(Press-News.org) A new machine learning model can predict traffic activity in different zones of cities. To do so, a Complexity Science Hub researcher used data from a main car-sharing company in Italy as a proxy for overall city traffic. Understanding how different urban zones interact can help avoid traffic jams, for example, and enable targeted responses of policy makers - such as local expansion of public transportation.
Understanding people's mobility patterns will be central to improving urban traffic flow. “As populations grow in urban areas, this knowledge can help policymakers design and implement effective transportation policies and inclusive urban planning”, says Simone Daniotti of the Complexity Science Hub.
For example, if the model shows that there is a nontrivial connection between two zones, i.e., that people commute from one zone to another for certain reasons, services could be provided that compensate for this interaction. If, on the flip side, the model shows that there is little activity in a particular location, policymakers could use that knowledge to invest in structures to change that.
MODEL ALSO FOR OTHER CITIES LIKE VIENNA
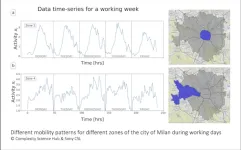
For this study a major car-sharing company provided the data: the location of all cars in their fleet in four Italian cities (Rome, Turin, Milan, and Florence) in 2017. The data was obtained by constantly querying the service provider's web APIs, recording the parking location of each car, as well as the start and end timestamps. "This information allows us to identify the origin and destination of each trip," Daniotti explains.
Daniotti used that as a proxy for all city traffic and created a model that not only allows accurate spatio-temporal forecasting in different urban areas, but also accurate anomaly detection. Anomalies such as strikes and bad weather conditions, both of which are related to traffic.
The model could also make predictions about traffic patterns for other cities such as Vienna. "However, this would require appropriate data," Daniotti points out.
OUTPERFORMING OTHER MODELS
While there are already many models designed to predict traffic behavior in cities, "the vast majority of prediction models on aggregated data are not fully interpretable. Even though some structure of the model connects two zones, they cannot be interpreted as an interaction" explains Daniotti. This limits understanding of the underlying mechanisms that govern citizens' daily routines.
Since only a minimal number of constraints are considered and all parameters represent actual interactions, the new model is fully interpretable.
BUT WHAT IS PREDICTION WITHOUT INTERPRETATION?
"Of course it is important to make predictions," Daniotti explains, "but you can make very accurate predictions, and if you don't interpret the results correctly, you sometimes run the risk of drawing very wrong conclusions."
Without knowing the reason why the model is showing a particular result, it is difficult to control for events where the model was not showing what you expected. “Inspecting the model and understanding it, helps us, and also policy makers, to not draw wrong conclusions,” Daniotti points out.
FIND OUT MORE:
The study “A maximum entropy approach for the modelling of car-sharing parking dynamics” has been published in Scientific Reports.
ABOUT THE COMPLEXITY SCIENCE HUB
The mission of the Complexity Science Hub (CSH Vienna) is to host, educate, and inspire complex systems scientists dedicated to making sense of Big Data to boost science and society. Scientists at the Complexity Science Hub develop methods for the scientific, quantitative, and predictive understanding of complex systems.
The CSH Vienna is a joint initiative of AIT Austrian Institute of Technology, Central European University CEU, Danube University Krems, Graz University of Technology, Medical University of Vienna, TU Wien, VetMedUni Vienna, Vienna University of Economics and Business, and Austrian Economic Chambers (WKO). https://www.csh.ac.at
END
Depression is more widespread among lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or questioning (LGBTQ) youth than heterosexual, cisgender youth, making parental support more important for these adolescents. A new study released in Child Development by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin looks at parental social support and psychological control in relation to depressive symptoms for LGBTQ youth in the United States. Psychological control attempts to intrude into the psychological and emotional development of the child (e.g., thinking processes, self-expression, emotions, and attachment to parents). Although ...
SUTD to Launch South-east Asia’s First O-RAN Open Testing and Integration Centre (OTIC)
Announced at the Mobile World Congress Barcelona (MWC) 2023, Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) will launch a new O-RAN[1] Asia & Pacific Open Testing and Integration Centre (OTIC) in Singapore. As part of Singapore’s S$70 million Future Communications R&D Programme (FCP) supported by Singapore’s Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) and the National Research Foundation, Singapore (NRF), the Asia & Pacific OTIC in Singapore ...
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar metals, which got their name because they typically occur at low concentrations (between 0.5 and 67 parts per million) within the Earth’s crust. Because they are indispensable in modern technology such as light emitting diodes, mobile phones, electromotors, wind turbines, hard disks, cameras, magnets, and low-energy lightbulbs, the demand for them has increased steadily over the past few decades, and is predicted to rise further by 2030.
As ...
A “biocomputer” powered by human brain cells could be developed within our lifetime, according to Johns Hopkins University researchers who expect such technology to exponentially expand the capabilities of modern computing and create novel fields of study.
The team outlines their plan for “organoid intelligence” today in the journal Frontiers in Science.
“Computing and artificial intelligence have been driving the technology revolution but they are reaching a ceiling,” said Thomas Hartung, a professor of environmental health sciences at ...
Amongst healthcare professionals, the feeling of being supported in the workplace can protect them against adverse mental health and burnout, according to a new study published in CMAJ Open by researchers at Queen Mary University of London and medical staff at various hospitals across the UK.
CoPE-HCP study was designed, during the early part of COVID-19 pandemic, when there was great concern for the mental health of healthcare professionals with no scientifically-proven mitigating strategies to reduce that impact. Funded by Barts Charity, this new longitudinal study found that feeling unsupported ...
LA JOLLA, CA—A clinical trial carried out at Scripps Research has shown that apremilast, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of psoriasis, cuts alcohol intake by more than half in people with severe alcohol use disorder (AUD). Collaborators at Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) and other institutions also showed that, in mice, apremilast boosts activity in an area of the brain known to be involved in AUD.
The research was published online ahead of ...
LA JOLLA, CA—The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) has awarded scientists at Scripps Research a $10 million grant to study the cellular and molecular changes in the brain that underlie alcohol use disorder (AUD). The grant will fund the Scripps Research Alcohol Research Center (TSRI-ARC) for five years, carrying the research into its 50th year of consecutive NIAAA funding—first beginning in 1977.
“A lot of exciting things have happened in the AUD field over the last 45 years, and the center has been at the forefront of many of them,” ...
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD]) is the first study to show that childhood obesity is associated with an increased risk of four of the five recently proposed subtypes of adult-onset diabetes. The study is by Yuxia Wei, Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and colleagues.
In 2018, a ground-breaking study identified five novel subtypes of adult-onset diabetes: severe autoimmune diabetes (SAID, including type 1 diabetes and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults [LADA]) and four ...
Nature has remained in balance for a long time, but climate change due to modern human activities is disrupting the balance of the natural system. The disruption makes it more difficult for humans – who must work with nature to survive – to predict the future. Moreover, developing countries with limited understanding and preparation for climate change are more vulnerable to climate change-driven social and economic damage. Recently, a research team from POSTECH corrected the biases of future regional climate model projection data to ...
Eliminating animal milk alone from the diet of adults with eosinophilic esophagitis, or EoE, is as effective at treating the disease as eliminating animal milk plus five other common foods, a clinical trial funded by the National Institutes of Health has found. For people with EoE whose disease remains active after they forgo animal milk, a more restrictive diet may help them achieve remission, according to the researchers. These findings were published today in the journal The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
“Diet-based therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis will be much ...