(Press-News.org) New predatory fish species which lived about 360 million years ago may have grown to over 2.5m long, according to analysis of South African fossils
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281333
Article Title: A high latitude Gondwanan species of the Late Devonian tristichopterid Hyneria (Osteichthyes: Sarcopterygii)
Author Countries: South Africa, Sweden
Funding: PEA: Wallenberg Scholarship (not numbered), from the Knut & Alice Wallenberg Foundation. https://kaw.wallenberg.org PEA: ERC Advanced Grant ERC-2020-ADG 10101963 "Tetrapod Origin", from the European Research Council. https://erc.europa.eu/homepage RWG: Millennium Trust, South Africa (no number). https://www.mtrust.co.za RWG: GENUS (DSI-NRF Centre of Excellence in Palaeosciences), South Africa (no number). https://www.genus.africa RWG: NRF of South Africa (no number). https://www.nrf.ac.za The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
New predatory fish species which lived about 360 million years ago may have grown to over 2.5m long, according to analysis of South African fossils
2023-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Influence of US weather conditions on tornado trends since 1980 explored by new model
2023-02-22
Influence of US weather conditions on tornado trends since 1980 explored by new model
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281312
Article Title: Long term temporal trends in synoptic-scale weather conditions favoring significant tornado occurrence over the central United States
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Cash transfers in LMICs may help alleviate depression and anxiety symptoms - especially if such transfers are unconditional
2023-02-22
Cash transfers in LMICs may help alleviate depression and anxiety symptoms - especially if such transfers are unconditional
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281283
Article Title: Do cash transfers alleviate common mental disorders in low- and middle-income countries? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Author Countries: UK, Germany
Funding: JS was supported by the Joachim Herz Foundation (https://www.joachim-herz-stiftung.de/en/). AR received funding from the Wellcome Trust (220206/Z/20/Z, ...
Two high status brothers had access to “brain surgery” in Bronze Age Israel
2023-02-22
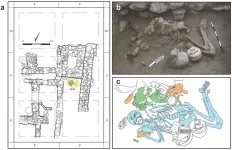
Two high status brothers buried in a Bronze Age tomb in Israel were severely ill but apparently had access to rare treatments including trephination, according to a study published February 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Rachel Kalisher of Brown University, Rhode Island, and colleagues.
In this study, authors examined the remains of two individuals buried in a tomb beneath an elite residence in the archaeological site of Tel Megiddo in Israel. The tomb dates to the Late Bronze Age (around 1550-1450 BC), and DNA testing suggests the buried individuals are brothers. Both skeletons show evidence of disease, providing an opportunity ...
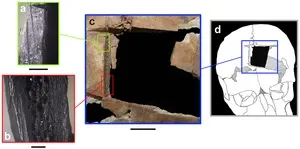
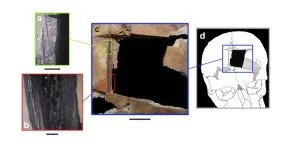
Archaeologists uncover early evidence of brain surgery in Ancient Near East
2023-02-22
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Archaeologists know that people have practiced cranial trephination, a medical procedure that involves cutting a hole in the skull, for thousands of years. They’ve turned up evidence that ancient civilizations across the globe, from South America to Africa and beyond, performed the surgery.
Now, thanks to a recent excavation at the ancient city of Megiddo, Israel, there’s new evidence that one particular type of trephination dates back to at least the late Bronze Age.
Rachel Kalisher, a Ph.D. candidate at Brown University’s Joukowsky ...
Keeping babies alive will lower population growth – new research
2023-02-22
Keeping babies alive will lower population growth – new research
New research showing high infant mortality rates are contributing to an incessant rise of the global human population supports arguments for greater access to contraception and family planning in low- and middle-income nations.
In an article published in PLOS ONE, research led by Professor Corey Bradshaw, Matthew Flinders Professor of Global Ecology from Flinders University and Peter Le Souëf, Professor of Paediatrics from The University of Western Australia has found that with higher baby death rates and larger household sizes (as an indicator of population density), ...
First transient electronic bandage speeds healing by 30%
2023-02-22
Wireless, battery-free bandage delivers electrical signals to help wounds heal
Bandage monitors healing, streaming data in real time to a smartphone or tablet
After healing is complete, bandage and electronics harmlessly absorb into the body
EVANSTON, Ill. — Northwestern University researchers have developed a first-of-its-kind small, flexible, stretchable bandage that accelerates healing by delivering electrotherapy directly to the wound site.
In an animal study, the new bandage healed ...
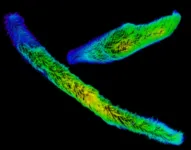
Giant proteins in a giant cell: Molecular basis behind fastest biological movement of single-celled eukaryotes
2023-02-22
In his famous letter to the Royal Society dated Oct. 9, 1676, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described a single-celled eukaryote (Vorticella) and its fascinating ultrafast cell contraction as the first set of discoveries. This kind of ultrafast cell contraction triggered by a Ca2+-dependent mechanism is distinct from the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-dependent mechanisms found in actin-myosin and dynein/kinesin-tubulin systems.
Spirostomum, is a genus of millimeter-scale single-celled protists that are known for their incredibly rapid movement like Vorticella. They are capable ...
Bow-and-arrow, technology of the first modern humans in Europe 54,000 years ago at Mandrin, France
2023-02-22
If the emergence of mechanically propelled weapons in prehistory is commonly perceived as one of the hallmarks of the advance of modern human populations into the European continent, the existence of archery has always been more difficult to trace. The recognition of these technologies in the European Upper Paleolithic has been hampered by ballistic overlaps between weapons projected with a thruster or a bow. Archery technologies are essentially based on the use of perishable materials; wood, fibers, leather, resins, and sinew, which are rarely preserved in European Paleolithic sites and make archaeological recognition ...
Climate change, urbanization drive major declines in L.A.’s birds
2023-02-22
Berkeley — Climate change isn’t the only threat facing California’s birds. Over the course of the 20th century, urban sprawl and agricultural development have dramatically changed the landscape of the state, forcing many native species to adapt to new and unfamiliar habitats.
In a new study, biologists at the University of California, Berkeley, use current and historical bird surveys to reveal how land use change has amplified — and in some cases mitigated — the impacts of climate ...
Twin-bioengine self-adaptive micro/nanorobots developed for gastrointestinal inflammation therapy
2023-02-22
Micro/nanorobots with self-propelling and -navigating capabilities have attracted extensive attention in drug delivery and therapy owing to their controllable locomotion in hard-to-reach body tissues.
However, developing self-adaptive micro/nanorobots that can adjust their driving mechanisms across multiple biological barriers to reach distant lesions is still a challenge.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. CAI Lintao from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy ...