(Press-News.org) Scientists in Japan have revealed a chemical compound that could be used for the treatment of various autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. These diseases occur when the body’s immune response goes wiry. The immune system, which normally attacks pathogens and infections, instead attacks healthy cells and tissues. For the millions of people who suffer from autoimmune diseases worldwide, the result can be debilitating—rheumatoid arthritis causes excessive joint pain, while multiple sclerosis can disable one’s brain and spinal cord function.
“The key to the development of autoimmune diseases, and thus the way to inhibit this development, lies in our cells, but the underlying mechanism has always been unclear,” stated Prof. Hiroki Ishikawa, who leads the Immune Signal Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST). “Now, our recent research has shed light on a compound that could suppress the development of these diseases.”
Prof. Ishikawa went on to explain that this research, published in Cell Reports, could lead to the development of treatments for autoimmune diseases.
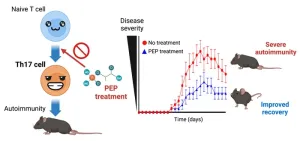
The research focused on T helper 17 cells, or Th17 cells. Th17 cells are a type of T cell—a group of cells, which form major parts of the immune system. These cells, which exist in high numbers in our guts, evolved to help us fight invasive pathogens but, sometimes, they’re overactivated and mistake normal, healthy tissue as pathogens, resulting in autoimmunity. The generation of Th17 cells requires glycolysis, a metabolic process in which glucose is broken down and converted to energy to support the metabolic needs of cells. Glycolysis is essential for the growth of not only Th17 cells but also a variety of cells in our body.
“What’s interesting in that excessive glycolysis seems to suppress Th17 cell activity,” stated first author, Mr. Tsung-Yen Huang, a PhD candidate in the Immune Signal Unit. “So, we hypothesized that molecules produced during glycolysis may inhibit the cells.”
Enter phosphoenolpyruvate, or PEP for short. This chemical compound is a metabolite produced when glucose is converted to energy. Since it is part of such an important process, PEP is generated every day in our bodies. The researchers found that treatment with PEP can inhibit the maturation of TH17 cells, leading to resolution of inflammatory response.
Mr. Huang explained how this was, at first, a confusing result, as it went against all other research on the topic, but he decided to persevere and take a closer look at what could be occurring.
The research led them to a protein called JunB, which is essential for the maturation of Th17 cells. JunB promotes Th17 maturation by binding to a set of specific genes. The researchers found that PEP treatment inhibits the generation of Th17 cells by blocking JunB activity.
Armed with this knowledge, the researchers went on to treat mice that had neuroinflammation caused by autoimmunity with PEP. This disease is very similar to multiple sclerosis and these mice showed positive signs of recovery. The scientists have now filed a patent to continue with this research.
“Our results show the clinical potential of PEP,” explained Mr. Huang. “But first we need to increase its efficiency.”
In the past, researchers who were interested in developing a treatment for autoimmune diseases, often looked at inhibiting glycolysis and thus Th17 cells. But glycolysis is essential to various types of cells in the body and inhibiting it could have significant side-effects. PEP has the potential to be used as a treatment without resulting in such side-effects.
END
Potential treatment of autoimmune diseases revealed in new study
Scientists have uncovered a chemical compound that holds potential as a therapeutical for various autoimmune diseases, and they’ve used it to treat mice.
2023-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Physical activity and tailored support fails to deliver lasting benefits for smokers not ready to quit
2023-03-06
Promoting physical activity and other behavioural support can help people wanting to reduce their smoking to quit in the short-term.
However, after nine months, physical activity delivers no noticeable benefits – compared with offering no additional support – in the rates of people stopping smoking, according to the findings of a major national study.
The Trial of physical Activity and Reduction of Smoking (TARS) study, led by the University of Plymouth with funding from the National Institute for Health and Care Research, took place across four cities – Plymouth, Nottingham, Oxford and ...
Death rates from lung cancer will fall overall in the EU and UK in 2023, but rise among women in France, Italy and Spain
2023-03-06
A total of 1,261,990 people will die from cancer in 2023 in the EU (EU-27). A further 172,314 people will die from the disease in the UK, according to new research published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Monday).
Researchers led by Carlo La Vecchia (MD), a professor at the University of Milan (Italy), estimate there will be a 6.5% fall in cancer death rates in men and a 3.7% fall in women between 2018 and 2023.
They predict that death rates from the ten most common cancers will continue to fall in most European countries in 2023, although the numbers of people dying will go up ...
