(Press-News.org) Leipzig. Intense fishing and overexploitation have led to evolutionary changes in fish stocks like cod, reducing both their productivity and value on the market. These changes can be reversed by more sustainable and far-sighted fisheries management. The new study by researchers from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), Leipzig University and the Institute of Marine Research in Tromsø, which was published in Nature Sustainability, shows that reversal of evolutionary change would only slightly reduce the profit of fishing, but would help regain and conserve natural genetic diversity.
The impact of global fisheries on marine ecosystems is severe: fish stocks have declined and the degradation of marine habitats as well as the loss of biodiversity have been accelerated. Less visible, intense fishing has also affected the age and size structure of fish stocks and caused evolutionary change, often towards lower growth rates, smaller maturation sizes and earlier reproduction age. For example, cod in the North Sea, which has been heavily exploited in the past, matures at sizes just above 50 cm, compared to more than 70 cm expected in an unfished population.
Earlier reproduction can increase stock resilience in the short-term, but over time results in populations with smaller fish that have less offspring. “At the end of the day, this can reduce both the productivity of a stock and the value on the market,” says first author Hanna Schenk from iDiv and Leipzig University. “Apart from this, we don’t know much about potential consequences such as trophic cascades and other ecosystem changes that feed back onto the harvested species and may interfere with critical ecological functions.”
Only long-term planning can reverse evolutionary decline
But evolution is not a one-way street. This is why the researchers from iDiv, Leipzig University and the Institute of Marine Research in Tromsø (Norway) wanted to find out what it takes to reverse evolutionary decline after decades of intensive exploitation, in particular with regard to planning horizons in fisheries management. For this, they developed a model that took various processes into account: Biological growth and reproduction as well as economic harvesting costs and consumer preferences. The researchers also analysed potential trade-offs between economic profit and conservation targets.
They found that evolutionary decline is profitable to reverse under century-long planning horizons. With more typical short-term planning, stock recovery in terms of biomass is achieved, but evolutionary decline continues, albeit at much lower rates. “Fisheries typically consider short planning horizons of a few years. This stands in contrast to long-term sustainability and biodiversity targets”, says Hanna Schenk. The researchers found that more far-sighted planning horizons would help to rebuild the stock but evolutionary decline continues. According to Schenk, reversing this process takes much longer than the recovery of the stock biomass and is only achieved with century-long planning horizons.
Appropriate conservation targets only slightly reduce profit
The researchers also show that setting conservation targets for restoring not only fish stocks, but also their genetic composition would only slightly reduce profits. The cost and time of evolutionary reversal could be reduced further if fisheries can select fish depending on their genes, which may be possible to some extent by choosing the time and place of harvest. However, current conservation agendas do not include the restoration of genetic diversity, for example target 14 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SGDs), which calls for an end to overfishing.
“More selective fishing could reverse evolutionary decline in the long term”, says senior author Professor Martin Quaas from iDiv and Leipzig University. Economic incentives alone may not be sufficient to achieve these sustainability goals, which is why genetic diversity and conservation should be included explicitly in sustainable development goals and UN biodiversity targets. “From an economist’s perspective, fishing should have largely avoided undesired evolutionary changes. Now that these changes have taken place, they are costly to reverse in the short run, but in the long run, this would pay off in economic terms.”
END
How fishermen benefit from reversing evolution of cod
Under long-term fisheries management, evolutionary change, that has resulted in smaller maturation sizes, can be reversed profitably.
2023-03-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Displays with more brilliant colors through a fundamental physical concept
2023-03-16
A research team from the University of Cologne (Germany) and the University of St Andrews (Scotland) has shown in a new study how a fundamental physical concept can be used to boost the colour brilliance of smartphone, computer or TV screens without cutbacks in energy efficiency. The results have been published in Nature Photonics.
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have conquered the market for displays in recent years – from high-resolution smartphone to wall-sized television screens. However, industry and science face several challenges in creating the next generation of devices ...
Hot topic – how heat flow affects the Earth’s magnetic field
2023-03-16
Hot topic – how heat flow affects the Earth’s magnetic field
Compass readings that do not show the direction of true north and interference with the operations of satellites are a few of the problems caused by peculiarities of the Earth’s magnetic field.
The magnetic field radiates around the world and far into space, but it is set by processes that happen deep within the Earth’s core, where temperatures exceed 5,000-degress C.
New research from geophysicists at the University of Leeds suggests that ...
