(Press-News.org) Public lecture: how can we have a good future with artificial intelligence?AI expert and educator Professor Anikó Ekárt to discuss one of today’s most provocative topics
Lecture will take place on 28 February at Aston University
Talk to explore artificial intelligence’s capabilities, benefits and pitfalls.
The potential impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on our daily lives will be explored in a public lecture at Aston University.
The University is inviting the public onto its campus on Tuesday 28 February to hear Professor Anikó Ekárt discuss one of today’s most provocative topics.
Research into AI began in the1950s and since then it has played an increasing role in daily lives, such as chatbots and digital assistants.
As an AI researcher and educator, Professor Ekárt will take a pragmatic view of the technology, arguing that society will benefit from it – but only if it is used responsibly.
She said: “Digital assistants based on speech recognition are now broadly accepted and successfully embedded in many business services.
“However, the most recent release of a chatbot with amazing writing capabilities has divided the world; some are relieved that their job may now become substantially easier, but others have questioned the impact of this on education.
“In the lecture, I’ll suggest three key directions; responsible use of AI, exploring many AI techniques rather than focusing on just one, and educating the public about AI’s capabilities, benefits and pitfalls.”
She will illustrate the success and further potential of less well-known AI techniques, such as evolutionary computation, genetic programming and symbolic regression, based on her 25 years of research.
Anikó who is a professor of artificial intelligence, joined Aston University in 2006 as a lecturer. She leads the artificial intelligence research theme within the School of Informatics and Digital Engineering.
Her research interests are centred around AI methods and their application, focusing on evolutionary algorithms and genetic programming. She has successfully contributed to applications of AI techniques to health, engineering, transport, and art. In 2022 she was the winner of the Evo* Award for Outstanding Contribution to Evolutionary Computation in Europe.
The free event will be taking place on 28 February from 6 pm to 8 pm and will be followed by a drinks reception. To sign up for a place visit https://www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/an-inaugural-lecture-by-professor-aniko-ekart-tickets-516518760517
END
Public lecture: how can we have a good future with artificial intelligence?
2023-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds parents serve as a safety net as grown kids navigate the workforce
2023-02-21
A new study underscores the role that parents play as a safety net for their young adult children as those children navigate the labor market, and highlights the challenges facing young adults who do not have access to parental support.
“In recent decades, we’ve seen a lot of changes in the labor market, from the decline of lifetime employment at one job to the rise of the so-called ‘gig economy,’” says Anna Manzoni, corresponding author of the study and an associate professor of sociology at North Carolina State University. “We wanted to see what role ...
Noble false widow spider found preying on pygmy shrew
2023-02-21
Scientists at University of Galway have published the first record of a noble false widow spider feeding on a pygmy shrew, a species of tiny mammal protected in Ireland.
The new study, recently published in the international journal Ecosphere, demonstrates further the potentially negative impact of the invasive and venomous noble false widow spider on native species.
A recording by Dawn Sturgess showing the spider interacting with the pygmy shrew be downloaded at https://bit.ly/3XPbDKU.
It is the first time a member of this family of spiders, ...
Starch gelatinization, retrogradation, and the world’s fluffiest white bread (video)
2023-02-21
WASHINGTON, Feb. 21, 2023 — If you want to make the fluffiest bread possible, you’re going to need to use chemistry. This week, we explore the science behind starch gelatinization, a phenomenon found in Chinese “tangzhong” and Japanese “yudane” techniques. Then, we put it to the test to see how much gelatinized starch it takes to make the fluffiest, tastiest and most stale-resistant loaf! https://youtu.be/3ziMBDPMuP8
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to ...
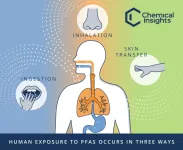
Chemical Insights Research Institute and Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health team to study the human health impact of PFAS chemical exposure
2023-02-21
ATLANTA – Feb. 21, 2023 – Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes and Emory University's Rollins School of Public Health have announced upcoming research to study human exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that approximately 97% of Americans have detectable PFAS levels in their blood. The joint study aims to understand how this exposure occurs and the potential health consequences.
Although humans may be exposed to PFAS by ingesting food or ...
These sports sensors could curb ‘bad calls’ and help players during practices
2023-02-21
If you watched the most recent Super Bowl, you know the importance of a referee’s call on the outcome of a game. Slow-motion replays and close-watching eyes help, but a new sensor technology could someday serve as an even more reliable tool for officials. Researchers reporting in ACS Applied Nano Materials have developed a self-powered, hybrid nanogenerator sensor that could help make more accurate calls and allow boxers and cricket players to practice more efficiently.
As sensors become less complicated and more ubiquitous, their applications have stretched into the world of sports, ...
Black patients more prone to dialysis graft failure
2023-02-21
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Compared to other races, African American patients are more likely to experience premature arteriovenous (AV) graft failure in the treatment of advanced kidney failure, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Chronic kidney disease affects roughly 37 million U.S. adults, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Over time, chronic kidney disease can result in kidney failure.
One treatment option for advanced kidney failure is hemodialysis, or dialysis, ...
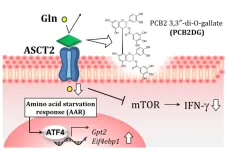
Polyphenols may be missing component in regulating inflammatory immune responses
2023-02-21
PCB2DG, a polyphenol with anti-inflammatory properties, works by targeting and directly interacting with the major glutamine transporter protein, alanine serine cysteine transporter 2 (ASCT2), to inhibit the uptake of glutamine, an important amino acid found in the blood. This reduction of intracellular glutamine accumulation in CD4+ T cells also reduces the production of interferon-gamma, or IFN-γ showing promise in the future of dietary polyphenol treatment for those suffering from autoimmune diseases. Additionally, the identification of ASCT2 as the target protein of PCB2DG is one ...
Study unlocks clues in mystery of naked mole-rats’ exceptional fertility
2023-02-21
Unlike humans and other mammals, which become less fertile with age, naked mole-rats can reproduce throughout their remarkably long lifespans. A new study, published today in Nature Communications, sheds light on unique processes that bestow the rodents with what seems like eternal fertility, findings that could eventually point to new therapies for people.
“Naked mole-rats are the weirdest mammals,” said lead author Miguel Brieño-Enríquez, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor at Magee-Womens Research Institute and the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine’s Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences. “They’re ...
Infants outperform AI in “commonsense psychology”
2023-02-21
Infants outperform artificial intelligence in detecting what motivates other people’s actions, finds a new study by a team of psychology and data science researchers. Its results, which highlight fundamental differences between cognition and computation, point to shortcomings in today’s technologies and where improvements are needed for AI to more fully replicate human behavior.
“Adults and even infants can easily make reliable inferences about what drives other people’s ...
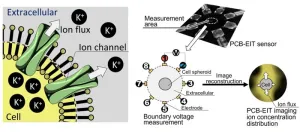
Non-invasive imaging of spatiotemporal ion distribution across cell membranes
2023-02-21
The cell membrane has numerous channels for the transport of various substances, including ions, between the cell and its environment. Ion transport determines the ion exchange rate (or the transmembrane transport coefficient), which, in turn, controls biological functions, such as nerve excitation, heartbeat, muscle contraction, and hormone secretion. It can also be anisotropic, wherein a non-uniform distribution of ions causes different ion exchange rates in different directions. This effect is quite pronounced in heterogeneous tissues. Therefore, the boundaries and overlap of tissues can be detected by measuring the associated anisotropic transmembrane transport.
Fluorescence ...