As urban populations soar wastewater treatment struggles to find sustainable solutions
2023-03-06
Globally, activated sludge treats the majority of urban wastewaters; yet it is one of the most complex biological processes used. It is a sophisticated microbial process fraught with operational problems leading to occasional failures in achieving required effluent quality standards. With the increasing problem of partially treated and raw sewage entering rivers and estuaries, the pressure on the process to cope with ever increasing volumes of wastewater has never been so great.
With increasing volumes of dilute wastewater entering treatment plants the high variability in hydraulic and organic ...
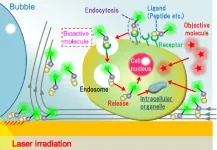
Light-induced acceleration of intracellular delivery
2023-03-06
Cell membranes are barriers that maintain cellular homeostasis, and the intracellular delivery of biologically functional molecules, including peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids to manipulate cellular functions. Conventional intracellular uptake processes require high concentrations of biofunctional molecules with low permeability to pass through the cell membrane. This results in low drug activity because the probability of the biofunctional molecules entering target cells and their organelles is low. In addition, many drugs damage healthy cells as well as the cells that are supposed to target due to poor selectivity, making ...
Physician workforce planning must adjust for aging population, changing practice patterns: New analysis
2023-03-06
Why are Canadians having problems accessing physicians despite historic highs in physician numbers? Factoring in changing demographics and physician work trends can help with physician workforce planning, according to a new analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221239.
"[T]he increasing [health care] needs of an aging population have been empirically important since around 2005, while the supply of physician service hours has simultaneously declined in a manner that is largely unrelated to the evolving age–sex composition of the physician workforce," writes Dr. Arthur Sweetman, ...
Pregnant people with schizophrenia have threefold risk of interpersonal violence
2023-03-06
Pregnant and postpartum people with schizophrenia have a more than threefold increase in the risk of an emergency department visit for interpersonal violence, compared with those without schizophrenia, according to a new study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.220689.
Interpersonal violence can include physical, sexual and psychological abuse by a family member, intimate partner, acquaintance or stranger.
"Though we found a threefold increased risk for individuals with schizophrenia, we also found that ...
Testing for ApoB protein may be a more accurate marker for heart disease risk than testing for cholesterol alone
2023-03-05
Getting tested for levels of HDL (the good) and LDL (the bad) cholesterol is part of the annual physical exam. But emerging research is showing that these standard tests may not be the most accurate way to test for heart disease risk.
Instead, emerging data suggest that testing for levels of Apolipoprotein B-100 (ApoB), a protein that carries fat molecules, including LDL cholesterol – the so-called “bad cholesterol” – around the body, may be a more accurate risk predictor of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, which occurs ...
Alert banners dramatically increase prescribing rates of life-saving heart failure medication
2023-03-05
An automated system that flags which patients could most benefit from an underused yet life-saving cardiology drug more than doubled new prescriptions, according to a pilot program test by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
“Our findings suggest that tailored electronic notifications can boost the prescription of life-saving drugs,” said study lead author and cardiologist Amrita Mukhopadhyay, MD, a clinical instructor in the Department of Medicine at NYU Langone Health. “By compiling key information in one place, the system may help providers to spend less time searching through medical records during a visit ...
Cardiovascular risk factor prevalence, treatment, control in young adults
2023-03-05
About The Study: In this study of nearly 13,000 U.S. adults ages 20 to 44, diabetes and obesity increased from 2009 to March 2020, while hypertension did not change and hyperlipidemia declined. The data from this study show a high and rising burden of most cardiovascular risk factors in young U.S. adults, especially for Black, Hispanic, and Mexican American individuals.
Authors: Rishi K. Wadhera, M.D., M.P.P., M.Phil., of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Transcatheter mitral valve repair in heart failure patients significantly reduces hospitalizations and improves survival
2023-03-05
Transcatheter mitral valve repair for heart failure patients with mitral regurgitation can reduce the long-term rate of hospitalizations by almost 50 percent, and death by nearly 30 percent, compared with heart failure patients who don’t undergo the minimally invasive procedure.
These are the breakthrough findings from a new study led by a researcher from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. This multi-center trial is the largest trial to examine the safety and effectiveness of transcatheter mitral-valve repair in a heart failure population using Abbott’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Potential treatment of autoimmune diseases revealed in new studyScientists have uncovered a chemical compound that holds potential as a therapeutical for various autoimmune diseases, and they’ve used it to treat mice.