Fresh understanding of ageing in the brain offers hope for treating neurological diseases
2023-03-08
(Press-News.org)
Scientists from the Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute (TBSI) have shed new light on ageing processes in the brain. By linking the increased presence of specialised immune cells to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury for the first time, they have unearthed a possible new target for therapies aimed at treating age-related neurological diseases.
The research, which benefited from a collaboration with experts at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and focused on microglia in the brain and spinal cord, is published today in leading international journal, Science Advances.
Microglia are a unique type of immune cell whose job it is to support nerve cells, defend against invading microbes, clear debris and remove dying nerve cells by engulfing and eating them. Emerging research indicates that microglia can have different functional responses depending on molecular and biochemical changes occurring within these specialised cells.
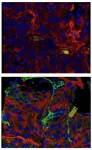
In fact, various subtypes of microglia can be distinguished based on a property called autofluorescence. This is the tendency of cells to emit light of one colour after they have absorbed light of another, and it occurs because specific substances inside the cells absorb light. The substances stored in specialised cellular compartments include fat molecules, cholesterol crystals, metals and other misfolded proteins.
David Loane, Assistant Professor of Neuroscience in Trinity’s School of Biochemistry and Immunology in TBSI is the lead author of the research. He said:
“As the brain ages, these materials build up inside autofluorescent microglia, which increase their autofluorescence as a result. Unfortunately, this accumulation of cellular debris also makes it harder for the microglia to perform their essential garbage collection tasks in the brain and to prevent neurological injury and neurodegenerative disease.
“In this study we found – in aged animals – that these microglia adopt a unique, dysfunctional state, which has a number of problematic impacts. For example, there is an increase in cellular stress and damage, an accumulation of fats and iron, alterations to metabolic processes and an increase in production of molecules that over-egg the immune response.”
In addition, the scientists demonstrated that autofluorescent microglia and associated inflammation were more pronounced under pathological conditions, such as in genetic risk factor models of Alzheimer’s disease, and – promisingly – were reversed by drug-assisted microglial replacement in aged animals.
Prof Loane added:
“Furthermore, environmental exposure to acute traumatic brain injury in animals accelerated the age of onset and tissue-wide distribution autofluorescent microglia by increasing oxidative stress damage in the brain of injured animals.
“As a result, increasing evidence now suggests that the accumulation of autofluorescent microglia contributes to diseases of ageing and neurodegeneration. If these sub-populations of microglia are highly inflammatory and damaging to the brain, then targeting them could be a new strategy for treating aging-related diseases.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-08
Research in animal models has demonstrated that stem-cell derived heart tissues have promising potential for therapeutic applications to treat cardiac disease. But before such therapies are viable and safe for use in humans, scientists must first precisely understand on the cellular and molecular levels which factors are necessary for implanted stem-cell derived heart cells to properly grow and integrate in three dimensions within surrounding tissue.
New findings from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) make it possible ...
2023-03-08
Coffee is important to the economies of coffee producing regions. A study published in PLOS Climate by Doug Richardson at CSIRO Oceans & Atmosphere, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia and colleagues suggests that climate change may significantly affect land where coffee is cultivated.
Coffee plants are sensitive to climate variability and change. However, the impact of synchronous climate hazards occurring in multiple areas important for coffee production is unknown. In order to better understand how large-scale climate modes such as El Niño ...
2023-03-08
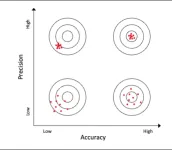
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Their popularity makes celebrities easy to spot. Strangers, however, can also get mistaken for celebrities, resulting in cases of false “celebrity sightings.” In attempting to explain the contradiction, a University of California, Riverside, study reports that celebrity faces are remembered more precisely but less accurately.
Precision, in this context, refers to how memories for a particular face resemble each other over repeated memory retrievals, which can be likened to the clustering of arrows on a target in archery. Accuracy measures ...
2023-03-08
New Haven, Conn. — The constant evolution of new COVID-19 variants makes it critical for clinicians to have multiple therapies in their arsenal for treating drug-resistant infections. Researchers have now discovered that a new class of oral drugs that acts directly on human cells can inhibit a diverse range of pathogenic SARS-CoV-2 strains.
In their newly published study, the team found a novel mechanism through which the gene that expresses angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2)—the cellular receptor to which SARS-CoV-2 ...
2023-03-08
March 8, 2023, Mountain View, CA – The SETI Institute and Swan Hellenic announce SETI Institute guest lecturers who will offer cruise guests expert insights into the history and latest discoveries in astronomy, astrophysics, astrobiology and planetary science, and the quest to find other forms of life within and beyond our solar system. This quest takes SETI Institute researchers to the planet’s most remote and inhospitable corners to explore life, including Antarctica, where the Swan Hellenic fleet is present for several months every year.
Outlining ...
2023-03-08
Boulder, Colo., USA: GSA’s dynamic online journal, Geosphere, posts articles online regularly. Topics this month include an analysis of geoscience job applications; Uturuncu volcano, Bolivia; Picture Gorge Basalt; and the Red Bluff Granite Suite. You can find these articles at https://geosphere.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent .
Critical workforce skills for bachelor-level geoscientists: An analysis of geoscience job advertisements
G.W. Shafer; K. Viskupic; A.E. Egger
Understanding the skills ...
2023-03-08
The European Innovation Council (EIC) has recently announced that it will award a Transition grant to SpiNNcloud Systems GmbH, a deep-tech startup based in Saxony, Germany.
The team from SpiNNcloud Systems GmbH, a spin-off from Professor Christian Mayr’s research group at Technische Universität Dresden, is receiving a grant of 2.5 million euros for their groundbreaking project, “SpiNNode: SpiNNaker2 on the edge.”
“SpiNNaker2 is a bio-inspired supercomputer which was developed at my Chair in collaboration with Prof. Steve Furber’s research group at the University of Manchester as part ...
2023-03-08
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America regularly publishes articles online ahead of print. GSA Bulletin topics studied this month include the nature and dynamics of China and Tibet; the Lower Mississippi Valley, USA; and the polarity of Mesozoic arcs along the western margin of North America. You can find these articles at https://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent .
Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of long-lived Nb-Ta-(Sn) mineralization in Lianyunshan, NE Hunan, South China
Nuerkanati Madayipu; Huan Li; Safiyanu Muhammad Elatikpo; Michael W. Förster; Hou-Xiang Zhou ...
The ...
2023-03-08
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Sticking with an exercise program can be tough, even during the best of times. But what about during a pandemic?
A new study by the University of Missouri and Oklahoma State University found that even when gyms were closed and there were other COVID-19 restrictions limiting face-to-face meetings, older adults who completed the Stay Strong, Stay Healthy exercise program — created at MU in 2005 — continued to maintain long-term exercise habits independently, which resulted in improved lifestyle changes and an increase in both physical energy and self-confidence.
“We ...
2023-03-08
People with a recent diagnosis of atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common irregular heart rhythm, have a modestly higher risk of developing dementia than people without the condition, according to research published today.
“Previous studies that have examined the link between atrial fibrillation and dementia have yielded conflicting results, and we hope that our study’s large sample size helps to establish confidence in our findings,” said Dr. Nisha Bansal, a professor of medicine at the University of Washington School of Medicine. “The study also included a community based, diverse population, which may increase the generalizability ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fresh understanding of ageing in the brain offers hope for treating neurological diseases