Unfortunately, spawning Chinook salmon are increasingly younger and concentrated within fewer age groups, with the oldest age classes of spawners rarely seen in recent years. The new study, published February 27 in the Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, suggests changes in hatchery practices and fishery management could help restore the age structure of the salmon population and make it more resilient to climate change.
The researchers focused on Sacramento River fall-run Chinook salmon, which contribute heavily to the salmon fisheries of California and southern Oregon. This population is particularly susceptible to the effects of increasingly severe drought conditions driven by climate change.
“As we get more variable climate conditions, with greater extremes of rainfall and drought, we are going to see more ‘boom-and-bust’ population dynamics unless we start to restore the age structure of the population, which can spread out the effects of good and bad years across time,” said senior author Eric Palkovacs, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology and director of the Fisheries Collaborative Program at UC Santa Cruz.
If most of the salmon return to spawn at the same age, one bad year could be devastating for the overall population. Spreading the risk over multiple years is an example of what ecologists call the “portfolio effect,” like a financial portfolio that spreads risk over multiple investments.
First author Paul Carvalho, a postdoctoral fellow with the Fisheries Collaborative Program, explained that juvenile salmon are especially vulnerable to the effects of drought as they migrate to the ocean from freshwater rivers and streams.
“We focused on the impacts of drought on the survival of juvenile salmon, but drought conditions can also increase mortality of returning adult salmon as they migrate upstream to spawn,” he said.
Carvalho developed a life cycle model of the Sacramento River fall-run Chinook salmon population to simulate the effects of different drought scenarios and other variables on the population. The model was grounded in data from field studies, such as research by NOAA Fisheries scientists that quantified the relationship between river flows and survival rates of juvenile salmon.
The model allowed the researchers to assess the effects of different mechanisms that can affect the age structure of the population. A century ago, most of the spawning salmon returning to the Sacramento River watershed were four years old, and some were as old as six years. Today, however, six-year-old fish are rarely observed and most of the spawners are three years old.
“Historically, you would have seen huge salmon coming back at older ages, but over the past century they’ve gotten smaller and younger,” Palkovacs said. “The dominant age class is now 3 years, and there are very few even at age 5, so there’s been a big shift in the age structure.”
Decreased size and age at maturity is a classic pattern of fisheries-induced evolution. A high mortality rate for older fish selects for fish that mature at earlier ages, because a fish that dies before it can spawn doesn’t pass on its genes. But fishing pressure is not the only factor driving changes in the age structure of the salmon population. Hatchery practices can also inadvertently select for earlier maturation.
“It’s pretty clear that current hatchery practices are resulting in very homogeneous populations returning at age three,” Palkovacs said. “Rather than producing a uniform product, it would be better to increase the diversity of the age structure by selecting older, larger fish and making sure you get as many of them into the spawning population as possible.”
Carvalho noted that improving the age structure of the population by selecting for fish that spend more years at sea (delayed maturation) would be most effective in combination with reduced harvest rates.
“Because the fish remain in the ocean longer, they are exposed to the fishery and other causes of mortality for a longer period, so that reduces the number returning to spawn if you don’t reduce fishing pressure on those older age classes,” he said.
Overall, the results show that maintaining or increasing the age structure through reduced mortality and delayed maturation improves the stability of the salmon population, buffering against the adverse effects of drought and making the population more resilient in an increasingly variable climate.
“Regardless of the mechanism, whether it’s reduced mortality or delayed maturation that’s driving it, increasing the diversity of the age structure will increase the stability of the population,” Carvalho said.
In addition to Carvalho and Palkovacs, the coauthors of the paper include William Satterthwaite, Michael O’Farrell, and Cameron Speir at the NOAA Southwest Fisheries Science Center. This work was supported by the Cooperative Institute for Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Systems (CIMEAS) and the NOAA Quantitative Ecology and Socioeconomics Training (QUEST) Program.
END
Shrinking age distribution of spawning salmon raises climate resilience concerns
Study suggests changes in hatchery practices could help increase population stability for Sacramento River fall-run Chinook salmon, the backbone of California’s salmon fishery
2023-02-27
(Press-News.org) By returning to spawn in the Sacramento River at different ages, Chinook salmon lessen the potential impact of a bad year and increase the stability of their population in the face of climate variability, according to a new study by scientists at UC Santa Cruz and NOAA Fisheries.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ipek receives funding to write book on everyday life of activism in Lebanon
2023-02-27
Yasemin Ipek, Assistant Professor, Global Affairs Program, received funding to write a book on diverse meanings and implications of being an activist in Lebanon.
The book, titled: "Crisiswork: Activism, Class-Making, and Bounded Futures in Lebanon," will be a study of the emergent forms of activism and political subjectivity in contemporary Lebanon in relation to lived experiences of crisis.
Ipek aims to answer the question: "How has the recent mobilization of civil society activism shaped politics and everyday life in Lebanon?"
She intends to answer that question by ethnographically studying activism as a contentious ...
