(Press-News.org) During the pandemic, medical doctors and researchers noticed that children and adolescents infected with COVID-19 became less ill than adults. A possible explanation for this is that children already had a prior level of immunity to COVID-19 provided by memory T cells generated by common colds.
After studying unique blood samples from children taken before the pandemic, researchers from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have now identified memory T cells that react to cells infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Four coronaviruses cause common colds
A possible explanation for this immunity in children is that they already had colds caused by one of the four coronaviruses causing seasonal common cold symptoms. This could stimulate an immune response with T cells able to also react to cells infected with SARS-CoV-2.
This new study reinforces this hypothesis and shows that T cells previously activated by the OC43 virus can cross-react against SARS-CoV-2.
“These reactions are especially strong early in life and grow much weaker as we get older,” says the study’s corresponding author Annika Karlsson, research group leader at the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Karolinska Institutet. “Our findings show how the T-cell response develops and changes over time and can guide the future monitoring and development of vaccines.”
Strong immunity at the age of two
The results indicate that the memory T-cell response to coronaviruses develops as early as the age of two. The study was based on 48 blood samples from two- and six-year-old children, and 94 samples from adults between the ages of 26 and 83. The analysis also included blood samples from 58 people who had recently recovered from COVID-19.
“Next, we’d like to do analogous studies of younger and older children, teenagers and young adults to better track how the immune response to coronaviruses develops from childhood to adulthood,” says Marion Humbert, postdoctoral researcher currently at the Department of Medicine Huddinge, Karolinska Institutet, joint first author with Anna Olofsson, doctoral student at the Department of Laboratory Medicine.
The paper is the result of a collaborative study among researchers at Karolinska Institutet, the universities of Bern (Switzerland), Oslo (Norway) and Linköping University (Sweden).
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council, Region Stockholm (CIMED), Karolinska Institutet, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation and the European Research Council. Karl-Johan Malmberg, Ebba Sohlberg and Soo Aleman receive fees from companies and organisations outside this research project (see the paper for more details); all other researchers report no conflicts of interest.
Publication: “Functional SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive CD4+ T cells established in early childhood decline with age”. Marion Humbert, Anna Olofsson, David Wullimann, Julia Niessl, Emma B. Hodcroft, Curtis Cai, Yu Gao, Ebba Sohlberg, Robert Dyrdake, Flora Mikaeloff, Ujjwal Neogi, Jan Albert, Karl-Johan Malmberg, Fridtjof Lund-Johansen, Soo Aleman, Linda Björkhem-Bergman, Maria C. Jenmalm, Hans-Gustaf Ljunggren, Marcus Buggert, Annika C. Karlsson. PNAS, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, online 14 March 2023, doi: 10.1073/pnas.2220320120.
END
Common cold gives children immunity against COVID-19
2023-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover way to reverse infertility by reducing HDL cholesterol
2023-03-14
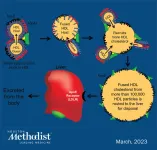
Houston Methodist scientists reversed infertility in sterile mice by reducing high-circulating cholesterol with a bacterial protein, showing further evidence that links high cholesterol to female infertility. This is a promising development, with one in every five women of childbearing age in the U.S. unable to get pregnant after trying for a year.
“We are working with a protein, called serum opacity factor, with unique characteristics,” said Corina Rosales, Ph.D., assistant research professor of molecular biology in medicine with the Houston Methodist ...
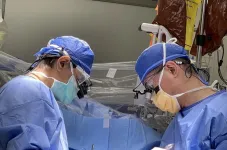
UK HealthCare’s Transplant Center celebrates 500th lung transplant
2023-03-14
LEXINGTON, Ky. (March 14, 2023) — The lung transplant team at UK HealthCare’s Transplant Center recently celebrated a major milestone, performing the 500th lung transplant since the lung transplant program was founded in 1991.
“This is an impressive milestone, and our whole staff — physicians, surgeons, nurse practitioners, nurse coordinators, pharmacists, nutritionists, social workers, therapists and support staff — should be very proud of their success,” said Sravanthi Nandavaram, M.D., medical director of the Lung Transplant Program. ...
