(Press-News.org) Glass nanoparticles trapped by lasers in extreme vacuum are considered a promising platform for exploring the limits of the quantum world. Since the advent of quantum theory, the question at which sizes an object starts being described by the laws of quantum physics rather than the rules of classical physics has remained unanswered.
A team formed by Lukas Novotny (Zurich), Markus Aspelmeyer (Vienna), Oriol Romero-Isart (Innsbruck), and Romain Quidant (Zurich) is attempting to answer precisely this question within the ERC-Synergy project Q-Xtreme. A crucial step on the way to this goal is to reduce the energy stored in the motion of the nanoparticle as much as possible, i.e. to cool the particle down to the so-called quantum ground-state.
Control over all dimensions of movement
The Q-Xtreme team has been working together on ground-state cooling of nanoparticles for a long time. Several experiments in Zurich and Vienna, supported by theoretical calculations by Dr. Gonzalez-Ballestero and Prof. Romero-Isart at the University of Innsbruck, have led to the first demonstrations of such ground-state cooling of a nanoparticle, either by dampening the particle motion using electronic control (active feedback) or by placing the particle between two mirrors (cavity-based cooling). So far in experiments, the ground state has been achieved only along one of the three directions of particle motion, leaving the motion along the other two directions "hot".
“Achieving ground-state cooling along more than one direction is key for exploring novel quantum physics,” emphasizes Gonzalez-Ballestero of the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the Austrian Academy of Sciences and the Department of Theoretical Physics at the University of Innsbruck. “But so far this achievement remained elusive as it was challenging to make the mirrors between which the particle is positioned interact efficiently with the motion along some of the three directions” The so-called “Dark Mode Effect” prevented cooling to the full ground state.
With different frequencies towards the goal
Now, the research at the Photonics Laboratory of ETH Zurich has succeeded for the first time in ground-state cooling of a nanoparticle along two directions of motion. A glass sphere, about a thousand times smaller than a grain of sand, is completely isolated from its environment in a high vacuum and held by a strongly focused laser beam while simultaneously being cooled to near absolute zero. Based on theoretical predictions from the Innsbruck team, the Swiss physicists were able to circumvent the dark-state problem. "To do so, we designed the frequencies at which the particle oscillates in the two directions differently and carefully adjusted the polarization of the laser light," says Lukas Novotny of ETH Zurich.
The work, published in Nature Physics, demonstrates that it is possible to reach the minimum energy state for the three motional directions. It also allows to create fragile quantum states in two directions, which could be used to create ultrasensitive gyroscopes and sensors.
The research was financially supported by the European Research Council ERC and the European Union, among others.
Publication: Simultaneous ground-state cooling of two mechanical modes of a levitated nanoparticle. Johannes Piotrowski, Dominik Windey, Jayadev Vijayan, Carlos Gonzalez-Ballestero, Andrés de los Ríos Sommer, Nadine Meyer, Romain Quidant, Oriol Romero-Isart, René Reimann, Lukas Novotny. Nature Physics 2023 DOI: 10.1038/s41567-023-01956-1 [arXiv: 2209.15326]
END
Two-dimensional quantum freeze
Nanoparticles cooled to quantum ground-state in two motional dimensions.
2023-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists twist chemical bonds beyond their limits
2023-03-06
A group of scientists from Durham University and University of York have twisted molecules to their breaking point in order to challenge the understanding of chemical bonds.
The researchers explored how far the chemical bonding in an aromatic ring can be twisted before its aromatic bonding breaks.
They achieved this by making overcrowded aromatic rings. Rather than benzene, they used tropylium, which shares electrons around a ring of seven carbon atoms.
Each of these carbon atoms can be functionalised and having seven attachment points in the ring, rather than the six carbon atoms of benzene, allowed ...
Siblings should be screened in cases of suspected child physical abuse
2023-03-06
Siblings of a child suspected of experiencing physical abuse should also be screened for abusive injuries, according to a new international consensus statement led by researchers at UCL (University College London) and Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children (GOSH).
The team of 27 researchers, from six different continents, are calling for a policy change to stop inconspicuous injuries being missed in contact children (i.e. siblings, cohabiting children, or children who are under the same care), and to help prevent further ...
Rewarding accuracy instead of partisan pandering reduces Republican-Democrat divide over the truth – study
2023-03-06
Offering a tiny cash reward for accuracy, or even briefly appealing to personal integrity, can increase people’s ability to tell the difference between misinformation and the truth, according to a new study.
