(Press-News.org) A total of 1,261,990 people will die from cancer in 2023 in the EU (EU-27). A further 172,314 people will die from the disease in the UK, according to new research published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Monday).
Researchers led by Carlo La Vecchia (MD), a professor at the University of Milan (Italy), estimate there will be a 6.5% fall in cancer death rates in men and a 3.7% fall in women between 2018 and 2023.
They predict that death rates from the ten most common cancers will continue to fall in most European countries in 2023, although the numbers of people dying will go up due to aging populations. A greater proportion of elderly people in the population means there is a greater number at the age where they are more likely to develop and die from cancer.
Compared to a peak in cancer death rates in 1988, the researchers calculate that nearly 5.9 million deaths will have been avoided in the 35 years between 1989 and 2023 in the EU-27. In the UK, 1.24 million deaths will have been avoided.
Prof. La Vecchia said: “If the current trajectory of declining cancer death rates continues, then it is possible there could be a further 35% reduction by 2035. More smokers quitting contribute to these favourable trends. In addition, greater efforts need to be made to control the growing epidemic in overweight, obesity and diabetes, alcohol consumption and infections, together with improvements in screening, early diagnosis and treatments.
“The advances in tobacco control are reflected in the favourable lung cancer trends but more could be done in this respect, particularly among women, as lung cancer death rates continue to rise among them. No deaths from lung cancer have been avoided in women, both in the EU-27 and the UK, during the period between 1989 and 2023.
“Pancreatic cancer is also a cause for concern, as death rates from this disease will not fall among men and will rise by 3.4% in women in the EU and 3.2% in women in the UK. Smoking can explain between about a quarter to a third of these deaths, and women, particularly in the middle and older age groups, did not give up smoking as early as men.”
The researchers analysed cancer death rates in the EU 27 Member States [2] as a whole and separately in the UK. They also looked at the five most populous EU countries (France, Germany, Italy, Poland and Spain) and, individually, for stomach, intestines, pancreas, lung, breast, uterus (including cervix), ovary, prostate, bladder and leukaemias for men and women [3]. Prof La Vecchia and his colleagues collected data on deaths from the World Health Organization and Eurostat databases from 1970 to 2018 for most of the EU-27 and the UK. This is the thirteenth consecutive year the researchers have published these predictions.
In the EU-27 countries the researchers predict that will be an age standardised rate (ASR) [4] of 123.8 deaths per 100,000 men by the end of 2023. In women, the age standardised death rate will be 79.3 per 100,000. In the UK, the death rates will be 106.5 and 83.5 per 100,000 for men and women, respectively.
Cancer death rates will fall for all cancers in men in the EU-27 and the UK. They will also fall for women in the UK. Among EU women, death rates will rise by 3.4% to nearly six per 100,000 for pancreatic cancer, and to just over 1% to 13.6 per 100,00 for lung cancer. Although there will be a 13.8% drop in lung cancer death rates among women in the UK, the death rate of 16.2 per 100,000 is still higher than among EU women because more UK women started smoking earlier than those in the EU. Lung cancer now kills more women in the UK than breast cancer, which has a death rate of 13.5 per 100,000.
When the researchers looked specifically at lung cancer death rates in five EU countries as well as the UK, they found that, although death rates are predicted to fall in men for all six countries, for women they will rise by nearly 14% in France, 5.6% in Italy and 5% in Spain. Among women in different age groups, the researchers found a decrease in predicted death rates from lung cancer among those aged 25 to 64, but an increase in those aged 65 to over 75 years, and consequently an increase overall.
“This is because women now aged 45 to 65, born in the 1960s and 1970s, have smoked less and stopped earlier than those born in the 1950s, who were in their twenties in the 1970s when smoking among young women was most prevalent,” said Prof. Eva Negri from the University of Bologna (Italy), co-leader of the research.
Colorectal (bowel) cancer will be the third biggest killer for women in both the EU and the UK: eight and ten per 100,000, respectively. Prostate cancer will be the third biggest killer for men: 9.5 and 11.2 per 100,000 in the EU and UK, respectively.
The researchers say that organised screening programmes using low dose computed tomography (CT scans) could reduce deaths from lung cancer by up to 20%. However, there are no such organised programmes in Europe, and it is too early to evaluate the impact of screening in the UK, following the Lung Cancer Screening trial.
The researchers highlight the role that overweight and obesity plays in cancers such as post-menopausal breast, endometrial (womb) cancer, stomach and colorectal cancer. Although death rates from stomach cancer are falling overall, mainly because of improved methods of food preservation, healthier diets and a decline in Helicobacter pylori infection, approximately a third of stomach cancers now occur in the cardia, the entrance to the stomach, and are associated with overweight and obesity and, hence, reflux, which is a risk factor for the development of cancer at this site. For colorectal cancer, death rates are falling in the EU but the decline has slowed in the UK.
“This is concerning as increases in both incidence and mortality from colorectal cancer in young women have been recorded in the UK. This can be partly explained by the prevalence of overweight and obesity, and alcohol and tobacco consumption,” said Prof. Negri.
The researchers caution that their estimates do not take account of the COVID pandemic, which occurred after the dates when data were available on cancer deaths. “The COVID-19 pandemic may have an effect on cancer mortality in 2023 as a result of delayed visits and procedures, influencing both secondary prevention and treatment, and disease management for cancer,” they write.
(ends)
Notes:
[1] “European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2023 with focus on lung cancer”, by M. Malvezzi et al. Annals of Oncology, doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.01.010
[2] At the time of this analysis, the EU had 27 member states, with the UK leaving in 2020. Cyprus was excluded from the analysis due to excessive missing data.
