(Press-News.org) As an indispensable tool for observing the microcosmos, optical microscopy has boosted the development of various fields, including biology, medicine, physics, and materials. However, optical diffraction imposes a spatial resolution restriction on optical microscopy, which hampers exploration of finer structures.
To overcome the resolution limitation, various super-resolution microscopy techniques based on diverse principles have been proposed. Yet these techniques commonly acquire super-resolution at the expense of reduced imaging speed, so achieving high-speed super-resolution imaging that can detect fast dynamics with fine structures has remained a great challenge.
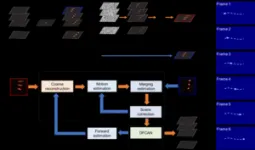
Recently, a research team from East China Normal University, Shenzhen University, and Peking University resolved the contradiction between the spatial resolution and imaging speed. As reported in Advanced Photonics, they achieved high-speed super-resolution by developing an effective technique termed temporal compressive super-resolution microscopy (TCSRM). TCSRM merges enhanced temporal compressive microscopy with deep-learning-based super-resolution image reconstruction. Enhanced temporal compressive microscopy improves the imaging speed by reconstructing multiple images from one compressed image, and the deep-learning-based image reconstruction achieves the super-resolution effect without reduction in imaging speed. Their iterative image reconstruction algorithm contains motion estimation, merging estimation, scene correction, and super-resolution processing to extract the super-resolution image sequence from compressed and reference measurements.
Their studies verified the high-speed super-resolution imaging ability of TCSRM in theory and experiment. To demonstrate the imaging capability of TCSRM, they imaged flowing fluorescent beads in a microchannel, achieving a remarkable frame rate of 1200 frames per second and spatial resolution of 100 nm.
According to corresponding author Shian Zhang, Professor and Deputy Director of the State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy at East China Normal University, “This work provides a powerful tool for the observation of high-speed dynamics of fine structures, especially in hydromechanics and biomedical fields, such as microflow velocity measurement, organelle interactions, intracellular transports and neural dynamics.” Zhang adds, “The framework of TCSRM can also offer guidance for achieving higher imaging speed and spatial resolution in holography, coherent diffraction imaging, and fringe projection profilometry.”
Read the Gold Open Access article by Y. He, Y. Yao, et al., “Temporal compressive super-resolution microscopy at frame rate of 1200 frames per second and spatial resolution of 100 nm,” Adv. Photon. 5(2), 026003 (2023), doi 10.1117/1.AP.5.2.026003.
END
High-speed super-resolution microscopy via temporal compression
New high-speed super-resolution imaging technique resolves a longstanding contradiction between spatial resolution and imaging speed
2023-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research Brief: Jewel beetles evolve to see new colors by duplicating their genes
2023-03-10
Jewel beetles are striking insects, easily recognized by their vivid colors and metallic sheen. Possessing large, well-developed eyes, jewel beetles use vision and color for a range of different behaviors, including finding mates and host plants.
Color vision in insects differs from our own. Special genes allow many insects to see ultraviolet (UV) light as well as blue and green. New research led by Camilla Sharkey, a postdoctoral associate at the Wardill Lab in the College of Biological Sciences, investigated the complex evolutionary history of jewel beetles’ vision. The research team included Jorge Blanco, formerly with the Wardill Lab ...
nTIDE February 2023 Jobs Report: People with disabilities engaging in labor force at record rates
2023-03-10
East Hanover, NJ – March, 10 2023 – The labor force participation rate reached an all-time high for people with disabilities in February, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD). Comparing the year-to-year job indicators, nTIDE experts reported narrowing of the employment gap between people with and without disabilities, consistent ...
Prenatal exposure to anti-nausea drug in ‘60s, ‘70s tied to increased risk of colorectal cancer
2023-03-10
Prenatal exposure to an anti-nausea drug commonly used in the 1960s and 1970s has been shown to increase risk of colorectal cancer in adult offspring, according to a study by researchers at UTHealth Houston.
The study, led by Caitlin Murphy, PhD, MPH, associate professor at UTHealth Houston School of Public Health, was published today in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
Incidence rates of colorectal cancer are increasing among adults born in and after the 1960s, which Murphy said implicates pregnancy-related exposures introduced at that time as risk factors. Dicyclomine – used to treat spasms caused by irritable bowel syndrome – was initially ...
