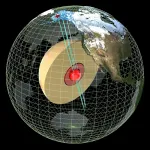
(Press-News.org) Data captured from seismic waves caused by earthquakes has shed new light on the deepest parts of Earth’s inner core, according to seismologists from The Australian National University (ANU).
By measuring the different speeds at which these waves penetrate and pass through the Earth’s inner core, the researchers believe they’ve documented evidence of a distinct layer inside Earth known as the innermost inner core -- a solid “metallic ball” that sits within the centre of the inner core.
Not long ago it was thought Earth’s structure was comprised of four distinct layers: the crust, the mantle, the outer core and the inner core. The findings, published in Nature Communications, confirm there is a fifth layer.
“The existence of an internal metallic ball within the inner core, the innermost inner core, was hypothesized about 20 years ago. We now provide another line of evidence to prove the hypothesis,” Dr Thanh-Son Phạm, from the ANU Research School of Earth Sciences, said.
Professor Hrvoje Tkalčić, also from ANU, said studying the deep interior of Earth’s inner core can tell us more about our planet’s past and evolution.
“This inner core is like a time capsule of Earth's evolutionary history – it’s a fossilised record that serves as a gateway into the events of our planet’s past. Events that happened on Earth hundreds of millions to billions of years ago,” he said.
The researchers analysed seismic waves that travel directly through the Earth’s centre and “spit out” at the opposite side of the globe to where the earthquake was triggered, also known as the antipode. The waves then travel back to the source of the quake.
The ANU scientists describe this process as similar to a ping pong ball bouncing back and forth.
“By developing a technique to boost the signals recorded by densely populated seismograph networks, we observed, for the first time, seismic waves that bounce back-and-forth up to five times along the Earth’s diameter. Previous studies have documented only a single antipodal bounce,” Dr Phạm said.
“The findings are exciting because they provide a new way to probe the Earth’s inner core and its centremost region.”
One of the earthquakes the scientists studied originated in Alaska. The seismic waves triggered by this quake “bounced off” somewhere in the south Atlantic, before travelling back to Alaska.
The researchers studied the anisotropy of the iron-nickel alloy that comprises the inside of the Earth’s inner core. Anisotropy is used to describe how seismic waves speed up or slow down through the material of the Earth’s inner core depending on the direction in which they travel. It could be caused by different arrangement of iron atoms at high temperatures and pressures or preferred alignment of growing crystals.
They found the bouncing seismic waves repeatedly probed spots near the Earth’s centre from different angles. By analysing the variation of travel times of seismic waves for different earthquakes, the scientists infer the crystallised structure within the inner core's innermost region is likely different to the outer layer.
They say it might explain why the waves speed up or slow down depending on their angle of entry as they penetrate the innermost inner core.
According to the ANU team, the findings suggest there could have been a major global event at some point during Earth’s evolutionary timeline that led to a “significant” change in the crystal structure or texture of the Earth’s inner core.
“There are still many unanswered questions about the Earth’s innermost inner core, which could hold the secrets to piecing together the mystery of our planet’s formation,” Professor Tkalčić said.
The researchers analysed data from about 200 magnitude-6 and above earthquakes from the last decade.
END
Bouncing seismic waves reveal distinct layer in Earth's inner core
2023-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers map mosquito cells that may help the insects choose tastiest humans
2023-02-21
In a bid to understand why mosquitoes may be more attracted to one human than another, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have mapped specialized receptors on the insects’ nerve cells that are able to fine-tune their ability to detect particularly “welcoming” odors in human skin.
Receptors on mosquito neurons have an important role in the insects’ ability to identify people who present an attractive source of a blood meal, according to Christopher Potter, Ph.D., associate professor of neuroscience at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “Understanding ...
US Census data vulnerable to attack without enhanced privacy measures
2023-02-21
Computer scientists at the University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science have designed a “reconstruction attack” that proves U.S. Census data is vulnerable to exposure and theft.
Aaron Roth, Henry Salvatori Professor of Computer & Cognitive Science in Computer and Information Science (CIS), and Michael Kearns, National Center Professor of Management & Technology in CIS, led a recent PNAS study demonstrating that statistics released by the U.S. Census Bureau can be reverse engineered to reveal ...
