(Press-News.org) Measuring a key blood molecule may help doctors diagnose whether or how much impaired blood flow to a patient’s brain is contributing to dementia or cognitive problems, according to a new study led by a UCLA Health researcher.
Cerebral small vessel disease, a common disease marked by damage to the cells lining the blood vessels in the brain, is a major driver of cognitive problems and dementia in older adults. However, it can be difficult for doctors to determine whether a patient’s cognitive impairments stem predominately from Alzheimer’s disease or vascular problems, the two most common causes of dementia. Doctors typically rely on MRIs or CAT scans to detect evidence of brain injury to help make that determination, but a certain amount of guesswork is involved.
In new research published Feb. 23 in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, researchers found that patients with higher levels of placental growth factor (PlGF) – a key molecule involved in the formation of new blood vessels, or angiogenesis – were more likely to have cognitive impairment or evidence of brain injury.
“Historically, diagnostic studies for cognitive impairment and dementia have been limited to structural brain imaging, but increasingly there’s a recognition that we can use the bloodstream as an available but imperfect tool to understand who maximally benefits from those structural and functional imaging tools,” said UCLA Associate Professor and Vice Chair of Research in Neurology Jason Hinman, MD, PhD, the study’s lead author. “It may also tell us who might be the best candidates for some of the really new emerging drugs that are available on the market to treat cognitive impairment and dementia.”
The study represents some of the first validation results reported by a NIH-funded consortium of academic medical centers working to identify biomarkers associated with vascular drivers behind cognitive impairment to help inform diagnosis and treatment. The consortium, known as MarkVCID, was formed in 2016 after researchers recognized they needed a better handle on precisely how vascular brain injury was contributing to dementia.
Researchers identified signaling involved in angiogenesis as potential biomarkers, theorizing that the body may respond to damaged small blood vessels in the brain with intensified efforts to grow more. For this study, researchers focused on just one of those signals, PlGF, which has previously been associated with cerebral blood flow regulation. Data also gathered by the consortium had suggested this may be a useful biomarker for identifying patients with cognitive impairment and dementia due to vascular brain injury.
At UCLA and four other research sites, 335 patients underwent brain imaging, cognitive testing and blood collection. Researchers found those in the top quartile for PlGF measurement were three times as likely to have cognitive impairment or dementia compared to those in the bottom quartile. Every unit increase in total PlGF in the bloodstream was also associated with a 22% increase in the likelihood of having cognitive impairment and a 16% increase in the likelihood of having imaging evidence of cerebral small vessel disease.
“The addition of a blood-based biomarker that is associated with the traditional measures of vascular injury could allow a provider to be able to distinguish the patient that has Alzheimer's-predominant dementia versus a significant vascular contribution,” Dr. Hinman said. “Right now it’s kind of the clinician’s best guess. This work can directly inform this diagnostic decision.”
The research consortium is still studying whether PlGF and a bundle of other angiogenic markers in the bloodstream could help predict the risk of future cognitive decline. Patients interested in enrolling in ongoing studies at UCLA can learn more and register here.
Other study authors include Fanny Elahi, Davis Chong, Hannah Radabaugh, Adam Ferguson, Pauline Maillard, Jeffrey F, Thompson, Gary A. Rosenberg, Abhay Sagare, Abhay Moghekar, Hanzhang Lu, Tiffany Lee, Donna Wilcock, Claudia L. Satizabal, Russell Tracy, Sudha Seshadri, Kristin Schwab, Karl Helmer, Herpreet Singh, Pia Kivisäkk, Steve Greenberg, Charlie DeCarli, and Joel Kramer.
MarkVCID is supported by NIH (grant numbers: U24NS100591, UH2NS100599, UH2/UH3NS100605, UH2NS100588, UH2NS100608, UH2NS100606, UH2NS100598, UH2NS100614, UF1NS125513). Drs. Satizabal and Seshadri are partly supported by P30 AG066546. Dr. Seshadri is also supported by the Bill and Rebecca Reed Endowment for Precision Therapies and Palliative Care and by an endowment from the Barker Foundation.
END
Researchers identify biomarker for diagnosing vascular dementia
Signaling in the bloodstream could make it easier for doctors to distinguish between most common sources of dementia
2023-02-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pairing students supports integration at universities
2023-02-23
The university world is international, but grapples with difficulties in integrating students from different countries. New research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, points to a method that both reduces academic and social gaps and increases well-being. The recipe for success is to work in pairs – as chosen by the teacher.
There is plenty of research indicating that integration is a decisive factor for a successful student life, both socially and academically, for the individual and for the university. Students who are involved in activities and feel connected to their fellow students can get higher grades and are more likely to continue ...
Novel air filter captures wide variety of pollutants
2023-02-23
PULLMAN, Wash. -- An air filter made out of corn protein instead of petroleum products can concurrently capture small particulates as well as toxic chemicals like formaldehyde that current air filters can’t.
