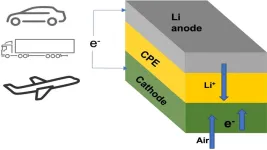
(Press-News.org) Many owners of electric cars have wished for a battery pack that could power their vehicle for more than a thousand miles on a single charge. Researchers at the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT) and U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have developed a lithium-air battery that could make that dream a reality. The team’s new battery design could also one day power domestic airplanes and long-haul trucks.
The main new component in this lithium-air battery is a solid electrolyte instead of the usual liquid variety. Batteries with solid electrolytes are not subject to the safety issue with the liquid electrolytes used in lithium-ion and other battery types, which can overheat and catch fire.
“The lithium-air battery has the highest projected energy density of any battery technology being considered for the next generation of batteries beyond lithium ion.” — Larry Curtiss, Argonne Distinguished Fellow
More importantly, the team’s battery chemistry with the solid electrolyte can potentially boost the energy density by as much as four times above batteries">lithium-ion batteries, which translates into longer driving range.
“For over a decade, scientists at Argonne and elsewhere have been working overtime to develop a lithium battery that makes use of the oxygen in air,” said Larry Curtiss, an Argonne Distinguished Fellow. “The lithium-air battery has the highest projected energy density of any battery technology being considered for the next generation of batteries beyond lithium-ion.”
In past lithium-air designs, the lithium in a lithium metal anode moves through a liquid electrolyte to combine with oxygen during the discharge, yielding lithium peroxide (Li2O2) or superoxide (LiO2) at the cathode. The lithium peroxide or superoxide is then broken back down into its lithium and oxygen components during the charge. This chemical sequence stores and releases energy on demand.
The team’s new solid electrolyte is composed of a ceramic polymer material made from relatively inexpensive elements in nanoparticle form. This new solid enables chemical reactions that produce lithium oxide (Li2O) on discharge.
“The chemical reaction for lithium superoxide or peroxide only involves one or two electrons stored per oxygen molecule, whereas that for lithium oxide involves four electrons,” said Argonne chemist Rachid Amine. More electrons stored means higher energy density.
The team’s lithium-air design is the first lithium-air battery that has achieved a four-electron reaction at room temperature. It also operates with oxygen supplied by air from the surrounding environment. The capability to run with air avoids the need for oxygen tanks to operate, a problem with earlier designs.
The team employed many different techniques to establish that a four-electron reaction was actually taking place. One key technique was transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of the discharge products on the cathode surface, which was carried out at Argonne’s Center for Nanoscale Materials, a DOE Office of Science user facility. The TEM images provided valuable insight into the four-electron discharge mechanism.
Past lithium-air test cells suffered from very short cycle lives. The team established that this shortcoming is not the case for their new battery design by building and operating a test cell for 1000 cycles, demonstrating its stability over repeated charge and discharge.
“With further development, we expect our new design for the lithium-air battery to also reach a record energy density of 1200 watt-hours per kilogram,” said Curtiss. “That is nearly four times better than lithium-ion batteries.”
This research was published in a recent issue of Science. Argonne authors include Larry Curtiss, Rachid Amine, Lei Yu, Jianguo Wen, Tongchao Liu, Hsien-Hau Wang, Paul C. Redfern, Christopher Johnson and Khalil Amine. Authors from IIT include Mohammad Asadi, Mohammadreza Esmaeilirad and Ahmad Mosen Harzandi. And Authors from the University of Illinois Chicago include Reza Shahbazian-Yassar, Mahmoud Tamadoni Saray, Nannan Shan and Anh Ngo.
The research was funded by the DOE Vehicle Technologies Office and the Office of Basic Energy Sciences through the Joint Center for Energy Storage Research.
About Argonne’s Center for Nanoscale Materials
The Center for Nanoscale Materials is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers, premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE’s Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge, Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit https://science.osti.gov/User-Facilities/User-Facilities-at-a-Glance.
The Joint Center for Energy Storage Research (JCESR), a DOE Energy Innovation Hub, is a major partnership that integrates researchers from many disciplines to overcome critical scientific and technical barriers and create new breakthrough energy storage technology. Led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, partners include national leaders in science and engineering from academia, the private sector, and national laboratories. Their combined expertise spans the full range of the technology-development pipeline from basic research to prototype development to product engineering to market delivery.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation’s first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America’s scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science.
TAGS: batteries-and-fuel-cells">Batteries And Fuel Cells, Scientific User Facilities
END
New design for lithium-air battery could offer much longer driving range compared with the lithium-ion battery
New batteries could one day power cars, airplanes, trucks
2023-02-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Parkinson’s disease patients experience significant reduction in symptoms with non-surgical focused ultrasound treatment
2023-02-23
VIDEOS: Interviews, B-Roll
https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fo/b1tpiamgunp5ekymyxaks/h?dl=0&rlkey=zk15bee6kru69ebryxaha0g3j
YouTube Video. Unlisted & only viewable w/ link until embargo lifts. https://youtu.be/Ceg7R3sw7Qs
Patients with Parkinson’s disease achieved a significant improvement in their tremors, mobility, and other physical symptoms after having a minimally invasive procedure involving focused ultrasound, according to a new study today published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The clinical trial was led by researchers at the ...
