(Press-News.org) Aston University to support more women carve out a career in photonics
Three new grants available for women from eligible countries across east Asia
Scholarships will be based in the College of Engineering and Physical Sciences.
Aston University and the British Council are aiming to support more women carve out a career in photonics.
The British Council is funding three grants for women who have recently completed a PhD or equivalent and are from eligible countries across east Asia.
This scholarship programme aims to increase opportunities in science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM) for women.
According to data from the UN Scientific Education and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), fewer than 30 percent of researchers worldwide are women and only 30 percent of female students select STEM-related fields in higher education.
Globally, the representation of female scientist is particularly low in information and communications technology (three percent), natural science, mathematics, and statistics (five percent), and engineering, manufacturing and construction (eight percent).
The scholarships will be based in the University’s College of Engineering and Physical Sciences and will be centred on the study of photonics – the science of light.
They are open to women with a passport and permanent resident of Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam who are not currently working in an academic role.
Director of Aston Institute of Photonic Technologies (AIPT) Professor Sergei Turitsyn said “This is a very exciting opportunity for women who wish to have a research experience at a UK university or research institution, converting their doctoral work into publications or other academic outputs, and establishing new research relationships.
“We are looking for candidates who are interested in a variety of areas of photonics such as nano-photonics, photonic technology for food industry, and machine learning for environmental sensing.
“They will be provided with a mentor, and support from AIPT which has a successful track record from medical lasers and bio-sensing for healthcare, to the high-speed optical communications tech that underpins the internet and the digital economy.”
Last year Aston University’s College of Engineering & Physical Sciences was awarded an Athena Swan Gold departmental award for its commitment to advancing the careers of women.
The closing date for applications is 23.59 hours BST on Wednesday 31 May 202. More details can be found at https://jobs.aston.ac.uk/Vacancy.aspx?ref=0047-23
END
Aston University and the British Council to help boost global number of female photonics experts
2023-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Marine mammal reproduction rests on a precarious tipping point of ocean resources
2023-03-08
Changing environmental conditions may threaten marine mammal populations by making it harder to find prey, and a new study shows how small, gradual reductions in prey could have profound implications for animal populations.
The reproductive success of female elephant seals depends on their ability to find prey and put on weight during their months-long foraging migrations. Researchers at UC Santa Cruz studied the relationships between elephant seal behavioral strategies in the open ocean, weight gain, and lifetime success at producing pups.
Their findings, published March 8 in Ecology Letters, reveal a sharp threshold in the relationship between ...
UCF researcher creates world’s first energy-saving paint – inspired by butterflies
2023-03-08
–EMBARGOED:
NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 2:00 p.m. EST, WEDNESDAY, 08 MARCH 2023–
UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL FLORIDA
UCF Researcher Creates World’s First Energy-saving Paint – Inspired by Butterflies
Instead of pigment-based colored paint, which requires artificially synthesized molecules, a UCF researcher has developed an alternative way to produce colored paint that is more natural, environmentally friendly and light weight.
ORLANDO, March 8, 2023 — University of Central Florida researcher Debashis Chanda, a professor in UCF’s NanoScience Technology Center, has drawn inspiration from butterflies to create the first environmentally ...
Researchers discover how too much oxygen damages cells and tissues
2023-03-08
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—March 8, 2023—When it comes to oxygen, you can have too much of a good thing. Breathing air that contains higher levels of oxygen than the usual 21 percent found in Earth’s atmosphere can cause organ damage, seizures, and even death in people and animals, particularly if it’s in excess of the body’s oxygen needs. Until now, however, scientists have mostly speculated about the mechanisms behind this phenomenon, known as oxygen toxicity, or hyperoxia.
Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes have discovered how excess oxygen changes a handful of proteins in our cells that ...
Colorectal cancer research
2023-03-08
Excessive iron absorption by tumor cells in the digestive tract is known to play a major role in driving colorectal cancer – the third most prevalent and third leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S.
In a new study published in the journal Advanced Science, University of New Mexico researchers describe the part played by the transferrin receptor (TFRC) gene in the growth of colorectal cancer tumors.
Iron is absorbed into intestinal cells both from the bloodstream and from iron-rich foods, such as red meat, said Xiang Xue, PhD, assistant professor ...
A pool at Yellowstone is a thumping thermometer
2023-03-08
While the crowds swarm around Old Faithful to wait for its next eruption, a little pool just north of Yellowstone National Park’s most famous geyser is quietly showing off its own unique activity, also at more-or-less regular showtimes. Instead of erupting in a towering geyser, though, Doublet Pool cranks up the bass every 20 to 30 minutes by thumping. The water vibrates and the ground shakes.
Doublet Pool’s regular thumping is more than just an interesting tourist attraction. A new study led by University of Utah researchers shows that the ...
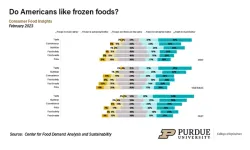
Americans planning frugal uses for their 2023 tax refunds
2023-03-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Americans likely are receiving smaller tax refunds than they have in recent years, and most people will not be going out to spend this money, according to the February 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report. This month’s report also looks more closely at religious demographics and includes new data on frozen food preferences.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, ...
Unprecedented increase in ocean plastic since 2005 revealed by four decades of global analysis
2023-03-08
A global dataset of ocean plastic pollution between 1979 and 2019 reveals a rapid and unprecedented increase in ocean plastics since 2005, according to a study published March 8, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marcus Eriksen from The 5 Gyres Institute, USA, and colleagues.
Understanding plastic accumulation in the oceans to date could provide a critical baseline to help address this form of pollution. Previous studies have focused primarily on northern-hemisphere oceans near the world’s most industrialized nations, ...
Places of worship linked with more neighborhood crime in Washington, D.C.
2023-03-08
A new analysis of crime statistics near hundreds of places of worship in Washington, D.C., shows that these sites are associated with higher levels of violent and property crime—even after accounting for other factors commonly linked with crime. James Wo of the University of Iowa, U.S., presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 8, 2023.
Prior research has established that places of worship foster social ties and community actions for the common good, suggesting that these sites would reduce crime in their neighborhoods. However, few studies have addressed the hypothesized ...
For educational attainment, it's more helpful to grow up in an affluent neighborhood than it is harmful to grow up in a poor one, per 23-year large Netherlands cohort study
2023-03-08
For educational attainment, it's more helpful to grow up in an affluent neighborhood than it is harmful to grow up in a poor one, per 23-year large Netherlands cohort study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281928
Article Title: Neighbourhood effects on educational attainment. What matters more: Exposure to poverty or exposure to affluence?
Author Countries: The Netherlands, UK
Funding: The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council (https://erc.europa.eu/) ...
After 6 months of disrupted schooling during COVID-19, German students scored substantially lower on intelligence tests than comparative earlier cohorts, with the gap persisting after 16 months.
2023-03-08
After 6 months of disrupted schooling during COVID-19, German students scored substantially lower on intelligence tests than comparative earlier cohorts, with the gap persisting after 16 months
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281779
Article Title: Students’ intelligence test results after six and sixteen months of irregular schooling due to the COVID-19 pandemic
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The study was supported by a grant awarded to M.B. by the Research Fund of ...