How neuroimaging can be better utilized to yield diagnostic information about individuals
2023-03-14
Since the development of functional magnetic resonance imaging in the 1990s, the reliance on neuroimaging has skyrocketed as researchers investigate how fMRI data from the brain at rest, and anatomical brain structure itself, can be used to predict individual traits, such as depression, cognitive decline, and brain disorders.
Brain imaging has the potential to reveal the neural underpinnings of many traits, from disorders like depression and chronic widespread pain to why one person has a better memory than another, and why some people’s memories are resilient as they age. But how reliable brain imaging is for detecting traits has been a subject of wide debate.
Prior research ...
NASA’s Webb Telescope captures rarely seen prelude to supernova
2023-03-14
The rare sight of a Wolf-Rayet star – among the most luminous, most massive, and most briefly detectable stars known – was one of the first observations made by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in June 2022. Webb shows the star, WR 124, in unprecedented detail with its powerful infrared instruments. The star is 15,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius.
Massive stars race through their lifecycles, and only some of them go through a brief Wolf-Rayet phase before going supernova, making Webb’s detailed observations of this rare phase valuable to astronomers. Wolf-Rayet stars are in the process of casting off their outer layers, ...
Potential treatment target for drug-resistant epilepsy identified
2023-03-14
Researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine and colleagues have identified a small molecule that may help treat people with epilepsy whose condition has become resistant to the benzodiazepine drugs usually used in managing seizures. The research, conducted in laboratory cells and rodents, was published online March 7 in Cell Reports Medicine.
Uncontrolled epilepsy can lead to frequent and prolonged seizures lasting five minutes or more that can cause brain cell damage and even death. The condition affects an estimated 3.4 million people in the U.S. and millions more worldwide.
Epilepsy occurs ...
New model provides improved air-quality predictions in fire-prone areas
2023-03-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Globally, wildfires are becoming more frequent and destructive, generating a significant amount of smoke that can be transported thousands of miles, driving the need for more accurate air pollution forecasts. A team of Penn State researchers developed a deep learning model that provides improved predictions of air quality in wildfire-prone areas and can differentiate between wildfires and non-wildfires.
“As climate change continues to cause ecological changes and challenges, it is likely that wildfire ...
New study finds early warning signs prior to 2002 Antarctic ice shelf collapse
2023-03-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In 2002, an area of ice about the size of Rhode Island dramatically broke away from Antarctica as the Larsen B ice shelf collapsed. A new study of the conditions that led to the collapse may reveal warning signs to watch for future Antarctic ice shelf retreat, according to a Penn State-led team of scientists.
“The collapse of the Larsen B ice shelf is generally thought of as an independent event,” said Shujie Wang, assistant professor of geography at Penn State. “Our ...
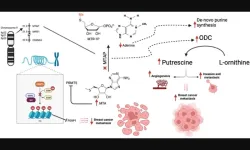
Oncotarget | MTAP loss in metastatic breast cancer patients: Genomic landscape
2023-03-14
“In breast cancer, MTAP downregulation activates ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) which in turn leads to formation of putrescine which promotes tumor migration, invasion and angiogenesis [15].”
BUFFALO, NY- March 14, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 11, 2023, entitled, “Genomic landscape of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients with methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) loss.”
Homozygous deletion of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) upregulates de novo synthesis ...
Tim Michalski selected as Jefferson Lab’s engineering manager
2023-03-14
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility has selected Tim Michalski to lead its Engineering Division as the Engineering Division Manager. In this role, Michalski oversees all aspects of the management and operation of the Engineering Division. The division includes more than 200 staff members and supports the Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility and the lab’s growing project portfolio.
“I am proud to name Tim as our newest Engineering Division Manager,” said Jefferson Lab Director Stuart Henderson. “Tim has ...
Princeton Chem, IAS uncover spatial patterns in distribution of galaxies
2023-03-14
In late 2021, Salvatore Torquato, on sabbatical from Princeton’s Department of Chemistry, reached across the aisle as it were and invited a young astrophysicist at the Institute for Advanced Study to apply the tools of statistical mechanics to his own work on the distribution of galaxies.
The astrophysicist, Oliver Philcox, now a postdoc at the Simons Foundation, was intrigued. A year-long collaboration ensued.
The questions at the heart of their unusual partnership were straightforward: can the statistical descriptors Torquato has worked with throughout his career find application in unlikely places like cosmology, and can they accurately characterize the complexity in the distribution ...