(Press-News.org) A phase 3 clinical trial (research study) of a targeted therapy called nirogacestat has found that the drug significantly shrank desmoid tumors in 41% of patients.
Desmoid tumors (also known as aggressive fibromatosis) are a rare type of soft tissue tumor, and MSK has a team of doctors who are dedicated to treating them.
When Dana Avellino, now 36, first noticed a lump near her groin in the summer of 2018, she thought it was related her recent cesarean section. Her younger daughter was only 2 months old at the time. When a biopsy revealed that the lump was a sarcoma, a type of tumor that affects the body’s soft tissues, her doctors recommended that she go to Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), known worldwide for expertise in treating sarcomas.
After other treatments left her with severe side effects, Dana’s MSK doctor, sarcoma expert Mrinal Gounder, MD, told her about a clinical trial testing an experimental targeted drug called nirogacestat. Dana has now been taking the drug for more than three years. Her tumor, a rare, noncancerous subtype of sarcoma called a desmoid tumor, has shrunk so much that she can hardly feel it anymore.
“When I agreed to participate in the trial, I didn’t know what the end result would be,” Dana says. “But the side effects from the drug have not been bad, and I’m not in any pain from the tumor. It’s been amazing.”
Phase 3 Trial of Nirogacestat for Desmoid Tumors Has Positive Results
On March 9, results from an international, randomized phase 3 clinical trial of nirogacestat led by Dr. Gounder were published in The New England Journal of Medicine. Nirogacestat, which blocks a protein called Notch, is a new type of targeted drug called a gamma-secretase inhibitor. The paper reported that 41% of patients’ tumors significantly shrank after they took nirogacestat.
After two years, tumors did not grow in more than 75% of patients on the targeted drug, compared with only 44% of patients in the placebo group. The most common side effects were fatigue (feeling tired), gastrointestinal problems, and skin rashes. Dana has experienced skin problems but is otherwise feeling good.
Diagnosing Desmoid Tumors, a Rare Subtype of Sarcoma
Dana’s first doctor at MSK was world-renowned sarcoma surgeon Samuel Singer, MD. Dr. Singer performed a second biopsy, and MSK sarcoma pathologist Meera Hameed, MD, determined that Dana’s soft tissue tumor was a type called a desmoid tumor (also known as aggressive fibromatosis).
Unlike most soft tissue sarcomas, desmoid tumors don’t spread to distant parts of the body. But these tumors can grow quite large and lead to disfigurement, disability, and debilitating pain. In rare cases, they invade vital organs, resulting in severe complications and even death.
Dr. Singer told Dana that he could perform surgery to remove her tumor, but there was a high likelihood that it would grow back. He referred her to Dr. Gounder, who is one of the world’s leading experts on desmoid tumors. Dr. Gounder has led a number of clinical trials studying drugs that target the defective proteins that cause these tumors to grow.
“Sarcoma itself is a rare disease, and desmoid tumors are a rare type of sarcoma,” Dr. Gounder explains, adding that only about 900 people are diagnosed with them in the United States every year. “MSK doesn’t only treat the major cancers,” he says. “We have expertise across more than 400 different types.”
Trying Different Desmoid Tumor Treatments Before the Nirogacestat Clinical Trial
Dr. Gounder first offered Dana treatment with sorafenib (Nexavar®). He had previously led studies that found this drug is effective in many people with desmoid tumors. But in Dana, the drug caused very high blood pressure. Another drug led to allergic reactions.
Meanwhile, the tumor in her lower abdomen continued to grow, to the point where she could no longer bend over to pick up her young daughters. Eventually, Dr. Gounder suggested that Dana consider the clinical trial for nirogacestat. In November 2019, she started taking the drug — three pills, twice a day.
MSK’s Expertise in Treating Desmoid Tumors
MSK has a multidisciplinary team that specializes in treating desmoid tumors. Dr. Gounder; sarcoma surgeon Aimee Crago, MD, PhD, who also studies desmoid tumors in her lab; and interventional radiologist Joseph Erinjeri, MD, PhD, work together to determine the best, most personalized treatment for each patient. The treatments may include medications like nirogacestat and sorafenib, surgery, an interventional procedure, or a combination of these.
