(Press-News.org) The latest evidence on the treatment of urgent heart problems will be revealed at ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).
Acute cardiovascular care focuses on patients with life-threatening conditions such as heart attack, cardiac arrest, acute heart failure and cardiogenic shock. The annual congress of the Association for Acute CardioVascular Care (ACVC), a branch of the ESC, takes place 24 to 26 March at the Marseille Parc Chanot Exhibition and Convention Centre in Marseille, France. Explore the scientific programme.
New scientific findings will be showcased in the abstracts. Among them:
Emergency cardiology department experience in wartime Ukraine.
Mental health after cardiac arrest – are women and men affected differently?
Should people aged 90 years and above with acute coronary syndromes receive stents?
Impact of COVID-19 on acute coronary syndrome patients.
Do heart attack symptoms vary between men and women?
Stay tuned for lively scientific sessions featuring the hottest topics in acute cardiovascular care. Not to miss: management of patients with acute chest pain in the emergency department.1 Should the diagnostic process vary according to gender? Professor Ingo Ahrens, Congress Chairperson, said: “Women and men present with different clinical symptoms, and whether diagnosis and treatment should be tailored is a major area of debate. Randomised clinical trials are investigating this issue. It is hugely important because diagnosis of the underlying severe acute cardiovascular disorder may be misinterpreted if gender-specific clinical presentation is not taken into account.”
Also on the agenda: artificial intelligence (AI) in acute cardiology.2 Find out how AI is currently being used and what is on the horizon. “In acute cardiology, AI is mainly used in imaging techniques, for example echocardiography, and for electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis,” said Professor Ahrens. “In the future AI will likely use the ECG and other measurements to predict the prognosis of individual patients including the likelihood of dying while in hospital with an acute cardiac condition and the risk of having another event after discharge. Hopefully that will allow us to provide personalised treatment to prevent adverse outcomes.”
Time is of the essence in cardiac arrest, and the first few minutes have a substantial impact on survival and brain function. Hear international experts share state-of-the-art evidence on achieving the best recovery and engaging members of the public to help victims.3 “Cardiac arrest happens suddenly and means that the heart stops pumping blood,” said Professor Ahrens. “People who witness a cardiac arrest can save lives by performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and using an automated external defibrillator (AED). Restoring circulation to the brain and heart quickly gives patients the best chance of returning to full health.”
Also of interest: managing cholesterol to prevent second heart attacks.4 Professor Ahrens said: “After an acute coronary syndrome, patients are at high risk of recurrent cardiovascular events, particularly within the first year after discharge from hospital.5 It is of utmost importance to ensure that low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels are as low as possible to reduce the likelihood of further events. Waiting to implement optimal cholesterol lowering measures puts patients at risk and key opinion leaders will outline why we should ‘strike early and strong’ to reduce LDL.”5
The meeting brings together cardiologists, intensivists, anaesthesiologists, internists, cardiac surgeons, nurses, paramedics and other allied professionals who care for acutely ill cardiac patients.
Register as press now for ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2023 and receive press releases from the leading scientific event in the field.
ENDS
END
ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2023: improving survival from cardiac emergencies
24 to 26 March in Marseille, France
2023-02-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Black women of childbearing age more likely to have high blood pressure, raising pregnancy risks
2023-02-27
Research Highlights:
Black women of childbearing age were more than twice as likely to have uncontrolled blood pressure than white women of similar age, putting them at an increased risk of pregnancy-related complications.
This disparity in high blood pressure persisted after adjusting for social determinants of health, health factors and modifiable health behaviors.
Food insecurity — lack of access to adequate healthy food — one of the social factors that may affect high blood pressure risk, was higher among Hispanic and Black women compared with white women.
The research is featured in a special Go Red for Women issue of the Journal of the American Heart Association focused ...
Reproductive factors in women contribute to risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-02-27
Peer-reviewed / Mendelian Randomization / People
An earlier first birth, a higher number of live births, and starting periods at a younger age are all linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular problems in women, according to new research.
The study, led by Imperial College London researchers, provides evidence for a causal relationship between sex-specific factors and cardiovascular disease in women, and identifies potential ways to mediate this increased risk.
The study is the most comprehensive analysis to date of reproductive factors specific to women and their links ...
New link between fatal muscle wasting disease gene and cancer discovered
2023-02-27
Mutations of the gene encoding dystrophins have long been known to cause the debilitating muscle-wasting disease DMD, which affects one in every 5,000 boys born. People with the condition will usually only live into their 20s or 30s.
