(Press-News.org) Ithaca, NY— Bald Eagles and dairy farmers exist in a mutually beneficial relationship in parts of northwestern Washington State. According to a new study, this "win-win" relationship has been a more recent development, driven by the impact of climate change on eagles' traditional winter diet of salmon carcasses, as well as by increased eagle abundance following decades of conservation efforts. The research is published in the journal Ecosphere.
"The narrative around birds of prey and farmers has traditionally been negative and combative, mainly due to claims of livestock predation," explained lead author Ethan Duvall in the Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology at Cornell University. "However, dairy farmers in northwestern Washington do not consider the eagles threats. In fact, many farmers appreciate the services that the eagles provide such as carcass removal and pest-deterrence."
Duvall, with collaborators Emily Schwabe and Karen Steensma from the University of Washington and Trinity Western University in Canada, conducted face-to face interviews with farmers on small, medium, and large dairy operations in Whatcom County to better understand this unique relationship. The study was motivated by Duvall's most recent research showing that eagles were redistributing from rivers to farmland in response to the declining availability of salmon carcasses during the past 50 years.
"Climate change has altered the chum salmon spawning schedule, causing them to run earlier in the winter," said Duvall. "Now the salmon are spawning when annual Nooksack River flooding is at its peak. The fish who spawn and die are swept away by the high water instead of being deposited on shore where the eagles can easily access them."
Duvall notes that the shift in timing has reduced the number of available carcasses on the local river, not the number of individual salmon. However, many rivers in the Pacific Northwest have experienced dramatic salmon population declines, also eliminating winter resources for eagles.
To make up for the reduction in their natural food supply, eagles have turned to the steady stream of dairy farm by-products resulting from the births and deaths of cows and prey on waterfowl populations which feed and rest in the agricultural areas. Bald Eagles also keep a lid on traditional farm pests, such as rodents and starlings.
"We know this positive interaction between farmers and Bald Eagles is not the norm in many other agricultural areas, especially near free-range poultry farms where the eagles snatch chickens," said Duvall. "But this study gives me hope that, moving forward, farmers, wildlife managers, and conservationists can come together to think critically about how to maximize benefits for people and wildlife in the spaces they share."
Reference:
Ethan. S. Duvall, Emily K. Schwabe, and Karen M.M. Steensma. A win–win between farmers and an apex-predator: investigating the relationship between bald eagles and dairy farms. Ecosphere. March 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.4456
END
Climate change alters a human-raptor relationship
Dairy farmers welcome Bald Eagles
2023-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A mechanistic and probabilistic method for predicting wildfires
2023-03-14
Spanning long distances across variable terrains, electric power systems can spark wildfires in the event of dry weather and high winds. This may occur when conductor cables oscillate in such a way to become close to the surrounding vegetation.
Data from the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection shows that between 2016-2020, at least five of the top 20 most destructive California wildfires started from power systems. Paired with the extreme weather conditions and nearby vegetation, ...
This is what happens when your phone is spying on you
2023-03-14
Smartphone spyware apps that allow people to spy on each other are not only hard to notice and detect, they also will easily leak the sensitive personal information they collect, says a team of computer scientists from New York and San Diego.
While publicly marketed as tools to monitor underage children and employees using their employer’s equipment, spyware apps are also frequently used by abusers to covertly spy on a spouse or a partner. These apps require little to no technical expertise from the abusers; offer detailed installation ...
New, non-invasive imaging tool maps uterine contractions during labor
2023-03-14
Researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health have developed a new imaging tool, called electromyometrial imaging (EMMI), to create real-time, three-dimensional images and maps of contractions during labor. The non-invasive imaging technique generates new types of images and metrics that can help quantify contraction patterns, providing foundational knowledge to improve labor management, particularly for preterm birth. The small study is supported in part by NIH’s Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) through its Human ...
