(Press-News.org) Excessive iron absorption by tumor cells in the digestive tract is known to play a major role in driving colorectal cancer – the third most prevalent and third leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S.
In a new study published in the journal Advanced Science, University of New Mexico researchers describe the part played by the transferrin receptor (TFRC) gene in the growth of colorectal cancer tumors.
Iron is absorbed into intestinal cells both from the bloodstream and from iron-rich foods, such as red meat, said Xiang Xue, PhD, assistant professor in the UNM Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology.
The TFRC pathway normally regulates how much iron is delivered from the blood to the intestine, but in cancer it goes awry. “TFRC is highly increased in tumor tissue compared to normal tissue,” he said. “That means it can help the cells to get more iron to proliferate.”
Xue’s lab found that when TFRC is inactivated, it extends the survival of animals that would otherwise develop cancer tumors. But the search for potential cancer treatments must walk a fine line between inhibiting excessive iron absorption to prevent tumor growth while not depriving the body of the normal amounts of iron it needs to function.
“If you limit TRFC you can limit the iron,” Xue said. “It’s potentially a therapeutic target, but it has its own intrinsic problems, because iron is needed for normal cell survival.”
Cancer cells that are deprived of iron suffer DNA damage and self-destruct, he said.
Going forward, Xue’s lab will study chelators – molecules that bind strongly with iron – to see whether these can be used to draw iron out of cancer cells in hopes of shrinking tumors.
“This paper just takes advantage of what we can easily do at the moment,” he said. “It validates our previous concepts. If you can reduce iron in the colon cancer cell it can potentially be therapeutic.”
Meanwhile Xue urges people to eat red meat in moderation, noting that some pursue fad diets in which they consume excessive quantities of meat, putting themselves at higher risk of developing colorectal cancer.
“I’m not going to say you’re not going to eat red meat,” he said. “There are still some nutrients you need to get from meat. I would just say don’t eat too much.”
END
Colorectal cancer research
UNM scientists describe how iron helps drive tumor development
2023-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A pool at Yellowstone is a thumping thermometer
2023-03-08
While the crowds swarm around Old Faithful to wait for its next eruption, a little pool just north of Yellowstone National Park’s most famous geyser is quietly showing off its own unique activity, also at more-or-less regular showtimes. Instead of erupting in a towering geyser, though, Doublet Pool cranks up the bass every 20 to 30 minutes by thumping. The water vibrates and the ground shakes.
Doublet Pool’s regular thumping is more than just an interesting tourist attraction. A new study led by University of Utah researchers shows that the ...
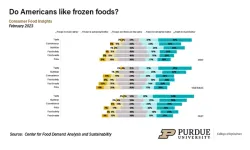
Americans planning frugal uses for their 2023 tax refunds
2023-03-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Americans likely are receiving smaller tax refunds than they have in recent years, and most people will not be going out to spend this money, according to the February 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report. This month’s report also looks more closely at religious demographics and includes new data on frozen food preferences.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, ...
Unprecedented increase in ocean plastic since 2005 revealed by four decades of global analysis
2023-03-08
A global dataset of ocean plastic pollution between 1979 and 2019 reveals a rapid and unprecedented increase in ocean plastics since 2005, according to a study published March 8, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marcus Eriksen from The 5 Gyres Institute, USA, and colleagues.
Understanding plastic accumulation in the oceans to date could provide a critical baseline to help address this form of pollution. Previous studies have focused primarily on northern-hemisphere oceans near the world’s most industrialized nations, ...
Places of worship linked with more neighborhood crime in Washington, D.C.
2023-03-08
A new analysis of crime statistics near hundreds of places of worship in Washington, D.C., shows that these sites are associated with higher levels of violent and property crime—even after accounting for other factors commonly linked with crime. James Wo of the University of Iowa, U.S., presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 8, 2023.
Prior research has established that places of worship foster social ties and community actions for the common good, suggesting that these sites would reduce crime in their neighborhoods. However, few studies have addressed the hypothesized ...
For educational attainment, it's more helpful to grow up in an affluent neighborhood than it is harmful to grow up in a poor one, per 23-year large Netherlands cohort study
2023-03-08
For educational attainment, it's more helpful to grow up in an affluent neighborhood than it is harmful to grow up in a poor one, per 23-year large Netherlands cohort study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281928
Article Title: Neighbourhood effects on educational attainment. What matters more: Exposure to poverty or exposure to affluence?
Author Countries: The Netherlands, UK
Funding: The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council (https://erc.europa.eu/) ...
After 6 months of disrupted schooling during COVID-19, German students scored substantially lower on intelligence tests than comparative earlier cohorts, with the gap persisting after 16 months.
2023-03-08
After 6 months of disrupted schooling during COVID-19, German students scored substantially lower on intelligence tests than comparative earlier cohorts, with the gap persisting after 16 months
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281779
Article Title: Students’ intelligence test results after six and sixteen months of irregular schooling due to the COVID-19 pandemic
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The study was supported by a grant awarded to M.B. by the Research Fund of ...
Participants in psychology studies are more likely than average to exhibit symptoms of personality disorders, potentially skewing the findings of such research
2023-03-08
Participants in psychology studies are more likely than average to exhibit symptoms of personality disorders, potentially skewing the findings of such research
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281046
Article Title: Self-selection biases in psychological studies: Personality and affective disorders are prevalent among participants
Author Countries: Poland, Spain, Italy
Funding: To conduct Face-to-Face Studies IK was supported by grants 2017/01/X/HS6/02022 from the National Center of Science ...
A surprising way to trap a microparticle
2023-03-08
New study finds obstacles can trap rolling microparticles in fluid
Through simulations and experiments, physicists attribute the trapping effect to stagnant pockets of fluid, created by hydrodynamics
Random motions of the molecules within the fluid then ‘kick’ the microroller into a stagnant pocket, effectively trapping it
Size of the obstacle also controls how easy it is to trap a microroller and how long it remains trapped
EVANSTON, Ill. — When physicists steered a tiny microparticle toward a cylindrical obstacle, they expected one of two outcomes to occur. The particle would either collide into the ...
Fresh understanding of ageing in the brain offers hope for treating neurological diseases
2023-03-08
Scientists from the Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute (TBSI) have shed new light on ageing processes in the brain. By linking the increased presence of specialised immune cells to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury for the first time, they have unearthed a possible new target for therapies aimed at treating age-related neurological diseases.
The research, which benefited from a collaboration with experts at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and focused ...
Cyborg technology analyzes the functional maturation of stem-cell derived heart tissue
2023-03-08
Research in animal models has demonstrated that stem-cell derived heart tissues have promising potential for therapeutic applications to treat cardiac disease. But before such therapies are viable and safe for use in humans, scientists must first precisely understand on the cellular and molecular levels which factors are necessary for implanted stem-cell derived heart cells to properly grow and integrate in three dimensions within surrounding tissue.
New findings from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) make it possible ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] Colorectal cancer researchUNM scientists describe how iron helps drive tumor development