(Press-News.org) In the issue of the renowned journal Science published today (10.3.23), the team led by Prof. Dr Ulf Peschel reports on measurements on a sequence of pulses that travel thousands of kilometres through glass fibres that are only a few microns thin. The researchers were surprised by the results. “We have found that the light pulses organize themselves after about a hundred kilometres and then behave more like molecules of a conventional gas, such as air, for example”, reports Prof. Ulf Peschel, the head of the group in Jena. In a gas the particles move back and forth at different speeds, but still they have a mean velocity defined by their temperature. Although light pulses propagate through the glass fibre at an average speed of about 200,000 kilometres per second , they are not all equally fast. “The statistical distribution of their velocities equals exactly that of a conventional gas with a fixed temperature”, says Peschel.
As the researchers have now demonstrated for the first time in their recent publication, this photon gas can be cooled, for example, by a process known as adiabatic expansion. As in a real gas, the velocity differences of the particles decrease during cooling and the order in the signal sequence automatically increases. When the absolute temperature zero of 0 Kelvin is reached, all pulses propagate at exactly the same velocity.
The reverse process is also possible. “When the optical gas is heated, velocity differences increase”, explains Peschel. If all pulse velocities occur equally often, the disorder is at a maximum and the temperature is infinite – a state which cannot be reached in a real gas as it would require an infinite amount of energy. “In contrast, a periodic modulation of the refractive index can limit the range of allowed pulse velocities in the glass fibre. In this way, all available velocity states can be equally excited, creating a photon gas of infinite temperature. If even more energy is added, states of extreme velocities are preferentially populated – the photon gas becomes hotter than infinitely hot.
“For this state, which has so far only been described theoretically for light, a temperature below absolute zero is mathematically assumed”, says Peschel. He and his colleagues have now been able to create such a photon gas with negative temperature and show for the first time that it obeys conventional laws of thermodynamics. “Our results will contribute to a better understanding of the collective behaviour of large ensembles of optical signals. If we take the laws of thermodynamics into account, we can make optical data transmission more robust and reliable, for example by structuring pulse distributions to better match thermal distributions.”
END
Hotter than infinity – light pulses can behave like an exotic gas
Physicists at the Universities of Jena and Central Florida investigate light with negative temperatures
2023-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cause of leukemia in trisomy 21
2023-03-10
FRANKFURT. Leukaemia (blood cancer) is a group of malignant and aggressive diseases of the blood-forming cells in the bone marrow. Very intensive chemotherapy and in some cases a bone marrow transplant are the only cure. Like all cancers, leukaemia is caused by changes in the DNA, the heredity material present in human cells in the form of 46 chromosomes. In many forms of leukaemia, large parts of these chromosomes are altered. People with Down syndrome, who have three copies of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21) are highly vulnerable: ...
A study analyzes the notion of spectacle through the figure of Antigone
2023-03-10
A research study at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) analyzes the notion of spectacle as an enunciative space that is located beyond mediatic logic. In contrast to the generalized concept of spectacle laden with negative connotations, the study proposes a distancing of that concept from that of entertainment. UC3M Full Professor Pilar Carrera, in her essay Antígona o la razón espectacular (2023), published in the review Signa,advocates the notion of spectacle from the perspective of spectacular distance ...
Outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms in deep learning tasks
2023-03-10
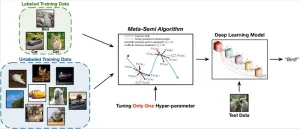
Deep learning based semi-supervised learning algorithms have shown promising results in recent years. However, they are not yet practical in real semi-supervised learning scenarios, such as medical image processing, hyper-spectral image classification, network traffic recognition, and document recognition. In these types of scenarios, the labeled data is scarce for hyper-parameter search, because they introduce multiple tunable hyper-parameters. A research team has proposed a novel meta-learning based semi-supervised learning algorithm called Meta-Semi, that requires tuning only one additional hyper-parameter. Their Meta-Semi approach outperforms state-of-the-art ...
