Drunk mice sober up after a hormone shot
2023-03-07
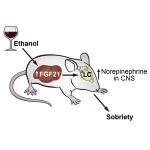
(Press-News.org) A hormone called fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) protects mice against ethanol-induced loss of balance and righting reflex, according to a study publishing on March 7 in the journal Cell Metabolism.
“We’ve discovered that the liver is not only involved in metabolizing alcohol but that it also sends a hormonal signal to the brain to protect against the harmful effects of intoxication, including both loss of consciousness and coordination,” says co-senior study author Steven Kliewer of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
“We’ve further shown that by increasing FGF21 concentrations even higher by injection, we can dramatically accelerate recovery from intoxication. FGF21 does this by activating a very specific part of the brain that controls alertness,” says Kliewer.
The consumption of ethanol produced by the natural fermentation of simple sugars in ripening fruits and nectars can cause intoxication, impairing mobility and judgement. Animals that consume fructose and other simple sugars have evolved liver enzymes to break down ethanol.
FGF21 is a hormone that is induced in the liver by a variety of metabolic stresses, including starvation, protein deficiency, simple sugars, and ethanol. In humans, ethanol is by far the most potent inducer of FGF21 described to date. Previous studies showed that FGF21 suppresses ethanol preference, induces water drinking to prevent dehydration, and protects against alcohol-induced liver injury.
In the new study, Kliewer and co-senior study author David Mangelsdorf of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center show that FGF21 plays a broader role in defending against the harmful consequences of ethanol exposure than previously thought. In mice, FGF21 stimulated arousal from intoxication without changing the breakdown of ethanol. Mice lacking FGF21 took longer than their littermates to recover their righting reflex and balance following ethanol exposure. Conversely, pharmacologic FGF21 administration reduced the time needed for mice to recover from ethanol-induced unconsciousness and lack of muscle coordination.
Surprisingly, FGF21 did not counteract sedation caused by ketamine, diazepam, or pentobarbital, indicating specificity for ethanol. FGF21 mediated its anti-intoxicant effects by directly activating noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus region in the brain, which regulates arousal and alertness. Taken together, the results suggest that the FGF21 liver-brain pathway evolved to protect against ethanol-induced intoxication. According to the authors, this pathway may modulate a variety of cognitive and emotional functions to enhance survival under stressful conditions.
Yet it remains to be determined whether activation of the noradrenergic system contributes to FGF21’s other effects, including those on metabolism and ethanol and sweet preference. Although both FGF21 and noradrenergic nervous system activity are induced by ethanol in humans, additional studies will also be required to determine whether FGF21’s anti-intoxicant activity translates to humans.
“Our studies reveal that the brain is the major site of action for FGF21’s effects,” Mangelsdorf says. “We are now exploring in greater depth the neuronal pathways by which FGF21 exerts its sobering effect.”
###
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Information about potential conflicts of interest can be found in the paper text.
Cell Metabolism, Choi et al. “FGF21 counteracts alcohol intoxication by activating the noradrenergic nervous system” https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(23)00041-4
Cell Metabolism (@Cell_Metabolism), published by Cell Press, is a monthly journal that publishes reports of novel results in metabolic biology, from molecular and cellular biology to translational studies. The journal aims to highlight work addressing the molecular mechanisms underlying physiology and homeostasis in health and disease. Visit http://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-07
At a glance:
New research suggests female mice show more stable exploratory behavior than male mice, despite hormone cycles
The results challenge a long-held assumption that hormones have a broad effect on behavior in female mice, making them less suitable for research
The findings make a strong scientific case for increasing the inclusion of female mice in neuroscience and other experiments
Mice have long been a central part of neuroscience research, providing a flexible model that scientists ...
2023-03-07
About The Study: This study of 24,000 participants age 45 or older found an independent association between perceived stress and both prevalent and incident cognitive impairment. The findings suggest the need for regular screening and targeted interventions for stress among older adults.