Dr. Erinjeri specializes in less-invasive, image-guided therapies. One of these is cryoablation, in which a specialized, chilled needle is used to create ice crystals within a tumor, destroying it. Another treatment uses microscopic beads loaded with chemotherapy drugs, which are injected directly into the arteries that feed the tumor.
“These treatments can be very effective in patients who don’t respond to medications and who are not candidates for surgery,” Dr. Erinjeri says. “We’ve found that in patients who have these procedures and who are considered low risk, the chances of the tumor coming back are low.”
Radiologist Robert Lefkowitz, MD, who specializes in imaging sarcomas, is another important member of the team. He reviewed all the scans of the patients in the recent trial. “There were some very good responses,” he notes. “Many of the tumors were measurably smaller, including Dana’s.”
Better Quality of Life for Younger Patients With Desmoid Tumors
Most people diagnosed with a desmoid tumor are in their teens, 20s, or 30s. These growths are more common in women than in men, although experts don’t know why. The trial was unique because it included surveys about patients’ quality of life during treatment. “When developing new sarcoma drugs, we want to determine whether they actually make patients feel better, in addition to shrinking their tumors,” Dr. Gounder says.
The tools to measure a patient’s quality of life were first developed at MSK in collaboration with the Desmoid Tumor Research Foundation (DTRF), a nonprofit patient advocacy group.
Another side effect of nirogacestat was that in many female patients it caused temporary ovarian dysfunction, which was reversible in most patients. Because of this, the trial also included follow-up research to study reproductive function. “This tumor affects many people who may want to have children, so this is an important part of finding better treatments,” Dr. Gounder adds.
Dana experienced these problems, but it was not a concern for her because she was not planning to have more children.
Desmoid Tumor Advocacy Group Helped Make Nirogacestat a Success
Nirogacestat has an interesting history. It was originally developed to treat Alzheimer’s disease, but ultimately was not effective. It was later tested against several types of cancer with equally disappointing results.
Just when the company that makes the drug was about to abandon it, the leaders of the patient advocacy group DTRF saw results suggesting it might be successful in treating desmoid tumors. The group worked with the pharmaceutical company and the National Cancer Institute to develop clinical trials and recruit patients to participate in them.
“Our partnership with DTRF is really an important part of this success story,” Dr. Gounder says. Drs. Gounder, Crago, and Lefkowitz all serve on DTRF’s Medical and Scientific Advisory Boards.
In addition to desmoid tumors, nirogacestat is now being evaluated in clinical trials for other cancers, including multiple myeloma.
Dana Continues To Live a Normal Life With Her Family
Dana, who lives in Pelham, New York, and whose daughters are now 4 and 7, has been able to continue working during most of her treatment. She teaches third grade special education at a public school in the Bronx. Although she had to travel into Manhattan during the first part of the trial, she is now able to receive scans and other tests at MSK Westchester, closer to her home and her work.
“That makes it much easier, because I don’t have to take the whole day off,” Dana says. “Participating in a clinical trial is a huge commitment, but definitely it was worth it for me.”
The trial was supported by SpringWorks Therapeutics Inc. Dr. Gounder was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute with a Cancer Center Support Grant to MSK (P30 CA008748).
END
Nirogacestat, a new desmoid tumor treatment, improves outcomes for people with sarcoma
2023-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ringing an electronic wave: Elusive massive phason observed in a charge density wave
2023-03-09
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have detected the existence of a charge density wave of electrons that acquires mass as it interacts with the background lattice ions of the material over long distances.
This new research, led by assistant professor Fahad Mahmood (Physics, Materials Research Laboratory) and postdoc Soyeun Kim (current postdoc at Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory), is a direct measurement of the Anderson-Higgs mechanism (of mass acquisition) and the first known demonstration of a massive phason in a charge ...
MSK Research Highlights, March 9, 2023
2023-03-09
New research from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) and the Sloan Kettering Institute — a hub for basic science and translational research within MSK — offers new proof-of-concept compounds against acute myeloid leukemia; reports results from a phase 1 clinical trial appraising two drugs against low-grade glioma; examines MSK’s first-in-the-nation program integrating herbal medicine into oncology care; and identifies how high-grade histologic patterns ...
New biosensor reveals activity of elusive metal that’s essential for life
2023-03-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A new biosensor engineered by Penn State researchers offers scientists the first dynamic glimpses of manganese, an elusive metal ion that is essential for life.