Social intelligence is the next frontier for AI, researchers say
2023-03-10
Siri and Google Assistant may be able to schedule meetings on request, but they don’t have the social understanding to independently prioritize the appointments — yet. According to researchers based in China, artificial intelligence (AI) may be smart, but it is stunted by a lack of social skills.
They published their review of the current state and call for future directions on March 10 in CAAI Artificial Intelligence Research.
“Artificial intelligence has changed our society and our daily life,” said first author Lifeng Fan, National Key Laboratory of General Artificial Intelligence, Beijing Institute for General Artificial ...
$3 million grant backs international effort to help children live healthier lives
2023-03-10
An international team of researchers has received $3 million to support an ambitious effort to understand how early gut development can profoundly shape children’s health throughout life.
The funding from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative will allow scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Boston Children’s Hospital, University of Mississippi Medical Center and Pakistan’s Aga Khan University to “map” the healthy gut in children ages 5 and younger down to the ...
Pandemic shift to telemedicine helped maintain quality of care for depression
2023-03-10
March 10, 2023 – The rapid transition from in-person to care to telemedicine visits at the start of the COVID‑19 pandemic did not adversely affect the quality of care – and even improved some aspects of care – for patients with major depression in a major integrated health system, according to a new report. The study appears as part of a special "Virtual Visits" supplement to Medical Care, published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"A rapid shift to virtual behavioral health care was possible without compromising health care-related practices," according to the new research, led by Nancy ...
Astrocyte cells critical for learning skilled movements
2023-03-10
From steering a car to swinging a tennis racket, we learn to execute all kinds of skilled movements during our lives. You might think this learning is only implemented by neurons, but a new study by researchers at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT shows the essential role of another brain cell type: astrocytes.
Just as teams of elite athletes train alongside staffs of coaches, ensembles of neurons in the brain’s motor cortex depend on nearby astrocytes to help them learn to encode when and how to move, and the ...
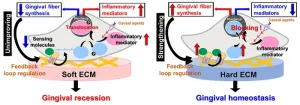
Study reveals that soft gums are more prone to inflammation
2023-03-10
The tissue area that surrounds our teeth is known as the gingiva, and healthy teeth will nestle firmly into the gums thanks to the many gingival fibers that connect the tooth to the gingiva. The gingiva is home to fibroblasts - cells that contribute to the formation of connective tissue. A group of scientists from Tohoku University have discovered that the gingiva stiffness influences the properties of gingival fibroblasts, which in turn affects whether inflammation is likely to occur and make gingival fibers difficult to form.
Their findings were published in the journal Scientific ...
HKU Marine Scientist contributes to research assessing the potential risks of ocean-based climate intervention technologies on deep-sea ecosystems
2023-03-10
The deep sea is one of the least well-known areas on Earth, comprising multiple vulnerable ecosystems that play critical roles in the carbon cycle. However, the deep sea is directly exposed to the effects of human-induced climate change and may now face additional challenges arising from efforts to counteract climate change artificially. These efforts have evolved into geoengineering solutions that could operate on vast spatial scales.
Ocean-based climate interventions (OBCIs) are increasingly claimed as promising solutions to mitigate climate change. These interventions use different technologies to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and sequester the carbon ...
The future of dentistry is digital
2023-03-10
Digitalisation, one of the megatrends of the future, has arrived in the world of dentistry. Modern technologies underpin precision applications while also making treatments less invasive for patients. At the beginning of June 2023, an international congress will bring dentistry experts from all over Europe to Vienna to discuss the broad range of application options opened up by the latest breakthroughs.
The University Clinic of Dentistry Vienna is a renowned international innovation driver, especially ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
[Press-News.org] Hotter than infinity – light pulses can behave like an exotic gasPhysicists at the Universities of Jena and Central Florida investigate light with negative temperatures