Pediatric Investigation review takes stock of history and current status of long-acting growth hormone therapy
The review article traces the clinical evolution of long-acting growth hormone therapy and its future trend in clinical medicine
2023-03-13
(Press-News.org)
In 1957, Maurice Raben successfully isolated and purified the growth hormone (GH) from the pituitary gland, opening up a potential avenue of GH therapies. Children who were born with a deficiency of this hormone could now receive medical intervention in the form of daily injections to substitute the product into their body, thus avoiding the ill-effects of GH deficiency. However, given that it was a product that had to be meticulously extracted from the pituitary of dead bodies, and was time-consuming as well as labor- and resource-intensive process, it remained available only in limited quantities, wherein only a few patients could be treated.
A few years later, in 1985, recombinant-DNA generated GH became available that could be produced in laboratories and in much larger quantities. As a result, it became more easily available and accessible for treating children with GH deficiency. However, one drawback these therapies suffered from was the need to take daily injections of the hormone to ensure that it was available in appropriate concentrations in the blood.
A recent review article published in Pediatric Investigation on 03 January 2023 has now taken stock of the clinical development in GH therapy since its isolation, outlining how far we have come and where we are headed with the use of GH therapy. “The physiological regulation of GH involves a complex mechanism that depends on several age-related and metabolic factors. This regulatory mechanism releases GH doses into the bloodstream every three hours. While this mechanism remained a theoretical interest from clinical perspectives, researchers tried to synthesize a recombinant GH that could integrate itself seamlessly into the mechanism,” explains corresponding author Dr. Paul Saenger, who is a professor at NYU Long Island School of Medicine. “The goal was to produce a pharmaceutical product that would remain active in the body and mimic this pulsatile release of the hormone such that a daily dose would not be necessary.”
A prototype of such a long-acting growth hormone (LAGH) was developed by LG Life Sciences in 2014 and the research data were made publicly available. Over the next few years, multiple research labs and pharmaceutical companies have fine-tuned this original prototype, developing many LAGH products.
The review begins with a discussion on the clinical evolution of GH therapy from a historical perspective, followed by a deep dive into the hormonal rationale for GH therapies, development phases and mechanisms involved in these different LAGH products. It then goes on to highlight the considerations patients and their families must keep in mind when planning a LAGH therapy, and its overall role in improving GH therapies.
The mechanisms underlying novel LAGH action involve either a formulation that forms a subcutaneous deposit to allow the release of native/modified GH hormone in a pulsatile manner similar to the actual GH release patterns in the body, or injecting it as a substance that can be easily absorbed in the bloodstream but is removed slowly such that the same pulsatile release can be maintained.
With these developments, LAGH therapies now only require a weekly or monthly dose instead of a daily intake, greatly reducing the burden of injection on the patient. This, in turn, is likely to improve patient compliance. LAGH-based products like Jintrolong and Lonapegsomatropin have already cleared phase 3 trials and are being marketed in China and USA respectively, while Somatrogon has been approved in Europe and Canada.
“The clinical use of GH is an exciting success story. We are now entering a new era of LAGH therapy with new formulations of GH, which will predictably be the preferred form of therapy for years to come. Additionally, the availability of new safety data will further establish its use in clinical medicine,” comments Dr. Saenger.
While further research on dosage regulation and timing is still underway for other forms of LAGH, their availability in international markets certainly paints a bright picture.
***
Reference
Authors: Margaret Steiner, Jacklyn Frank, and Paul Saenger
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ped4.12358
Affiliations:
NYU Langone Health-Long Island, 101 Mineola Boulevard, Mineola, New York, USA
About Dr. Paul Saenger
Dr. Paul Saenger is a Professor of Pediatrics Emeritus,Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Professor of Pediatrics at NYU Langone Hospital—Long Island, Visiting Professor of Munich University, Visiting Professor of Beijing Children's Hospital. He received his training at the New York Hospital/Cornell Medical Center in Pediatric Endocrinology. He treats patients with growth disorders, diabetes mellitus, and disorders of puberty and the thyroid. Taking care of both children and their families, he helps them formulate realistic expectations and cope with their diagnoses. With more than 40 years of experience in the field, he has trained more than 45 fellows who currently work in pediatric endocrinology.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-13
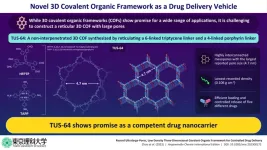
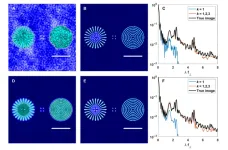
Materials science is constantly evolving research area as researchers strive to discover and synthesize novel functional materials with desirable properties suited to a variety of applications. One example on this front is furnished by covalent organic frameworks (COFs), a class of materials characterized by crystalline porous polymers connected in the form of a network via covalent bonds.
