(Press-News.org) Feb. 22, 2022 — In this high-tech era, wearable devices such as smartwatches have proven to be invaluable companions for the health conscious. But a new study from the University of Utah shows that for a small group of people, some of these electronic fitness gadgets could possibly be risky to their health — even potentially deadly.
University of Utah electrical and computer engineering assistant professor Benjamin Sanchez Terrones and U associate professor of medicine Benjamin Steinberg have published a new study that shows wearable devices such as the Samsung Galaxy watch 4, Fitbit smart scales, or Moodmetric smart rings, among others, have sensing technology that could interfere with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) such as pacemakers, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), and cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices.
“This study raises a red flag,” says Sanchez Terrones. “We have done this work in simulations and benchtop testing following Food and Drug Administration accepted guidelines, and these gadgets interfere with the correct functioning of the CIEDs we tested. These results call for future clinical studies evaluating the translation of our findings to patients wearing CIEDs and using these wearable devices.”
Their study was published in the newest edition of the scientific journal, Heart Rhythm. The paper, authored by U electrical and computer engineering graduate student Gia-Bao Ha, Sanchez Terrones, Steinberg, U internal medicine professor Roger Freedman, and Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona cardiology professor Antoni Bayés-Genís, can be read here.
At issue are specific wearable smartwatches, at-home smart scales, and smart rings that utilize bioimpedance, a type of sensing technology that emits a very small, imperceptible current of electricity (measured in microamps) into the body. For smartwatches like the Samsung Galaxy Watch 4 or the Fitbit Aria 2 smart scale, the electrical current flows through the body and the response is measured by the sensor to determine the person’s body composition such as skeletal muscle mass or fat mass. For smart rings like the Moodmetric smart ring, bioimpedance sensing technology is used to measure a person’s level of stress.
But after conducting comprehensive testing of bioimpedance on three cardiac CRT devices from manufacturers Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott, Sanchez Terrones’ team learned the slight electrical currents from these wearable gadgets can interfere and sometimes confuse cardiac implantable devices into operating incorrectly.
In the case of a pacemaker, which sends small electrical impulses to the heart when it is beating too slowly, the bioimpedance’s tiny electrical current could trick the heart into thinking it is beating fast enough, preventing the pacemaker from doing its job when it is supposed to.
“We have patients who depend on pacemakers to live,” Steinberg, a cardiac electrophysiologist, says. “If the pacemaker gets confused by interference, it could stop working during the duration that it is confused. If that interference is for a prolonged time, the patient could pass out or worse.”
For other types of medical devices such as implantable cardioverter-defibrillators, which not only act as a pacemaker but can also shock the heart to restore a regular heart rhythm, a wearable device with bioimpedance could trick the defibrillator into delivering the patient an unneeded electric shock, which can be painful.
Nearly all if not all implantable cardiac devices already warn patients about the potential for interference with a variety of electronics due to magnetic fields, such as carrying a mobile phone in your breast pocket near a pacemaker. But Sanchez-Terrones says this is the first time a study has discovered problems associated with a gadget’s bioimpedance sensing technology.
“The scientific community doesn’t know about this,” he says. “No one has looked at whether this is a real concern or not.”
Sanchez Terrones and Steinberg emphasize that the research does not convey an immediate or clear risk to patients who use these kinds of wearable devices, but they believe it’s a first step for further study.
“We need to test across a broader cohort of devices and possibly in patients with these devices,” Steinberg said.
“Ultimately, more studies are needed to evaluate the clinical translation of our findings and ensure the health of our patients,” Sanchez Terrones added.
This news release and photos may be downloaded from attheu.utah.edu/category/news-releases.
END
Shock to the system
University of Utah study shows certain wearable gadgets could interfere with implantable cardiac electronic devices
2023-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Promising new ENIGMA study launches to determine factors contributing to brain aging
2023-02-22
As part of an effort to address a diversity crisis in brain research, a USC-led brain research consortium is launching a massive data-gathering initiative in India. By 2050, 79% of the world's population over age 60 will live in developing countries, with 20% in India, according to the United Nations. Yet most brain research has been conducted in Caucasian populations from relatively wealthy backgrounds. This lack of ethnic diversity means that we do not know if predictors of health and disease generalize to other ethnic groups, and researchers struggle ...
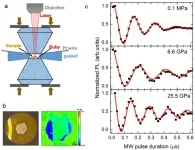
Novel quantum detection method developed to solve the problem of in-situ sensitive magnetic measurement under high pressure
2023-02-22
Substances exhibit many novel properties under high pressure, for example, pressure can induce insulator-metal or even superconductor transition. However, in-situ magnetic measurement is always a difficult problem in high pressure research and restricts the study of superconductor's Meissner effect and magnetic phase transition behavior of magnetic materials at high pressures.
A new high pressure in-situ magnetic detection method was developed recently by a collaborated research group of Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences, ...
