(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study of 398,000 adult outpatients with COVID-19, the absolute risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) was low. Several patient-level factors were associated with higher VTE risk; these findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who may benefit from more intensive surveillance or VTE preventive strategies.
Authors: Margaret C. Fang, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.2338)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.2338?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=031323
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Assessment of the risk of venous thromboembolism in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19
JAMA Network Open
2023-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Remote blood pressure management program enhanced care during pandemic
2023-03-13
BOSTON – Hypertension is the leading risk factor for death worldwide. During the COVID-19 pandemic, routine blood pressure assessments decreased because of global disruptions to medical care delivery. However, new research has found that a remote hypertension program, operated by Mass General Brigham since 2019, successfully supported patients through the pandemic in achieving their blood pressure goals, with patients who enrolled during the pandemic reaching and maintaining their goal blood pressures an average of two months earlier than in the pre-pandemic period. The results, published in Journal ...
Too little sleep could make vaccination less effective
2023-03-13
How strongly a vaccine protects you may depend on getting enough sleep in the days before and after inoculation, finds a new meta-analysis examining the relationship between sleep duration and the body’s response to vaccination.
Sleeping fewer than six hours per night around the time of vaccination was associated with a robust decrease in antibody response, according to the multi-institution study published March 13 in Current Biology. Adults are typically recommended to get between seven and nine hours of sleep per night.
The meta-analysis included data on the association between sleep duration and antibody responses for the ...
Not getting enough sleep could blunt antibody response to vaccination, leaving you more vulnerable to infection
2023-03-13
In reviewing data from previous studies, a team lead by researchers at the University of Chicago and the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research (Inserm) found that individuals who had fewer than six hours of sleep per night in the days surrounding vaccination had a blunted antibody response. That indicates efforts to promote heathy sleep duration ahead of an immunization could be an easy way to improve vaccine effectiveness. The study was published March 13 in Current Biology.
The latest work builds off a 2002 study by members of the team showing that restricting sleep ...
A new immune pathway sheds light on ALS
2023-03-13
While drugs are on the market to slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, there are still no cures. But researchers at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School are looking for new pathways for slowing neuronal dysfunction and treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a fatal motor neuron disease. The team found that proteins involved in the innate immune system could be at the root of the disease.
“The unmet need for therapies for neurodegenerative diseases is huge, and our work opens up a whole new ...
Study shows how biodiversity of coral reefs around the world changes with depth
2023-03-13
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (March 13, 2023) — In a paper published today in Current Biology, researchers from the California Academy of Sciences Hope for Reefs initiative, along with Brazilian collaborators from the University of São Paulo, Federal University of Espírito Santo, and the Instituto Nacional da Mata Atlântica, show that mesophotic coral reefs function much differently than their shallower counterparts and are unlikely to offer a refuge for shallow water fishes trying to escape climate-change driven warming on the ocean’s surface.
The research is based on hundreds of dives totaling ...
Benefits of the net-zero emissions strategy for Nepal
2023-03-13
Achieving the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement will require the combined efforts of states and companies around the world. How can developing countries achieve carbon neutrality and boost their resilience while pursuing economic growth and improved living standards? A study by the Research Institute for Sustainability (RIFS) draws on the example of Nepal to analyse the benefits of a net-zero emissions strategy.
Nepal is among the 10 countries most vulnerable to climate-change-related disasters and risks. However, its contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions is minor. As Nepal prepares to graduate ...
Pediatric Investigation review takes stock of history and current status of long-acting growth hormone therapy
2023-03-13
In 1957, Maurice Raben successfully isolated and purified the growth hormone (GH) from the pituitary gland, opening up a potential avenue of GH therapies. Children who were born with a deficiency of this hormone could now receive medical intervention in the form of daily injections to substitute the product into their body, thus avoiding the ill-effects of GH deficiency. However, given that it was a product that had to be meticulously extracted from the pituitary of dead bodies, and was time-consuming as well as labor- and resource-intensive process, it remained ...
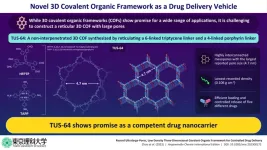
Towards a novel 3D covalent organic framework with record large pores for efficient drug delivery
2023-03-13
Materials science is constantly evolving research area as researchers strive to discover and synthesize novel functional materials with desirable properties suited to a variety of applications. One example on this front is furnished by covalent organic frameworks (COFs), a class of materials characterized by crystalline porous polymers connected in the form of a network via covalent bonds.
Owing to their structural diversity, high porosity, and easily accessible active sites, COFs can be designed for a range of applications such as gas storage and separation, catalysis, and drug delivery. ...
Equipping employers to address costly health inequities, improve workforce well-being
2023-03-13
Embargoed until 8:00 a.m. CT / 9:00 a.m. ET Monday, March 13, 2023
DALLAS and ALEXANDRIA, Va., March 13, 2023 — Health inequities can be detrimental to employees’ emotional, psychological and physical health and place a significant economic burden on employers. To improve employee well-being and reduce health inequities nationwide, the American Heart Association—a global force for longer, healthier lives for all—introduces the Health Equity in the Workforce initiative in collaboration with the Deloitte Health Equity Institute and the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) Foundation.
The Health Equity ...
Too hot to handle
2023-03-13
Metal organic frameworks, or MOFs, are kind of like LEGOs.
The pieces are simple to connect, yet they’re capable of building highly sophisticated structures. These structures can be used to filter toxic gasses out of the air or to store fuel for natural or hydrogen gas-powered engines.
LEGOs melt when they interact with heat. But, what happens to MOFs?
A new study from the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering found that MOFs heat up significantly when they soak up gasses and if they ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
[Press-News.org] Assessment of the risk of venous thromboembolism in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19JAMA Network Open