Lum and Koper receive funding for application of evidence-based policing to investigations in Seattle police department
2023-02-27
Cynthia Lum, Professor and Director, Evidence-Based Crime Policy (CEBCP), Criminology, Law and Society, and Christopher Koper, Associate Professor, Criminology, Law and Society, received funding for: "Application of Evidence-Based Policing to Investigations in the Seattle Police Department."
The purpose of this contract is to provide the Seattle Police Department with an evidence-based assessment of its investigations practices and to make recommendations on improving the alignment of the agency with evidence-based approaches in this area.
Lum and Koper received $121,363 from ...
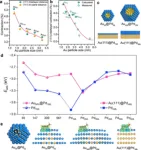
Researchers reveal conjugated dual size effect of core-shell bimetallic nanocatalysts
2023-02-27
Recently, a team led by Prof. LU Junling collaborating with Prof. LI Weixue’s and Prof. WEI Shiqiang’s team, revealed the conjugated dual size effect of core-shell bimetallic nanocatalysts for the first time, with the activity of the catalysts increases with the core size in the benzyl alcohol oxidation reaction. Their work was published in Nature Communications.
Bimetallic catalysts are widely used in different chemical synthesis for their bimetallic synergy varying with compositions and structures. Compared to alloy catalysts, the peculiar lattice ...
Babies born preterm decreased slightly and stillborn rates unchanged during first wave of COVID-19 lockdowns
2023-02-27
Babies born preterm decreased and stillborn rates remained unchanged during the first four months of COVID-19 lockdowns, according to a largescale international study.
The research of 52 million births from 26 countries, published in Nature Human Behavior, reported a 3-4 per cent reduction overall in preterm births, averting almost 50,000 preterm pregnancies during the first month of lockdown alone. But the decrease in preterm births was limited to only high-income countries including Australia.
The International Perinatal Outcomes in the Pandemic (iPOP) Study, ...
Plugging immune cell leakage from tumors could improve skin cancer treatment
2023-02-27
The number of specialized immune cells available for fighting skin cancer doubled when a new treatment blocked their escape from melanoma tumors, experiments in mice and human cells show.
Researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center who led the study found that combining a chemical blocker of immune cell exit with another drug type, an immunotherapy, stopped melanoma tumor enlargement in more than half of mice tested. Immunotherapy alone had previously failed to prevent the cancers’ growth.
Recent advances in immunotherapies, medications designed to help the body’s immune defense system ...
Corralling ions improves viability of next generation solar cells
2023-02-27
Researchers have discovered that channeling ions into defined pathways in perovskite materials improves the stability and operational performance of perovskite solar cells. The finding paves the way for a new generation of lighter, more flexible, and more efficient solar cell technologies suitable for practical use.
Perovskite materials, which are defined by their crystalline structure, are better at absorbing light than silicon is. That means that perovskite solar cells can be thinner and lighter than silicon solar cells without sacrificing the cell’s ...
Cleveland Clinic study finds common artificial sweetener linked to higher rates of heart attack and stroke
2023-02-27
Monday, February 27, 2023, Cleveland: New Cleveland Clinic research showed that erythritol, a popular artificial sweetener, is associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. Findings were published today in Nature Medicine.
Researchers studied over 4,000 people in the U.S. and Europe and found those with higher blood erythritol levels were at elevated risk of experiencing a major adverse cardiac event such as heart attack, stroke or death. They also examined the effects of adding erythritol to either whole blood or isolated platelets, which are cell fragments that clump together to stop bleeding and contribute to blood clots. Results revealed that ...
For-profit hospices deliver lower quality care than nonprofit hospices
2023-02-27
Patients receiving care from for-profit hospices have substantially worse care experiences than patients who receive care from not-for-profit hospices, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Analyzing surveys completed by family caregivers of patients treated by more than 3,100 hospices nationally, RAND researchers found that family members reported worse care experiences on average from for-profit hospices across all of the domains assessed, including help for pain and other symptoms and getting timely care.
The study found ...
Myocarditis or pericarditis after BNT162b2 vaccination in youth in Ontario
2023-02-27
About The Study: The results of this study of 1.65 million doses of BNT162b2 (Comirnaty [Pfizer-BioNTech]) vaccinations among adolescents in Ontario, Canada, suggest that there was variation in the reported incidence of myocarditis or pericarditis. However, the risk of these events after vaccination remains very rare and should be considered in relation to the benefits of COVID-19 vaccination.
Authors: Sarah E. Wilson, M.D., M.Sc., of Public Health Ontario in Toronto, is the corresponding ...
Association of cardiovascular health with life expectancy free of major chronic disease
2023-02-27
About The Study: A high level of cardiovascular health (CVH) was associated with substantially longer life expectancy free of four major chronic diseases (cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, and dementia) in both men and women in this study of 135,000 adults from the UK Biobank study. The disease-free life expectancy was similar between low and other socioeconomic groups among participants with high CVH. These findings support improvement in population health by promoting a high CVH level, which may also narrow health disparities associated with socioeconomic status.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., Ph.D., of Tulane University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] Shrinking age distribution of spawning salmon raises climate resilience concernsStudy suggests changes in hatchery practices could help increase population stability for Sacramento River fall-run Chinook salmon, the backbone of California’s salmon fishery