegg's current work focusses on rock outcrops, where some Jacquemontia species are found, although the new species described in the paper are found on Andean slopes.
"Rock outcrops come in many forms across South America, with different geologies and different plants living on them," she said.
"As well as identifying plants, we want to learn more about these habitats and the role they play in wider ecosystems.
"Jacquemontia and other plants on rock outcrops are able to survive in very harsh conditions, so through them we can learn more about how plants might respond and adapt to climate change."
John Wood, of the University of Oxford and Kew, said: "Collaboration between UK institutions working alongside colleagues in Bolivia is important for the identification and conservation of species and their habitats."
Clegg's research at the University of Exeter is funded by the NERC GW4+ Doctoral Training Programme.
The five newly described species are named: Jacquemontia boliviana, Jacquemontia cuspidata, Jacquemontia longipedunculata, Jacquemontia mairae and Jaquemontia chuquisacensis.
The paper, published in the journal Kew Bulletin, is entitled: "Jacquemontia (Convolvulaceae) in Bolivia and Peru."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Child mental health services lacking in high-income countries: SFU study finds
2021-07-23
Most children with a mental health disorder are not receiving services to address their needs--according to a new study from researchers at Simon Fraser University's Children's Health Policy Centre. Their research was published this week in the journal Evidence-Based Mental Health.
Researchers found that of the one in eight children (12.7 per cent) who experience a mental disorder, less than half (44.2 per cent) receive any services for these conditions.
"We have illuminated an invisible crisis in children's mental health and unacceptable service shortfalls in high-income countries -- including in Canada -- to a degree that violates children's rights," says study author Charlotte Waddell, ...
Device cracks milk protein
2021-07-23
After gaining world attention by 'unboiling' egg protein, Flinders University scientists have now used an Australian-made novel thin film microfluidic device to manipulate Beta-lactoglobulin (β-lactoglobulin), the major whey protein in cow's, sheep's and other mammals.
The so-called Vortex Fluidic Device has previously been used in an array of experiments to successfully 'un-boil' egg protein and even break the molecular bonds of one of the world's hardest material, carbon nanotubes.
In the latest application, published in Molecules, College of Science and Engineering experts have combined the capabilities of the VFD with a new form of biosensor called TPE-MI, which is an aggregation-induced emission luminogen (AIEgen).
"In the human body, protein folding is ...
Research identifies potential role of 'junk DNA' sequence in aging, cancer
2021-07-23
The human body is essentially made up of trillions of living cells. It ages as its cells age, which happens when those cells eventually stop replicating and dividing. Scientists have long known that genes influence how cells age and how long humans live, but how that works exactly remains unclear. Findings from a new study led by researchers at Washington State University have solved a small piece of that puzzle, bringing scientists one step closer to solving the mystery of aging.
A research team headed by Jiyue Zhu, a professor in the College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, recently identified a DNA region known as VNTR2-1 that appears to drive the activity of the telomerase gene, which has been shown to prevent ...
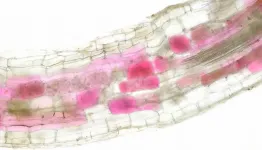
Blushing plants reveal when fungi are growing in their roots
2021-07-23
Almost all crop plants form associations with a particular type of fungi - called arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi - in the soil, which greatly expand their root surface area. This mutually beneficial interaction boosts the plant's ability to take up nutrients that are vital for growth.
The more nutrients plants obtain naturally, the less artificial fertilisers are needed. Understanding this natural process, as the first step towards potentially enhancing it, is an ongoing research challenge. Progress is likely to pay huge dividends for agricultural productivity.
In a study published in the journal PLOS Biology, researchers used the bright red pigments of beetroot - called betalains - to visually track soil fungi as they colonised plant roots in a living plant.
"We can now ...
Bacteria navigate on surfaces using a 'sense of touch'
2021-07-23
Many disease-causing bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa crawl on surfaces through a walk-like motility known as "twitching". Nanometers-wide filaments called type IV pili are known to power twitching, but scientists ignore which sensory signals coordinate the microbes' movements.
Now, EPFL researchers have found that Pseudomonas bacteria use a mechanism similar to our sense of touch to navigate on surfaces. "This study changes the way we think about motility in bacteria," says senior author Alexandre Persat, a tenure track assistant professor at EPFL's School of Life Sciences.
Scientists have known that ...
Oncotarget: Fgr and Numb in retinoic differentiation and G0 arrest of non-APL AML cells
2021-07-23
Oncotarget published "Role for Fgr and Numb in retinoic acid-induced differentiation and G0 arrest of non-APL AML cells" which reported that retinoic acid is a fundamental regulator of cell cycle and cell differentiation.
Using a leukemic patient-derived in vitro model of a non-APL AML, these authors previously found that RA evokes activation of a macromolecular signaling complex, a signalosome, built of numerous MAPK-pathway-related signaling molecules; and this signaling enabled Retinoic-Acid-Response-Elements to regulate gene expression that results in cell differentiation/cell cycle arrest. Toward mechanistic ...
Shedding light on the dark side of firm lobbying
2021-07-23
Researchers from George Mason University, University of Manitoba, Colorado State University, and Georgetown University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines an unintended customer consequence of lobbying, decreased customer satisfaction, and also explains marketing-focused efforts that can help prevent it.
The study, forthcoming in the the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Shedding Light on the Dark Side of Firm Lobbying: A Customer Perspective" and is authored by Gautham Vadakkepatt, Sandeep Arora, Kelly Martin, and Neeru Paharia.
Lobbying, ...
Southeastern US herbaria digitize three million specimens, now freely available online
2021-07-23
A network of over 100 herbaria spread out across the southeastern United States recently completed the herculean task of fully digitizing more than three million specimens collected by botanists and naturalists over a span of 200 years. The project, which was funded by the National Science Foundation, is part of a larger, ongoing effort by natural history institutions worldwide to make their biological collections easily accessible to researchers studying broad patterns of evolution, extinction, range shifts, and climate change.
In a END ...
Meet the Martian meteorite hunters
2021-07-23
A team at the Natural History Museum (NHM), London is paving the way for future rovers to search for meteorites on Mars. The scientists are using the NHM's extensive meteorite collection to test the spectral instruments destined for the ExoMars rover Rosalind Franklin, and develop tools to identify meteorites on the surface of the red planet. The project is being presented today (23 July) at the virtual National Astronomy Meeting 2021.
The cratered surface of our nearest planetary neighbour has a long and complex history, and searching for rocks amidst more rocks may seem like a futile activity. Despite this, Martian rovers statistically have a significantly higher 'find per mile' success rate than dedicated meteorite hunts on ...
New dietary treatment for epilepsy well tolerated and reduced seizures
2021-07-23
The first clinical trial of a new dietary treatment for children and adults with severe forms of epilepsy, co-developed by UCL researchers and based on the ketogenic diet, has been successfully completed.
For the study, published in Brain Communications, clinicians evaluated the use of K.Vita®, (also known as Betashot), an oral liquid dietary supplement developed by UCL in collaboration with Royal Holloway, University of London, and Vitaflo International Ltd.
The ketogenic diet (KD) consists of high-fat, low-carbohydrate and adequate protein consumption and mimics the fasting state, altering the metabolism to use body fat as the primary fuel source. This switch from carbohydrates to fat for body ...