The researchers engineered the sensor from a natural protein called lanmodulin, which binds rare earth elements with high selectivity and was discovered 5 years ago by some of the Penn State researchers involved in the present study.
They were able to genetically reprogram the protein to favor manganese over other common transition ...
Deconstructing Lignin
2023-03-09
It’s a tough job, but someone’s got to do it. In this case, the “job” is the breakdown of lignin, the structural biopolymer that gives stems, bark and branches their signature woodiness. One of the most abundant terrestrial polymers on Earth, lignin surrounds valuable plant fibers and other molecules that could be converted into biofuels and other commodity chemicals — if we could only get past that rigid plant cell wall.
Fortunately, the rather laborious process already occurs in the guts of large herbivores through the actions of anaerobic microbes that cows, goats and sheep rely on to release the nutrients ...
People don’t know what a preprint is. Here’s why that matters
2023-03-09
New research from the University of Georgia suggests most people don’t understand the difference between a preprint and a published academic journal article.
Preprints are research papers that haven’t undergone peer review, the process by which studies’ findings are validated by experts who weren’t involved with the research themselves.
The study found the majority of readers have little to no understanding of what a preprint actually is. That lack of understanding could lead to public distrust in science since findings and how those findings are described can change between the preprint phase and ...
Ontario sees big jump in amphetamine-related emergency visits
2023-03-09
Ontario’s emergency departments are seeing a dramatic rise in visits related to the use of unregulated amphetamines and their street equivalent: crystal meth.
In a new paper published in the Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, researchers found that individuals accessing the emergency department (ED) for amphetamine- and methamphetamine-related concerns grew from 233 in 2003 to 4,146 individuals annually by 2020.
“That’s a nearly 15-fold increase – pretty dramatic. If we consider ED visits as a crude proxy for how prevalent unregulated amphetamine use is, then the observed trend is highly concerning,” said the paper’s lead author, ...
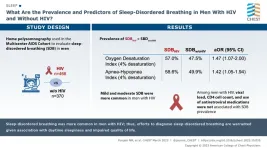
Highlights from the journal CHEST®, March 2023
2023-03-09
Glenview, Illinois – Published monthly, the journal CHEST® features peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research in chest medicine: Pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine and related disciplines. Journal topics include asthma, chest infections, COPD, critical care, diffuse lung disease, education and clinical practice, pulmonary vascular disease, sleep, thoracic oncology and the humanities.
The March issue of the CHEST journal contains 44 articles, including clinically relevant research, reviews, case series, commentary and more. Each month, the journal also offers complementary ...
Nutrition educators support nutrition incentives for food and nutrition security programs to promote increased intake of fruit and vegetables
2023-03-09
Philadelphia, March 9, 2023 – The Gus Schumacher Nutrition Incentive Program (GusNIP), funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, includes Nutrition Incentive (NI) and Produce Prescription (PPR) programs. These programs provide financial incentives for healthy eating by increasing individuals’ purchase and consumption of fruits and vegetables and reducing food insecurity in order to prevent and treat nutrition-related diseases. A study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, explores how nutrition educators work with NI and PPR programs ...
Diverse approach key to carbon removal
2023-03-09
RICHLAND, Wash.—Diversification reduces risk. That’s the spirit of one key takeaway from a new study led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. The effective path to limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by the end of this century likely requires a mix of technologies that can pull carbon dioxide from Earth’s atmosphere and oceans.
Overreliance on any one carbon removal method may bring undue risk, the authors caution. And we’ll likely need them all to remove the necessary amount ...
New class of drugs may prevent infection by wide range of COVID-19 variants
2023-03-09
Study Title: Pharmacologic disruption of mSWI/SNF complex activity restricts SARS-CoV-2 infection
Publication: Nature Genetics https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-023-01307-z
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Cigall Kadoch, PhD
Summary:
A new class of oral drugs can inhibit a wide range of SARS-CoV-2 variants, researchers report, potentially identifying new antiviral agents providing broad activity against the constantly emerging new strains of the COVID-19 virus. The researchers discovered that the mammalian SWI/SNF (also called BAF) chromatin remodeling complex, a regulator of gene expression –controls the expression of the ACE2, the ...