Case report of first mixed race woman possibly cured of HIV published in Cell
2023-03-16
A new method to cure HIV—by transplanting HIV-resistant stem cells from umbilical cord blood—has yielded long-term successful results, say scientists. The approach was successfully used to treat the “New York patient,” a middle-aged woman with leukemia and HIV who self-identifies as mixed race, who has been without HIV since 2017. Using stem cells from cord blood rather than from compatible adult donors, as has been done previously, increases the potential to cure HIV via stem cell transplantation ...
Genomic analysis shows the Amazon’s Ashaninka people are made up of two subgroups with distinct histories
2023-03-16
The Ashaninka are the most numerous Indigenous people living in the rainforests of Peru and Brazil where they inhabit a crucial area between the Andes and sources of the Amazon River. And yet, despite the size of the population and their importance in the past and present, their genetic history has remained understudied.
Now a team of researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on March 16 has analyzed the genomes of more than 50 individuals to clarify the group’s interactions with nearby South American regions, including Central America and the Caribbean. ...
Indigenous Ashaninka DNA helps geneticists write new chapters of pre-colonial history in South America
2023-03-16
Geneticists have written new chapters in the reconstruction of pre-colonial Americas history after using DNA from the indigenous Ashaninka people from Amazonian Peru. They have discovered previously unexpected levels of genetic variation in this group and uncovered a strong hint that these people were involved in a South-to-North migration that led to the transition from an archaic to ceramic culture in the Caribbean islands.
The dramatic impact of European colonisation during the second half of the last millennium has strongly influenced the genetic history of the Americas, making the reconstruction ...
Financial hardship and employment loss among adults with disabilities during COVID-19
2023-03-16
About The Study: This survey study found that people with disabilities were more likely to report household employment loss and financial hardship during the initial COVID-19 pandemic, which are especially pronounced among racial and ethnic minority respondents. These findings suggest people with disabilities may be disproportionately affected by the initial pandemic and may require additional resources and policy strategies (e.g., training programs, workplace accommodations) as several labor markets adapt to the pandemic (e.g., shifting to remote working).
Authors: Kea Turner, Ph.D., M.P.H., M.A., of the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center ...
Readmission rates, episode costs for Alzheimer disease and related dementias
2023-03-16
About The Study: In this study of 722,000 hospitalization episodes, patients with Alzheimer disease and related dementias (ADRD) had higher readmission rates and overall readmission and episode costs than their counterparts without ADRD. Hospitals may need to be better equipped to care for patients with ADRD, especially in the post-discharge period. Considering that any type of hospitalization may put patients with ADRD at a high risk of 30-day readmission, judicious preoperative assessment, postoperative discharge, and ...
Preterm babies do not habituate to repeated pain
2023-03-16
Preterm infants do not get used to repeated pain in the way that full-term infants, children and adults do habituate to pain, finds a study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The authors of the new Current Biology paper say that if preterm infants have not yet developed the mechanism that enables people to get used to moderate pain, medical procedures in their first few weeks of life could potentially impact their development.
Lead author Dr Lorenzo Fabrizi (UCL Neuroscience, Physiology & Pharmacology) said: “The way that we can get used to things can be seen as the simplest example of behavioural and brain plasticity, and it is ...
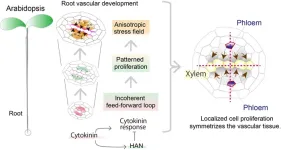
Compressive stress shapes the symmetry of Arabidopsis root vascular tissue
2023-03-16
Ikoma, Japan – The generation and maintenance of tissue boundaries are fundamental to the development of functional organs in both plants and animals. In general, tissue boundaries are initially set among primordial cells, and their shapes and arrangements are refined during subsequent organ growth. In this process, cell migration plays a curtail role for boundary refinement in animal systems, however, plant tissue lacks such cell fluidity due to its cell walls. Despite significant progress in understanding the initial patterning of tissue boundaries in several ...
How countries can benefit from linking data
2023-03-16
A recent study makes it clear: Countries like Sweden that can link data from different areas - such as the labor market and health care - have a decisive advantage when it comes to setting targeted actions.
A research team from the Complexity Science Hub, together with scientists from Sweden, Denmark and the Netherlands, investigated the extent to which mental and somatic illnesses influence integration into the labor market and whether there is a difference here between refugee and Swedish-born young adults. "In total, we analyzed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] How fishermen benefit from reversing evolution of codUnder long-term fisheries management, evolutionary change, that has resulted in smaller maturation sizes, can be reversed profitably.