UTA research explores how T-cells detect cancer
2023-02-23
A University of Texas at Arlington bioengineering professor is leading a state-funded project that will try to identify what T-cells are detecting in cancerous cells to better craft a personalized cancer immunotherapy.
George Alexandrakis received a $250,000 Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) grant titled “Ultrasensitive Nanosensor-Based Detection of Tumor Immunogenic Peptides to Enable Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy.”
“One of the challenges with cancer is that it is so variable. It changes all the time and is different in all people,” Alexandrakis said. ...
After 25 years of AI health tech research computers are slowly beginning to listen to patients
2023-02-23
Patients experiences of health conditions are slowly being integrated into healthcare AI studies, a review of 25 years of studies has found.
In a new paper published in Lancet Digital Health along with an associated opinion piece, experts from the University of Birmingham and University Hospitals Birmingham have looked at more than 600 interventional studies on AI healthcare technologies.
While the team, funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), found that only 24% of studies have a patient reported outcome element included in their study, there has been an increase in the number in recent years with 2021 and 2022 seeing nearly two thirds of all studies ...
Prioritise tackling toxic emissions from tyres, urge Imperial experts
2023-02-23
Imperial experts are calling for more to be done to limit the potentially harmful impact of toxic tyre particles on health and the environment.
The researchers, from Imperial College London’s Transition to Zero Pollution initiative, warn that even though electric vehicles remove the problem of fuel emissions, we will continue to have a problem with particulate matter because of tyre wear.
Six million tonnes of tyre wear particles are released globally each year, and in London alone, 2.6 million vehicles emit around nine thousand tonnes of tyre wear particles annually.
Despite this, research on the environmental ...
Surge in nitrous oxide abuse: New guidelines to help clinicians recognise cases and prevent spinal cord damage
2023-02-23
Recommendations from research published today on the diagnosis and treatment of spinal cord damage caused by nitrous oxide abuse have been simultaneously adopted as official clinical practice guidelines by the Association of British Neurologists. The unprecedented speed in translating research into practice is necessary as medical cases of nitrous oxide abuse surge in parallel with increased use of what is now the second most popular recreational drug among young people in the UK.
Recreational use of nitrous oxide (N2O - also known as laughing gas) ...
Technical adequacy of artificial intelligence body composition assessed in external CT
2023-02-23
Leesburg, VA, February 23, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), certain reasons for AI tool failure relating to technical factors may be largely preventable through proper acquisition and reconstruction protocols.
“The automated AI body composition tools had high technical adequacy rates in a heterogeneous sample of external CT examinations, supporting the tools’ generalizability and potential for broad use,” concluded head researcher B. Dustin Pooler, MD, from the University of ...
New predatory fish species which lived about 360 million years ago may have grown to over 2.5m long, according to analysis of South African fossils
2023-02-22
New predatory fish species which lived about 360 million years ago may have grown to over 2.5m long, according to analysis of South African fossils
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281333
Article Title: A high latitude Gondwanan species of the Late Devonian tristichopterid Hyneria (Osteichthyes: Sarcopterygii)
Author Countries: South Africa, Sweden
Funding: PEA: Wallenberg Scholarship (not numbered), from the Knut & Alice Wallenberg Foundation. https://kaw.wallenberg.org PEA: ERC Advanced ...
Influence of US weather conditions on tornado trends since 1980 explored by new model
2023-02-22
Influence of US weather conditions on tornado trends since 1980 explored by new model
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281312
Article Title: Long term temporal trends in synoptic-scale weather conditions favoring significant tornado occurrence over the central United States
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Cash transfers in LMICs may help alleviate depression and anxiety symptoms - especially if such transfers are unconditional
2023-02-22
Cash transfers in LMICs may help alleviate depression and anxiety symptoms - especially if such transfers are unconditional
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281283
Article Title: Do cash transfers alleviate common mental disorders in low- and middle-income countries? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Author Countries: UK, Germany
Funding: JS was supported by the Joachim Herz Foundation (https://www.joachim-herz-stiftung.de/en/). AR received funding from the Wellcome Trust (220206/Z/20/Z, ...
Two high status brothers had access to “brain surgery” in Bronze Age Israel
2023-02-22
Two high status brothers buried in a Bronze Age tomb in Israel were severely ill but apparently had access to rare treatments including trephination, according to a study published February 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Rachel Kalisher of Brown University, Rhode Island, and colleagues.
In this study, authors examined the remains of two individuals buried in a tomb beneath an elite residence in the archaeological site of Tel Megiddo in Israel. The tomb dates to the Late Bronze Age (around 1550-1450 BC), and DNA testing suggests the buried individuals are brothers. Both skeletons show evidence of disease, providing an opportunity ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
[Press-News.org] New design for lithium-air battery could offer much longer driving range compared with the lithium-ion batteryNew batteries could one day power cars, airplanes, trucks