The findings suggest that fake news thrives on social media not only because people are tricked into believing it, but also due to a motivational imbalance: users have more incentive to get clicks and likes than to spread accurate content.
Social psychologists from the University of Cambridge and New York University argue that their study, published in the journal ...
New study compares human contributions to Mississippi river delta land loss, hints at solutions
2023-03-06
Research from scientists at Louisiana State University and Indiana University reveals new information about the role humans have played in large-scale land loss in the Mississippi River Delta—crucial information in determining solutions to the crisis.
The study published today in Nature Sustainability compares the impacts of different human actions on land loss and explains historical trends. Until now, scientists have been unsure about which human-related factors are the most consequential, and why the most rapid land loss in the Mississippi River Delta occurred between the 1960s and 1990s and ...
UCLA engineers design solar roofs to harvest energy for greenhouses
2023-03-06
As countries around the globe seek sustainable energy sources and the U.S. endeavors to become a net-zero emissions economy by 2050, renewable energy sources such as solar panels are in high demand.
However, solar panels can take up significant space and are often difficult to scale. Enter the new field of agrivoltaics, which focuses on the simultaneous use of land for both solar power generation and agriculture. For example, replacing the glass in greenhouses with solar panels could power the lamps and water controls in the greenhouse, or even the whole farm. But how does one build solar panels that can absorb energy from sunlight without blocking the light ...
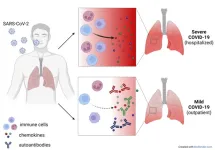
'Good autoantibodies' could help against long Covid
2023-03-06
Sometimes in the laboratory there are unexpected results. "Previously it had been observed that autoantibodies are common in severe Covid patients, those who end up in intensive care," says Jonathan Muri, postdoctoral fellow at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB, affiliated with the Università della Svizzera italiana) and co-author of the study. "Instead, in this case we discovered the opposite."
The autoantibodies in question neutralize chemokines, molecules that direct immune cell trafficking. "Chemokines are a bit like traffic lights: they tell our immune cells when and where to go in the case ...
Drones and deep learning: researchers develop a new technique to quantify rice production
2023-03-06
Rice, a major food crop, is cultivated on nearly 162 million hectares of land worldwide. One of the most commonly used methods to quantify rice production is rice plant counting. This technique is used to estimate yield, diagnose growth, and assess losses in paddy fields. Most rice counting processes across the world are still carried out manually. However, this is extremely tedious, laborious, and time-consuming, indicating the need for faster and more efficient machine-based solutions.
Researchers from China ...
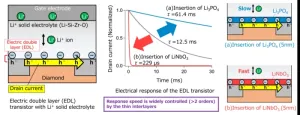
Controlling electric double layer dynamics for next generation all-solid-state batteries
2023-03-06
In our quest for clean energy and carbon neutrality, all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries (ASS-LIBs) offer considerable promise. ASS-LIBs are expected to be used in a wide range of applications including electric vehicles (EVs). However, commercial application of these batteries is currently facing a bottleneck—their output is reduced owing to their high surface resistance. Moreover, the exact mechanism of this surface resistance is hitherto unknown. Researchers have alluded it to a phenomenon called the “electric ...
Study finds silicon, gold and copper among new weapons against COVID-19
2023-03-06
New Curtin research has found the spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2, a strain of coronaviruses that caused the COVID-19 pandemic, become trapped when they come into contact with silicon, gold and copper, and that electric fields can be used to destroy the spike proteins, likely killing the virus.
Lead researcher Dr Nadim Darwish, from the School of Molecular and Life Sciences at Curtin University said the study found the spike proteins of coronaviruses attached and became stuck to certain types of surfaces.
“Coronaviruses have spike proteins on their periphery that allow them to penetrate host cells and cause infection and we have found these proteins becomes stuck to the surface ...
Electronic messages improved influenza vaccination rates in nationwide Danish study
2023-03-06
Approximately one billion people are infected with influenza around the world each year, with more than half a million deaths estimated to result from the disease. Despite the disease’s potential severity, especially among older populations and those with cardiometabolic risk factors, approximately 30 percent of U.S. adults over age 65 were not vaccinated during the 2019-2020 flu season. To evaluate best strategies for increasing vaccination rates, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Two-dimensional quantum freezeNanoparticles cooled to quantum ground-state in two motional dimensions.