[3] The paper contains individual tables of cancer death rates for each of the six countries.
[4] Age-standardised rates per 100,000 of the population reflect the annual probability of dying adjusted to reflect the age distribution of a population.
END
Death rates from lung cancer will fall overall in the EU and UK in 2023, but rise among women in France, Italy and Spain
2023-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
As urban populations soar wastewater treatment struggles to find sustainable solutions
2023-03-06
Globally, activated sludge treats the majority of urban wastewaters; yet it is one of the most complex biological processes used. It is a sophisticated microbial process fraught with operational problems leading to occasional failures in achieving required effluent quality standards. With the increasing problem of partially treated and raw sewage entering rivers and estuaries, the pressure on the process to cope with ever increasing volumes of wastewater has never been so great.
With increasing volumes of dilute wastewater entering treatment plants the high variability in hydraulic and organic ...
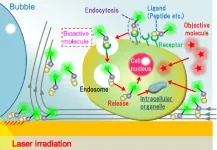
Light-induced acceleration of intracellular delivery
2023-03-06
Cell membranes are barriers that maintain cellular homeostasis, and the intracellular delivery of biologically functional molecules, including peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids to manipulate cellular functions. Conventional intracellular uptake processes require high concentrations of biofunctional molecules with low permeability to pass through the cell membrane. This results in low drug activity because the probability of the biofunctional molecules entering target cells and their organelles is low. In addition, many drugs damage healthy cells as well as the cells that are supposed to target due to poor selectivity, making ...
Physician workforce planning must adjust for aging population, changing practice patterns: New analysis
2023-03-06
Why are Canadians having problems accessing physicians despite historic highs in physician numbers? Factoring in changing demographics and physician work trends can help with physician workforce planning, according to a new analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221239.
"[T]he increasing [health care] needs of an aging population have been empirically important since around 2005, while the supply of physician service hours has simultaneously declined in a manner that is largely unrelated to the evolving age–sex composition of the physician workforce," writes Dr. Arthur Sweetman, ...
Pregnant people with schizophrenia have threefold risk of interpersonal violence
2023-03-06
Pregnant and postpartum people with schizophrenia have a more than threefold increase in the risk of an emergency department visit for interpersonal violence, compared with those without schizophrenia, according to a new study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.220689.
Interpersonal violence can include physical, sexual and psychological abuse by a family member, intimate partner, acquaintance or stranger.
"Though we found a threefold increased risk for individuals with schizophrenia, we also found that ...
Testing for ApoB protein may be a more accurate marker for heart disease risk than testing for cholesterol alone
2023-03-05
Getting tested for levels of HDL (the good) and LDL (the bad) cholesterol is part of the annual physical exam. But emerging research is showing that these standard tests may not be the most accurate way to test for heart disease risk.
Instead, emerging data suggest that testing for levels of Apolipoprotein B-100 (ApoB), a protein that carries fat molecules, including LDL cholesterol – the so-called “bad cholesterol” – around the body, may be a more accurate risk predictor of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, which occurs ...
Alert banners dramatically increase prescribing rates of life-saving heart failure medication
2023-03-05
An automated system that flags which patients could most benefit from an underused yet life-saving cardiology drug more than doubled new prescriptions, according to a pilot program test by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
“Our findings suggest that tailored electronic notifications can boost the prescription of life-saving drugs,” said study lead author and cardiologist Amrita Mukhopadhyay, MD, a clinical instructor in the Department of Medicine at NYU Langone Health. “By compiling key information in one place, the system may help providers to spend less time searching through medical records during a visit ...
Cardiovascular risk factor prevalence, treatment, control in young adults
2023-03-05
About The Study: In this study of nearly 13,000 U.S. adults ages 20 to 44, diabetes and obesity increased from 2009 to March 2020, while hypertension did not change and hyperlipidemia declined. The data from this study show a high and rising burden of most cardiovascular risk factors in young U.S. adults, especially for Black, Hispanic, and Mexican American individuals.
Authors: Rishi K. Wadhera, M.D., M.P.P., M.Phil., of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Transcatheter mitral valve repair in heart failure patients significantly reduces hospitalizations and improves survival
2023-03-05
Transcatheter mitral valve repair for heart failure patients with mitral regurgitation can reduce the long-term rate of hospitalizations by almost 50 percent, and death by nearly 30 percent, compared with heart failure patients who don’t undergo the minimally invasive procedure.
These are the breakthrough findings from a new study led by a researcher from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. This multi-center trial is the largest trial to examine the safety and effectiveness of transcatheter mitral-valve repair in a heart failure population using Abbott’s ...
COVID-19 infection leads to increased rates of chest pain six months to a year after infection in patients
2023-03-05
Even patients with mild COVID-19 infections can suffer from health complications for months, even years, post infection. Nearly 19% of U.S. adults who had previously tested positive for COVID-19 report having “Long COVID,” where they experience signs and symptoms for four weeks or more after the initial phase of infection.
In an effort to quantify what Long COVID means now, and could mean in the future for these patients, researchers from Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City studied nearly 150,000 ...
Humanity’s quest to discover the origins of life in the universe
2023-03-04
“We are living in an extraordinary moment in history,” says Didier Queloz, who directs ETH Zurich’s Centre for Origin and Prevalence of Life and the Leverhulme Centre for Life in the Universe at Cambridge. While still a doctoral student Queloz was the first to discover an exoplanet - a planet orbiting a solar-type star outside of Earth’s solar system. A discovery for which he would later receive a Nobel Prize in physics. Within a generation, scientists have now discovered more than 5,000 exoplanets and predict the potential existence of trillions more in the Milky Way galaxy alone. Each ...