Owing to their structural diversity, high porosity, and easily accessible active sites, COFs can be designed for a range of applications such as gas storage and separation, catalysis, and drug delivery. ...
2023-03-13
Embargoed until 8:00 a.m. CT / 9:00 a.m. ET Monday, March 13, 2023
DALLAS and ALEXANDRIA, Va., March 13, 2023 — Health inequities can be detrimental to employees’ emotional, psychological and physical health and place a significant economic burden on employers. To improve employee well-being and reduce health inequities nationwide, the American Heart Association—a global force for longer, healthier lives for all—introduces the Health Equity in the Workforce initiative in collaboration with the Deloitte Health Equity Institute and the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) Foundation.
The Health Equity ...
2023-03-13
Metal organic frameworks, or MOFs, are kind of like LEGOs.
The pieces are simple to connect, yet they’re capable of building highly sophisticated structures. These structures can be used to filter toxic gasses out of the air or to store fuel for natural or hydrogen gas-powered engines.
LEGOs melt when they interact with heat. But, what happens to MOFs?
A new study from the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering found that MOFs heat up significantly when they soak up gasses and if they ...
2023-03-13
Annapolis, MD; March 13, 2023—Black widow spiders have earned a fearsome reputation for their venomous bite. But in parts of the southern United States these spiders have much to fear themselves—from spider relatives who really don't like their company.
In the past couple decades, researchers have noticed black widow spiders commonly being displaced by the brown widow, a fellow species in the same genus, Latrodectus. But new research suggests this isn't a just simple case of one species winning the competition for food or habitat. Instead, a study shows brown widow spiders have a striking propensity to seek out and kill nearby ...
2023-03-13
Researchers from Colorado State University and the Colorado School of Mines have thought up a new computational imaging strategy that exploits the best of both the quantum and classical worlds. They developed an efficient and robust algorithm that fuses quantum and classical information for high-quality imaging. The results of their research were published Dec. 21 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Recently, the quantum properties of light have been exploited to enable superresolution microscopy. While quantum information brings new possibilities, it has its own set of limitations.
The researchers’ approach is based on classical and quantum ...
2023-03-13
Surprisingly, bitter taste receptors are not only located in the mouth, but also elsewhere in the body, including the airways. Activating those receptors opens up lung passageways, so they’re a potential target for treating asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Now, researchers report in ACS’ Journal of Medicinal Chemistry that they have designed a potent and selective compound that could lead the way to such therapies.
Among the 25 different types of bitter taste receptors, the TAS2R14 subtype is one of the most widely distributed in tissues outside the mouth. Scientists are uncertain about ...
2023-03-13
A new study published in PeerJ Life & Environment and featured in the International Association for Biological Oceanography Hub evaluates the use of DNA metabarcoding to identify fish eggs. The study assessed the performance of DNA metabarcoding to increase throughput and reduce financial and labor costs associated with a long-term fish egg monitoring program.
The study found:
Egg identifications were consistent with prior species distributions observed from individual egg DNA barcoding, and spatial ...
2023-03-13
Date: 13 March 2023, 08:30 CET
13 to 15 April in Malaga, Spain
Get ready for practice-changing science at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).
The annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC), a branch of the ESC, takes place 13 to 15 April at the Trade Fair and Congress Centre of Malaga (FYCMA - Palacio de Ferias y Congresos de Malaga) in Malaga, Spain. Explore the scientific programme.
Novel research ...
2023-03-13
Climate models used by the UN’s IPCC and others to project climate change are not accurately reflecting what the Arctic’s future will be. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg argue that the rate of warming will be much faster than projected.
Due to the Arctic´s sea ice cover and its harsh climate, relatively few observations are made in that part of world. This means that the climate models used for projecting the future of the Arctic have not been calibrated to the same extent there as in other parts of the world.
Two recent ...
2023-03-13
Patients with ‘blinding’ headaches known as Idiopathic Intercranial Hypertension (IIH) could be treated with an injectable peptide used for type 2 diabetes, a new trial has found.
The study, published in the journal Brain, today reports on a phase two trial of a drug called exenatide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, as a potential treatment for IIH.
The IIH Pressure Trial led by a team of neurologists from the University of Birmingham and University Hospitals Birmingham found that for the seven ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pediatric Investigation review takes stock of history and current status of long-acting growth hormone therapy
The review article traces the clinical evolution of long-acting growth hormone therapy and its future trend in clinical medicine