Authors: Ambar Kulshreshtha, M.D., Ph.D., of the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.1860)
Editor’s ...
2023-03-07
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that despite initial telemedicine gains at rural Veterans Affairs (VA) health care sites, the pandemic was associated with an increase in the rural-urban telemedicine divide across the VA health care system. To ensure equitable access to care, the VA health care system’s coordinated telemedicine response may benefit from addressing rural disparities in structural capacity (e.g., internet bandwidth) and from tailoring technology to encourage adoption among rural users.
Authors: Lucinda B. Leung, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System in Los Angeles, is the corresponding ...
2023-03-07
A United States Food and Drug Administration mandate to limit the dosage of acetaminophen in pills that combine acetaminophen and opioid medications is significantly associated with subsequent reductions in serious liver injury, according to a study led by investigators at the University of Alabama and Weill Cornell Medicine. The federal mandate was announced in 2011 and implemented in 2014. The results were reported March 7 in the medical journal JAMA.
“After researchers found that more than 40 percent of acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure cases involved combination acetaminophen and opioid medications, and an FDA advisory ...
2023-03-07
The selective breeding of grain crops is one of the main reasons why domesticated plants produce such excellent yields. Selecting the best candidates for breeding is, however, a remarkably complex task. On one hand, it requires a skilled breeder with trained eyes to assess plant resistance to disease and pests, crop growth, and other factors. On the other hand, it also requires precise tool-assisted measurements such as grain size, mass, and quality.
Although all these standard measures are useful, none of them takes into account the number ...
2023-03-07
Safe live microorganisms are found in a variety of foods we eat every day, from yogurt and other fermented foods, to raw fruits and vegetables. Despite the widespread idea that these mixtures of live microbes contribute to health, convincing evidence linking live dietary microbes to health benefits has been lacking.
A new study provides some of the first real-world evidence that higher consumption of live microbes may promote health. A group of scientists led by the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) classified over 9,000 individual ...
2023-03-07
The International Vaccine Institute (IVI), an international organization with a mission to discover, develop, and deliver safe, effective, and affordable vaccines for global health, announced the start of a multi-country study to better understand the burden of Human papillomavirus (HPV) among girls and women in low- and lower middle-income countries. This study received $14.99 million USD in funding from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation with $1 million USD co-funding from the Swedish government and will help inform intervention implementation and prioritization of research and development efforts that have the greatest potential public health ...
2023-03-07
Sustainable energy solutions cannot be pulled out of thin air. However, combining air with metal and other frameworks may pave the way for environmentally friendly energy conversion and storage, according to a research team based in China.
They published their review of novel porous materials — called metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and covalent organic frameworks (COFs) — and their potential to advance metal-air batteries on 03 March in Nano Research Energy.
The porous crystal material frameworks comprise various arrangements of bonded materials that can induce desired properties, including the ability to accelerate reactions between oxygen and metals ...
2023-03-07
Macrophages are highly specialized cells of the immune system that help the body detect and fight deadly pathogens. In particular, M1-like macrophages detect and destroy tumor cells, and release protective chemokines such as interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor-necrosis factor α (TNF α), thus shielding the body from life-threatening pathologies like cancer. However, not all macrophages show anti-tumor potential. Certain types of macrophages, i.e., M2-like macrophages, promote tumor growth. Luckily, the desired macrophage phenotype—a set of traits resulting from the genetic makeup of the macrophage—can be activated by modulating the ...
2023-03-07
OAK BROOK, Ill. – An artificial intelligence (AI) tool can accurately identify normal and abnormal chest X-rays in a clinical setting, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Chest X-rays are used to diagnose a wide variety of conditions to do with the heart and lungs. An abnormal chest X-ray can be an indication of a range of conditions, including cancer and chronic lung diseases.
An AI tool that can accurately differentiate between normal and abnormal chest X-rays would greatly alleviate the heavy workload experienced by radiologists globally.
“There is an exponentially growing demand for medical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Drunk mice sober up after a hormone shot