(Press-News.org) Inflammatory neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), can arise when cell-to-cell communication between cells in the central nervous system (CNS) goes awry. But exactly how this cellular crosstalk leads to the molecular changes that drive disease remain unknown. To address this, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, developed a platform that allows them to perform genetic screens of cell-cell interactions to identify genes that control biologic processes. The new tool, known as systematic perturbation of encapsulated associated cells followed by sequencing, or SPEAC-seq, combines CRISPR-Cas9 and droplet microfluidics. Using this platform, the team studied interactions between two types of CNS cells—microglia and astrocytes—and identified a potential suppressor of disease-promoting astrocytes in preclinical models of MS and in clinical samples.
“SPEAC-Seq allows the high-throughput and systematic identification of cell-cell communication mechanisms,” said corresponding author Francisco Quintana, PhD, of the Brigham’s Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases. “There are many potential applications for this platform, such as combining it with epigenome or transcriptome analyses to identify therapeutics that could change cell-cell interactions. We look forward to exploring these possibilities in the future.”
in Science.
END
New platform allows researchers to listen in on cell-cell crosstalk
2023-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
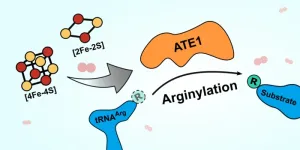
Enzyme ATE1 plays role in cellular stress response, opening door to new therapeutic targets
2023-03-11
A new paper in Nature Communications illuminates how a previously poorly understood enzyme works in the cell. Many diseases are tied to chronic cellular stress, and UMBC’s Aaron T. Smith and colleagues discovered that this enzyme plays an important role in the cellular stress response. Better understanding how this enzyme functions and is controlled could lead to the discovery of new therapeutic targets for these diseases.
The enzyme is named ATE1, and it belongs to a family of enzymes called arginyl-tRNA transferases. These enzymes add arginine (an amino acid) to proteins, which often flags the proteins for destruction in the cell. Destroying ...
Experiment unlocks bizarre properties of strange metals
2023-03-11
Physicists are learning more about the bizarre behavior of “strange metals,” which operate outside the normal rules of electricity.
Theoretical physicist Yashar Komijani, an assistant professor at the University of Cincinnati, contributed to an international experiment using a strange metal made from an alloy of ytterbium, a rare earth metal. Physicists in a lab in Hyogo, Japan, fired radioactive gamma rays at the strange metal to observe its unusual electrical behavior.
Led by Hisao Kobayashi with the University of Hyogo and RIKEN, the study was published in the journal Science. The experiment revealed unusual fluctuations in the strange metal’s electrical charge.
“The ...
New research in JNCCN highlights the negative impact of continued exclusion of racial groups from research on cancer genomics
2023-03-11
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [March 10, 2023] — New research in the March 2023 issue of JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network highlights how the lack of genomic research for people with African ancestry, particularly those from the Sub-Saharan region, is hampering efforts to reduce disparities for people with cancer. In a first-of-its-kind study, the researchers evaluated molecular genetic results for 113 Black South African men diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer to find evidence for ...
Family’s participation key to advancing diabetes research
2023-03-11
Individuals with Type 1 diabetes have a smaller pancreas than people without diabetes. This is surprising because insulin-producing beta cells account for just a small fraction of the pancreas, so the loss of beta cells in Type 1 diabetes would not be expected to reduce pancreas size.
Now, a study of one family from Alabama has led Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers to discover that insulin deficiency, independent of the autoimmunity associated with Type 1 diabetes, is the principal factor leading to a markedly smaller pancreas.
Four ...
Male or female urologist? Depends how much it hurts, research shows
2023-03-11
Urology involves some of the most intimate medical conditions, yet patients don’t necessarily always prefer to be treated by a urologist of their own gender, new research has found.
In some situations, male and female patients would prefer a male urologist but in others – if they have a painful condition, for example – both men and women would choose to be treated by a female doctor.
The study, by researchers from University Hospital Munich, is being presented today at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Congress ...
Urine gene test can predict bladder cancer years before diagnosis
2023-03-11
Testing for genetic mutations in urine can detect bladder cancer years before the disease shows clinical symptoms, new research has shown.
The study, by researchers from France, Iran and the United States, identified mutations across ten genes that were able to predict the most common type of bladder cancer up to 12 years in advance of diagnosis.
The findings are presented today at the European Association of Urology (EAU) annual Congress in Milan.
Bladder cancer is not a rare disease – it is one of the top ten most common cancers in ...
HSS study shows MISB, a minimally invasive procedure for treating bunions, does not affect flatfoot
2023-03-11
Existing thought in the orthopedic world is that treating a bunion with the minimally invasive procedure MISB may make a person’s flatfoot worse. A new study by researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) in New York City shows that this procedure does not make flatfoot worse in people with asymptomatic flatfoot and may even improve the condition. The findings were presented today at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS).
“Because of the way the bunion correction is performed with MISB, there is a thought that it may not help stabilize the ...
Neural network learns how to identify chromatid cohesion defects
2023-03-11
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have used machine learning to automate the identification of defects in sister chromatid cohesion. They trained a convolutional neural network (CNN) with microscopy images of individual stained chromosomes, identified by researchers as having or not having cohesion defects. After training, it was able to successfully classify 73.1% of new images. Automation promises better statistics, and more insight into the wide range of disorders which cause cohesion defects.
Chromosomes consist of long DNA molecules that contain a portion of our genes. When cells divide, ...
Remarkable squirting mussels captured on film
2023-03-11
Cambridge researchers have observed a highly unusual behaviour in the endangered freshwater mussel, Unio crassus. In spring, female mussels were seen moving to the water’s edge and anchoring into the riverbed, with their back ends raised above the waterline. Then they squirted out regular water jets, which landed in the water up to a metre away. Squirting cycles lasted 3-6 hours. This behaviour has never been seen in any other mussel species. The jets disturb the river surface and attract ...
First images released from James Webb Space Telescope’s largest general observer program
2023-03-10
The first images from the largest program in the James Webb Space Telescope’s first year show many types of galaxies, including dazzling examples of spiral galaxies, gravitational lensing, and evidence of galaxy mergers. Scientists from the COSMOS-Web program released mosaic images taken in early January by JWST’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) and Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI).
COSMOS-Web aims to map the earliest structures of the universe and will create a wide and deep survey of up to 1 million galaxies. Over the course of 255 hours of observing time, COSMOS-Web ...