Wayne State researcher publishes new research to bring Brillouin microscopy closer to widespread use in diagnostic medicine
2023-03-10
Diagnostic imaging offers physicians and scientists critical visual representations of internal body structures, greatly enhancing clinical analysis and medical intervention. Researchers continue to break new ground on how various imaging technologies can provide a better understanding of human health.
Jitao Zhang, assistant professor of biomedical engineering (BME) at Wayne State University and a scientific member of the Karmanos Cancer Institute’s Molecular Imaging Program, is an award-winning researcher who holds three patents on a novel imaging technique called Brillouin microscopy ...
By studying sediment, UTA researcher will help stabilize Texas shorelines
2023-03-10
A University of Texas at Arlington civil engineering researcher is filling in an information gap for the state by determining how much sediment is lost by Texas rivers to the ocean.
Yu Zhang, associate professor in the Department of Civil Engineering, received a $150,000 Texas Water Development Board grant to assess the amount of sediment transported from Texas rivers to the Gulf of Mexico. The project is titled “Best Practices in Modeling Sediment Transport and Budget Along Texas Coast.” He and his team will also work with the General Land Office to develop a Sediment Management Plan for the state.
Zhang said the Brazos River is ...
Meta-analysis shows association between autism in children and cardiometabolic diseases
2023-03-10
A study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) from 2009 to 2017 determined that approximately 1 in 44 children ages 3-17 are diagnosed with some form of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Research also has established that children with ASD have an increased risk of obesity, and obesity has been linked to increased risks for cardiometabolic disorders such as diabetes and dyslipidemia (high level of cholesterol or fat in the blood). However, the question of whether or not there is an association between autism, cardiometabolic disorders and obesity remains largely unanswered.
To help provide an insight ...
Microbes can create a more peaceful world: Scientists call to action
2023-03-10
Microorganisms should be ‘weaponised’ to stave off conflicts across the globe, according to a team of eminent microbiologists.
The paper ‘Weaponising microbes for peace’ by Anand et al, outlines the ways in which microbes and microbial technologies can be used to tackle global and local challenges that could otherwise lead to conflict, but warns that these resources have been severely underexploited to date.
Professor Kenneth Timmis, Founding Editor of AMI journals Environmental Microbiology, Environmental Microbiology Reports and ...
University of Freiburg establishes Eva Mayr-Stihl Chair for Multi-Scale Characterization of Materials Systems
2023-03-10
New analytical methods and approaches to research are enhancing sustainability and materials research with particular reference to engineering science/technology at the University of Freiburg: Dr. Oana Cojocaru-Mirédin is taking on the new Eva Mayr-Stihl Chair for Multi-Scale Characterization of Materials Systems which has been established at the University’s Department of Sustainable Systems Engineering (INATECH).
Cojocaru-Mirédin, who previously researched and taught at RWTH Aachen, specializes in the application of various characterization techniques in the study of materials ...
Immune cells have a backup mechanism
2023-03-10
The enzyme TBK1 is an important component of the innate immune system that plays a critical role in the defense against viruses. Upon mutation-induced loss of TBK1 function, patients show an increased susceptibility to viral infections. Strikingly, if TBK1 is not expressed at all, this clinical effect is not seen. The mechanism behind this supposed discrepancy has now been elucidated by researchers led by Prof. Martin Schlee from the University Hospital Bonn and the Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation2 at the University of Bonn. The study was published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
In the human body, viral particles are ...
Researchers discover therapeutic target to aid in glaucoma treatment
2023-03-10
INDIANAPOLIS—Indiana University School of Medicine researchers have identified a new therapeutic target that could lead to more effective treatment of glaucoma.
Glaucoma is a neurodegenerative disease that causes vision loss and blindness due to a damaged optic nerve. More than 200,000 people are affected by glaucoma in the United States each year. Unfortunately, there is currently no treatment. In a newly published paper in Communications Biology, researchers found neurons use mitochondria for a steady source of energy, and restoring mitochondrial homeostasis in the diseased neurons can protect the optic nerve cells from being damaged.
“Age-related ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
[Press-News.org] High-speed super-resolution microscopy via temporal compressionNew high-speed super-resolution imaging technique resolves a longstanding contradiction between spatial resolution and imaging speed