Now, a study, led by the University of Portsmouth, has found that the same gene has a role in oncology. A team of international researchers analysed a broad spectrum of malignant tissues, including from breast, ovarian, and gastrointestinal cancer patients.
The DMD gene expression was reduced in 80 per cent of these tumours. This low expression of dystrophins was associated with a more advanced stage of cancer and reduced ...
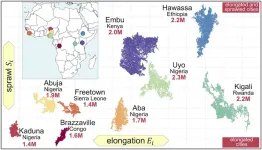
Measuring 6,000 African cities: Double the population means triple the energy costs
2023-02-27
Using a new dataset, Rafael Prieto-Curiel of the Complexity Science Hub and colleagues analyzed the coordinates and surface of 183 million buildings in nearly 6,000 cities across all 52 countries in Africa. With their model, they quantify the shape of cities. Thus, they show that if a city's population doubles, the energy demand associated with commuting triples. These results clearly show how important it will be to plan fast-growing cities in a sustainable way.
“Our model allows us to estimate African cities’ transport requirements and energy needs with a never before seen accuracy,” Prieto-Curiel, researcher at the Complexity ...
National Comprehensive Cancer Network announces collaboration with blood cancer experts in Poland
2023-02-27
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [February 27, 2023] — Today, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—a not-for-profit alliance of leading United States cancer centers—announced a new collaboration with the Institute of Hematology and Transfusion Medicine in Poland (IHIT), and the Alliance For Innovation—Polish-American Foundation (AFI). The three organizations have signed an agreement enabling clinicians to share their established expertise and international experience in order to improve quality of care and outcomes for patients with hematologic ...
Black people less likely to receive dementia-related medications
2023-02-27
MINNEAPOLIS – Black people are receiving medications for dementia less often than white people, according to a preliminary study released today, February 26, 2023, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 75th Annual Meeting being held in person in Boston and live online from April 22-27, 2023.
“Previous research has shown that due to racial disparities, people with dementia do not always receive the same access to medications that may be beneficial in nursing homes and hospitals,” said Alice Hawkins, MD, of Mount Sinai in New York, New York, and a member of the ...
Voluntary UK initiatives to phase out toxic lead shot for pheasant hunting have had little impact
2023-02-27
Three years into a five-year pledge to completely phase out lead shot in UK game hunting, a Cambridge study finds that 94% of pheasants on sale for human consumption were killed using lead.
The pledge, made in 2020 by nine major UK game shooting and rural organisations, aims to protect the natural environment and ensure a safer supply of game meat for consumers. Lead is toxic even in very small concentrations, and discarded shot from hunting poisons and kills tens of thousands of the UK’s wild birds each year.
A Cambridge-led team of 17 volunteers bought whole pheasants from butchers, game ...
Genes & Cancer | Severe herpesvirus infection beats adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
2023-02-25
“Although contracting herpes simplex or herpes zoster is unpleasant, the mechanism by which these herpesvirus infections can produce a therapeutic effect […]”
BUFFALO, NY- February 24, 2023 – A new editorial was published in Genes & Cancer on January 19, 2023, entitled, “Severe herpesvirus infection beats adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.”
In this recently published editorial, researcher Tatsuro Jo from the Japanese Red Cross Nagasaki Genbaku Hospital’s Department of Hematology discussed aggressive type adult T-cell ...
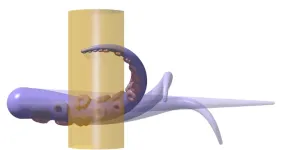
Reaching like an octopus: A biology-inspired model opens the door to soft robot control
2023-02-25
Octopus arms coordinate nearly infinite degrees of freedom to perform complex movements such as reaching, grasping, fetching, crawling, and swimming. How these animals achieve such a wide range of activities remains a source of mystery, amazement, and inspiration. Part of the challenge comes from the intricate organization and biomechanics of the internal muscles.
This problem was tackled in a multidisciplinary project led by Prashant Mehta and Mattia Gazzola, professors of mechanical science & engineering at the University of Illinois ...
Notable inaccuracies found in insurers’ mental health care provider directories in California
2023-02-25
As the mental health crisis continues across the nation, many people struggle to find the care they need. Health insurers publish directories of mental health providers to help consumers obtain care; however, inaccurate directories and a shortage of providers within many insurance networks can make finding covered mental health services challenging.
The U.S. federal government and those of many states have put regulations in place to ensure provider directory accuracy, with California having some of the most stringent rules. However, research on the accuracy of mental health care provider directories has been limited. Simon Haeder, PhD, associate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2023: improving survival from cardiac emergencies24 to 26 March in Marseille, France