Regional ECT, lithium, and clozapine use linked to lower suicide rates in male adolescents
2023-03-14
A new study from Karolinska Institutet suggests that electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), lithium, and clozapine may reduce suicide rates in adolescent men with severe mental illness, consistent with previous findings in adults. The study, published in Nature Communications, compared treatment and suicide rates across different regions in Sweden.
Annually, there are 800,000 suicide deaths worldwide. Suicide is the leading cause of death among teenagers and young adults, with up to 90 percent of those affected having a serious psychiatric illness ...
Imaging tech produces real-time 3D maps of uterine contractions during labor
2023-03-14
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed new imaging technology that can produce 3D maps showing the magnitude and distribution of uterine contractions in real time and across the entire surface of the uterus during labor. Building on imaging methods long used on the heart, this technology can image uterine contractions noninvasively and in much greater detail than currently available tools, which only indicate the presence or absence of a contraction.
The ...
Tech could help BC farmers reach customers, mitigate climate change impacts
2023-03-14
Technology exists that the BC government could leverage to help small farmers connect directly with consumers and also mitigate climate change impacts, say new findings from UBC Okanagan.
Dr. John Janmaat and Dr. Joanne Taylor co-authored new research that examines how farmers in the Okanagan and Cariboo regions of BC are adapting compared to farmers in China’s Shaanxi province. One of the key differences was how Chinese farmers used technology and social media, an option that’s not as widely used in ...
High winds can worsen pathogen spread at outdoor chicken farms
2023-03-14
PULLMAN, Wash. – Farmers who keep their chickens outdoors may want to watch the weather. A study of chicken farms in the West found that high winds increased the prevalence of Campylobacter in outdoor flocks, a bacterial pathogen in poultry that is the largest single cause of foodborne illness in the U.S.
Researchers found that about 26% of individual chickens had the pathogen at the “open environment” farms in the study, which included organic and free-range chicken farms. High winds the week prior to sampling and the farms’ location in more intensive agricultural settings were linked to a greater prevalence of ...
Environmental justice scholar Joan Martinez-Alier named 2023 Holberg Prize Laureate
2023-03-14
Joan Martinez-Alier is Professor Emeritus at the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology, at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB). He will receive the award of NOK 6,000,000 (approx. EUR 550,000) during an 8 June ceremony at the University of Bergen, Norway.
Martinez-Alier receives the Holberg Prize for his ground-breaking research in ecological economics, political ecology and environmental justice. He is known for criticizing established economic theory and traditional approaches to economic growth. Martinez-Alier is also a major figure and leading public intellectual in the burgeoning movement for ’degrowth’.
Degrowth ...
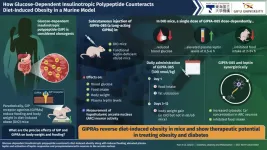
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide prevents diet-induced obesity in mice
2023-03-14
The hormone glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) is considered obesogenic. In contrast, GIP receptor agonists (GIPRAs) have shown reduced feeding and body weight in an obese mouse model. Therefore, the precise effects exerted by GIP and GIPRAs remain elusive. Recently, researchers demonstrated acute feeding inhibition and lowered body weight in mice with diet-induced obesity treated with GIPFA-085, a long-acting GIPRA. Their findings provide a scientific basis for GIP therapy for diabetes and obesity.
Obesity, ...
Protecting messengers of the gods: Conservation of Nara Park deer has resulted in unique genetic lineage
2023-03-14
The existing wildlife of a region is heavily shaped over generations by environmental factors and human activity. Activities like urbanization and hunting are known to reduce wildlife populations. However, some cultural or religious practices have, on occasion, preserved local animal populations. For instance, the forests around religious shrines in Japan have historically forbidden hunting and, as a consequence, provide refuge for certain animal species. A well-known example of this is the Japanese sika deer (Cervus nippon), which has historically been considered a holy creature.
A revered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
[Press-News.org] Climate change alters a human-raptor relationshipDairy farmers welcome Bald Eagles