How the brain paints the beauty of a landscape
Researchers investigate how our brains proceed from merely seeing a landscape to feeling its aesthetic impact
2021-07-23
(Press-News.org) How does a view of nature gain its gloss of beauty? We know that the sight of beautiful landscapes engages the brain's reward systems. But how does the brain transform visual signals into aesthetic ones? Why do we perceive a mountain vista or passing clouds as beautiful? A research team from the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics has taken up this question and investigated how our brains proceed from merely seeing a landscape to feeling its aesthetic impact.
In their study, the research team presented artistic landscape videos to 24 participants. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), they measured the participants' brain activity as they viewed and rated the videos. Their findings have just been published in the open-access journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. First author A. Ilkay Isik encapsulates:
"We would have expected the aesthetic signals to be limited to the brain's reward systems, but surprisingly, we found them already present in visual areas of the brain while the participants were watching the videos. The activations occurred right next to brain regions deployed in recognizing physical features in movies, such as the layout of a scene or the presence of motion."
Senior author Edward Vessel suggests that these signals may reflect an early, elemental form of beauty perception:
"When we see something beyond our expectations, local patches of brain tissue generate small 'atoms' of positive affect. The combination of many such surprise signals across the visual system adds up to make for an aesthetically appealing experience."
With this new knowledge, the study not only contributes to our understanding of beauty, but may also help clarify how interactions with the natural environment can affect our sense of well-being. The results might have potential applications in a variety of fields where the link between perception and emotion is important, such as clinical health care and artificial intelligence.
INFORMATION:
Original Publication:
Isik, A.I. and Vessel, E.A. (2021). From Visual Perception to Aesthetic Appeal: Brain Responses to Aesthetically Appealing Natural Landscape Movies.
Front. Hum., 21 July 2021 Neurosci. 15:676032.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-23
As Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University researchers completed their research on coloured architectural concrete, they found a surprising result--green pigmented cement had impurities that produced porous, poor quality concrete. Meanwhile, red and blue pigments had little effect.
The research was conducted by Mehreen Heerah, a graduate of XJTLU's Department of Civil Engineering, Dr Graham Dawson of XJTLU's Department of Chemistry, and Isaac Galobardes of Mohammed VI Polytechnic University.
Pigmented architectural concrete is used as a visually appealing alternative to grey concrete, such as in Barcelona's Ciutat de la Justícia, explains Dr Dawson. As the demand for pigmented architectural concrete grows, so does the importance of this research.
Not easy ...
2021-07-23
New research from the University of Otago debunks a long-held belief about our ancestors' eating habits.
For more than 60 years, researchers have believed Paranthropus, a close fossil relative of ours which lived about one to three million years ago, evolved massive back teeth to consume hard food items such as seeds and nuts, while our own direct ancestors, the genus Homo, is thought to have evolved smaller teeth due to eating softer food such as cooked food and meats.
However, after travelling to several large institutes and museums in South Africa, Japan and the ...
2021-07-23
About six gigatons -- roughly 12 times the mass of all living humans -- of carbon appears to be emitted over land every year, according to data from the Chinese Global Carbon Dioxide Monitoring Scientific Experimental Satellite (TanSat).
Using data on how carbon mixes with dry air collected from May 2017 to April 2018, researchers developed the first global carbon flux dataset and map. They published their results in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences.
The map was developed by applying TanSat's satellite observations to models of how greenhouse gasses are exchanged among Earth's atmosphere, land, ...
2021-07-23
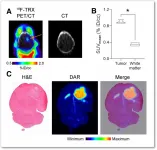
Reston, VA--A new radiotracer that detects iron in cancer cells has proven effective, opening the door for the advancement of iron-targeted therapies for cancer patients. The radiotracer, 18F-TRX, can be used to measure iron concentration in tumors, which can help predict whether a not the cancer will respond to treatment. This research was published in the July issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
All cancer cells have an insatiable appetite for iron, which provides them the energy they need to multiply. As a result, tumors have higher levels of iron than normal tissues. Recent advances in chemistry have led scientists to take advantage of this altered state, targeting the expanded cytosolic ...
2021-07-23
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center was one of 28 clinical sites around the world that participated in the LOTIS-2 trial to test the efficacy of Loncastuximab tesirine, a promising new treatment for aggressive B-cell lymphoma. The results of the single-arm, phase 2 trial were published online in May 2021 in Lancet Oncology.
Brian Hess, M.D., a Hollings researcher and lymphoma specialist at MUSC Health, was instrumental in bringing the phase 2 trial to Hollings. The manufacturer of Loncastuximab tesirine, ADC Therapeutics S.A., sponsored the trial.
B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a blood cancer that begins in the lymph nodes, spleen or bone marrow. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of aggressive NHL. New treatment options are vital for patients with DLBCL. ...
2021-07-23
Due to the global efforts to meet sustainability standards, many countries are currently looking to replace concrete with wood in buildings. France, for example, will require that all new public buildings will be made from at least 50 percent wood or other sustainable materials starting in 2022.
Because wood is prone to degradation when exposed to sunlight and moisture, protective coatings can help bring wood into wider use. Researchers at Aalto University have used lignin, a natural polymer abundant in wood and other plant sources, to create a safe, low-cost and high-performing coating for use in construction.
'Our new coating has great potential to ...
2021-07-23
A new optogenetic tool, a protein that can be controlled by light, has been characterized by researchers at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB). They used an opsin - a protein that occurs in the brain and eyes - from zebrafish and introduced it into the brain of mice. Unlike other optogenetic tools, this opsin is not switched on but rather switched off by light. Experiments also showed that the tool could be suitable for investigating changes in the brain that are responsible for the development of epilepsy.
The teams led by Professor Melanie Mark from the Behavioural Neurobiology Research Group and Professor Stefan Herlitze from the Department ...
2021-07-23
As the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 continues to evolve, immunologists and infectious diseases experts are eager to know whether new variants are resistant to the human antibodies that recognized initial versions of the virus. Vaccines against COVID-19, which were developed based on the chemistry and genetic code of this initial virus, may confer less protection if the antibodies they help people produce do not fend off new viral strains. Now, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and collaborators have created an "atlas" that charts how 152 different antibodies attack a major ...
2021-07-23
Many species within Kenya's Tana River Basin will be unable to survive if global temperatures continue to rise as they are on track to do - according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published in the journal PLOS ONE today outlines how remaining within the goals of the Paris Agreement would save many species.
The research also identifies places that could be restored to better protect biodiversity and contribute towards global ecosystem restoration targets.
Researcher Rhosanna Jenkins carried out the study as part of her PhD at UEA's School of Environmental Sciences.
She said: "This research shows how many species within Kenya's Tana River Basin will be unable to survive if global temperatures continue to rise as they are on track to do.
"But remaining ...
2021-07-23
For young soccer players, participating in repetitive technical training activities involving heading during practice may result in more total head impacts but playing in scrimmages or actual soccer games may result in greater magnitude head impacts. That's according to a small, preliminary study released today that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's Sports Concussion Conference, July 30-31, 2021.
"Headers are a fundamental component to the sport of soccer. Therefore, it is important to understand differences in header frequency and magnitude across practice and game settings," said study author Jillian Urban, PhD, MPH, of Wake ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How the brain paints the beauty of a landscape
Researchers investigate how our brains proceed from merely seeing a landscape to feeling its aesthetic impact