Excess nutrients lead to dramatic ecosystem changes in Cape Cod’s Waquoit Bay; the bay is a harbinger for estuaries worldwide, say researchers
2023-02-21
Woods Hole, Mass. (Feb. 21, 2023) -- When the Covid-19 pandemic hit in 2020 with associated travel restrictions, Matthew Long thought his students could shift their overseas research projects to instead study the seagrass meadow ecosystem in Waquoit Bay. It’s a shallow, micro-tidal estuary on the south side of Cape Cod in Massachusetts, near the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) where Long is an associate scientist in the Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Department.
However, when Long and his students looked for seagrass meadows where he had seen them in previous years, there were only a few shoots of dying Zostera marina eelgrass, ...
New AGA guideline recommends blood and stool tests for monitoring ulcerative colitis
2023-02-21
Bethesda, MD (Feb. 21, 2023) — In new evidence-based guidelines, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) recommends non-invasive biomarkers as a first-line strategy for monitoring many patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). These guidelines were published today in Gastroenterology.
The AGA guidelines outline use cases for three biomarkers that provide accurate insights into ulcerative colitis disease activity: serum C-reactive protein (CRP) (blood), fecal calprotectin (stool) and fecal lactoferrin (stool).
“For decades we have regarded endoscopy as the gold ...
RIT researcher awarded NSF CAREER funding to develop advanced computer memory and devices
2023-02-21
Kai Ni was awarded a National Science Foundation CAREER Award to improve computing memory through the use of ferroelectric materials and capacity.
The assistant professor of electrical and microelectronic engineering in RIT’s Kate Gleason College of Engineering, Ni has been at the forefront of advancing ferroelectric memory, a familiar but never widely adopted technology that has the potential to meet the growing demand for more energy-efficient computing performance.
“The appetite for semiconductors just keeps growing. With the data we are generating every day, we need ways to process ...
CHOP researchers develop first effective preclinical models for most common genetic cause of Leigh Syndrome
2023-02-21
Philadelphia, February 21, 2023 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) developed two new zebrafish models for studying a specific genetic form of mitochondrial disease that represents the most common cause of Leigh syndrome. Using these models, the team identified two drugs already approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for other conditions that could be repurposed to treat this specific cause of Leigh syndrome. The findings were recently published in the journal Human Molecular Genetics.
SURF1 deficiency ...
Public lecture: how can we have a good future with artificial intelligence?
2023-02-21
Public lecture: how can we have a good future with artificial intelligence?AI expert and educator Professor Anikó Ekárt to discuss one of today’s most provocative topics
Lecture will take place on 28 February at Aston University
Talk to explore artificial intelligence’s capabilities, benefits and pitfalls.
The potential impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on our daily lives will be explored in a public lecture at Aston University.
The University is inviting the public onto its campus on Tuesday 28 February to hear Professor ...
Study finds parents serve as a safety net as grown kids navigate the workforce
2023-02-21
A new study underscores the role that parents play as a safety net for their young adult children as those children navigate the labor market, and highlights the challenges facing young adults who do not have access to parental support.
“In recent decades, we’ve seen a lot of changes in the labor market, from the decline of lifetime employment at one job to the rise of the so-called ‘gig economy,’” says Anna Manzoni, corresponding author of the study and an associate professor of sociology at North Carolina State University. “We wanted to see what role ...
Noble false widow spider found preying on pygmy shrew
2023-02-21
Scientists at University of Galway have published the first record of a noble false widow spider feeding on a pygmy shrew, a species of tiny mammal protected in Ireland.
The new study, recently published in the international journal Ecosphere, demonstrates further the potentially negative impact of the invasive and venomous noble false widow spider on native species.
A recording by Dawn Sturgess showing the spider interacting with the pygmy shrew be downloaded at https://bit.ly/3XPbDKU.
It is the first time a member of this family of spiders, ...
Starch gelatinization, retrogradation, and the world’s fluffiest white bread (video)
2023-02-21
WASHINGTON, Feb. 21, 2023 — If you want to make the fluffiest bread possible, you’re going to need to use chemistry. This week, we explore the science behind starch gelatinization, a phenomenon found in Chinese “tangzhong” and Japanese “yudane” techniques. Then, we put it to the test to see how much gelatinized starch it takes to make the fluffiest, tastiest and most stale-resistant loaf! https://youtu.be/3ziMBDPMuP8
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to ...