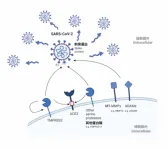
HKUMed identifies novel host protease determinants for SARS-CoV-2 infection
2023-02-22
Researchers from Department of Microbiology, School of Clinical Medicine, LKS Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), has identified novel host protease determinants, that facilitate the infection of SARS-CoV-2, including the Omicron variant, which provided new targets for combating the pandemic. In addition to the host protease determinants, members from the membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase (MT-MMP) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) families were found to be able to mediate SARS-CoV-2 entry, with an increase efficiency against Omicron BA.1. This finding suggests that a new treatment strategy at MMP inhibition should be explored to effectively combat ...
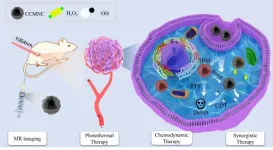
Novel method with carbon-coated magnetite nanoclusters proposed in cancer synergistic therapy
2023-02-22
Recently, Prof. WANG Hui, together with Prof. LIN Wenchu and associate Prof. QIAN Junchao from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a NIR- II -responsive carbon-coated iron oxide nanocluster which was guided by magnetic resonance image and capable of combined photothermal and chemodynamic therapy (CDT).
Relevant results were published in SCIENCE CHINA Materials.
As a promising treatment strategy, CDT has become a hot spot in treating cancer because of its simple operation and low side effects. The basic ...
New research reveals 12 ways aquaculture can benefit the environment
2023-02-22
Aquaculture, or the farming of aquatic plants and animals, contributes to biodiversity and habitat loss in freshwater and marine ecosystems globally, but when used wisely, it can also be part of the solution, new research shows.
Published today in Conservation Biology, University of Melbourne researchers have identified 12 potential ecological benefits of aquaculture. These include species recovery, habitat restoration, rehabilitation and protection, and removal of overabundant species.
Lead ...
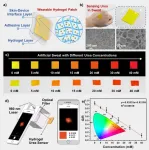
New approach allows faster test of urea in body fluids
2023-02-22
Recently, a research team from the Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a wearable sensing patch and realized rapid quantitative analysis of urea.
The related results have been published in prestigious international journal Analytical Chemistry.
Urea, which is excreted through sweat, urine, saliva and blood, is considered an important indicator of renal function in clinical diagnosis. Effective detection of urea level is crucial for early detection of disease. Wearable fluorescence-based sensors have attracted much attention of users, but traditional fluorescent hydrogels ...
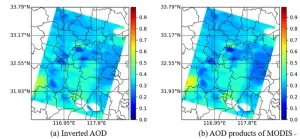
Novel algorithm proposed for inversion of aerosol optical depth
2023-02-22
To meet the requirements of single-angle and multi-band polarization aerosol detection, a research team led by Professor SUN Xiaobing from Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed an optimal inversion algorithm based on the combined utilization of multi-band intensity and polarization information.
The result was published in Remote Sensing recently.
Aerosol optical depth (AOD) is used to characterize the extinction effect of aerosol on solar radiation, which plays ...
Therapeutic importance of Ganoderma lucidum highlighted in recent review paper
2023-02-22
According to the research published in Food & Functions recently, a team led by Prof. Huang Qing at the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), reported for the first time an update and a comprehensive summary of the studies on the immunomodulatory therapies and nutritional significance of Ganoderma lucidum (G. lucidum) from 2010 to 2022, and confirmed that G. lucidum is an essential prebiotic for increasing bacterial flora and a health encouraging agent because of its ...
Alliance for Science and Boyce Thompson Institute launch SciFun Book: A biotechnology program for high school learners
2023-02-22
NAIROBI, KENYA, February 22, 2023 - Alliance for Science (the Alliance) and Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) are excited to launch the SciFun Book, a biotechnology program for high school learners, at the Safari Park Hotel in Nairobi on February 23, 09:00 AM EAT. The SciFun program is designed for Form 2 and Form 3 learners and aims to enhance their understanding of biotechnology through hands-on experience in extracting DNA from fruits and vegetables while making observations about the process.
The curriculum for the SciFun program is a collaborative product of Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO) Science Centre and BTI, and Alliance for Science. Additional ...
A 5-minute PCR, faster than self-diagnosis kits
2023-02-22
PCR technology is a molecular diagnostics technology that detects target nucleic acids by amplifying the DNA amount. It has brought marked progress in the life sciences field since its development in 1984. This technology has recently become familiar to the public due to the COVID-19 pandemic, since PCR can detect nucleic acids that identify the COVID-19 virus. However, due to the technical nature of the PCR test, results cannot be immediately delivered. It takes at least 1 to 2 hours for the test as it requires repeated temperature cycles (60~95℃).
Dr. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] Shock to the systemUniversity of Utah study shows certain wearable gadgets could interfere with implantable cardiac electronic devices