The research could lead to better air purifiers, particularly in regions of the world that suffer from very poor air quality. Washington State University engineers report on the design and tests of materials for this bio-based filter in the journal Separation and Purification Technology.
“Particulate matter is not that challenging to filter but to simultaneously capture various kinds of chemical ...
Patients with high blood pressure who partnered with community health workers more likely to achieve blood pressure control
2023-02-23
Patients with hypertension paired with a community health worker (CHW) through their primary care practice were more than three and a half times as likely to achieve blood pressure control within six months compared to patients who were not. New research, led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, suggest that similar CHW inventions could help other underserved, immigrant communities experiencing similar disparities.
Published online today in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, the findings focus on community health workers (CHWs), lay members of a community who usually share ethnicity, language, income level, and/or life experiences with the people ...
Dr. Omar Abdul-Rahman named Chief of Division of Medical Genetics in Pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital
2023-02-23
Dr. Omar Abdul-Rahman, a leading specialist in pediatric genetic medicine, has been named chief of the Division of Medical Genetics in the Department of Pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, effective March 1.
The Division of Medical Genetics provides inpatient and outpatient consultation and medical care for children and adolescents with common and rare genetic conditions, including screening and counseling for inherited disease risk during pregnancy. Dr. Abdul-Rahman, who was recruited ...
New treatment regimen may decrease mortality in patients with cardiotoxicity from immune checkpoint inhibitors
2023-02-23
Bottom Line: Among cancer patients who developed cardiotoxicity after treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, those treated with abatacept (Orencia), ruxolitinib, and/or mechanical ventilation as needed had a significantly lower mortality rate than those treated with standard-of-care corticosteroids.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Joe-Elie Salem, MD, PhD, a professor at Sorbonne Université, and executive assistant director of one of France’s Clinical Investigation Centers focused on cardio-metabolism
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors comprise ...
U.S. Department of Energy announces $68 million for small businesses developing technologies to cut emissions and study climate
2023-02-23
WASHINGTON, D.C.—The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced awards totaling more than $68 million that will go to 53 small businesses that are solving scientific problems. Projects include developing tools for climate research and advanced materials and technologies for clean energy conversion. Understanding the climate and the ability to convert and store energy are instrumental to meeting President Biden’s goal of a completely clean electrical grid by 2035 and net-zero greenhouse-gas emissions ...
Researchers identify breakthrough in understanding fentanyl abuse
2023-02-23
The ongoing opioid epidemic continues to take a heavy toll on American communities, with more than 80,000 opioid-related deaths reported in 2021, according to the National Institutes of Health. Despite the severity of this issue, the neurological mechanisms underlying opioid addiction, withdrawal and relapse are not fully understood.
A study recently published in Cell Reports sheds light on the subject. Jun Wang, associate professor in the Department of Neuroscience and Experimental Therapeutics at the Texas A&M University School of Medicine, and members ...
Simplified HIV treatment options just as effective: Major clinical trial
2023-02-23
(SEATTLE, Wednesday 22 February 2023) Two newer simplified treatment options are at least as effective as current approaches, according to the results of a world-first international clinical trial into second-line HIV therapy led by the Kirby Institute at UNSW Sydney and presented today at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in Seattle.
Second-line treatment is the name given to the range of treatment options available to a person for whom the first HIV treatment offered to them does not work. Worldwide, this is about 10% of people ...
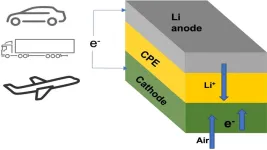
New design for lithium-air battery could offer much longer driving range compared with the lithium-ion battery
2023-02-23
Many owners of electric cars have wished for a battery pack that could power their vehicle for more than a thousand miles on a single charge. Researchers at the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT) and U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have developed a lithium-air battery that could make that dream a reality. The team’s new battery design could also one day power domestic airplanes and long-haul trucks.
The main new component in this lithium-air battery is a solid electrolyte instead of the usual liquid variety. Batteries with solid electrolytes ...
Parkinson’s disease patients experience significant reduction in symptoms with non-surgical focused ultrasound treatment
2023-02-23
VIDEOS: Interviews, B-Roll
https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fo/b1tpiamgunp5ekymyxaks/h?dl=0&rlkey=zk15bee6kru69ebryxaha0g3j
YouTube Video. Unlisted & only viewable w/ link until embargo lifts. https://youtu.be/Ceg7R3sw7Qs
Patients with Parkinson’s disease achieved a significant improvement in their tremors, mobility, and other physical symptoms after having a minimally invasive procedure involving focused ultrasound, according to a new study today published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The clinical trial was led by researchers at the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify biomarker for diagnosing vascular dementiaSignaling in the bloodstream could make it easier for doctors to distinguish between most common sources of dementia